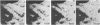Abstract
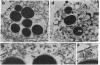
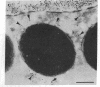
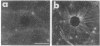
Melanophore preparations of Fundulus heteroclitus that have been treated with the detergent Brij 58 can aggregate their pigment in response to epinephrine. On the basis of several criteria, it appears that cell lysis occurs under the detergent conditions used. Electron microscopic examination of detergent-treated cells shows progressive disruption of the melanophore plasma membrane during the time in which pigment aggregation occurs. Brij-treated cells are accessible to ferritin, a large electron-dense probe that is effectively excluded from non-detergent-treated controls. In cells incubated with detergent, fixed, and treated first with rat monoclonal antibodies against tubulin and then with fluorescein-isothiocyanate-labeled goat anti-rat IgG, a characteristic radical pattern of microtubule staining can be visualized by fluorescence microscopy. Control preparations treated similarly, but without detergent, do not stain. Vanadate, an inhibitor of ciliary and flagellar dynein ATPase, blocks melanosome aggregation in response to epinephrine in detergent-treated preparations but has no effect on intact melanophores. erythro-9-[3-(2-hydroxynonyl)]Adenine, another inhibitor of dynein ATPase, also inhibits pigment aggregation in Fundulus melanophores. The possibility that a dynein-like molecule plays a role in pigment aggregation is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. D., Allen N. S., Travis J. L. Video-enhanced contrast, differential interference contrast (AVEC-DIC) microscopy: a new method capable of analyzing microtubule-related motility in the reticulopodial network of Allogromia laticollaris. Cell Motil. 1981;1(3):291–302. doi: 10.1002/cm.970010303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckerle M. C., Porter K. R. Inhibitors of dynein activity block intracellular transport in erythrophores. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):701–703. doi: 10.1038/295701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard P., Penningroth S. M., Cheung A., Gagnon C., Bardin C. W. erythro-9-[3-(2-Hydroxynonyl)]adenine is an inhibitor of sperm motility that blocks dynein ATPase and protein carboxylmethylase activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1033–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers H. R., Porter K. R. Transformations in the structure of the cytoplasmic ground substance in erythrophores during pigment aggregation and dispersion. I. A study using whole-cell preparations in stereo high voltage electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):541–558. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cande W. Z. Inhibition of spindle elongation in permeabilized mitotic cells by erythro-9-[3-(2-hydroxynonyl)] adenine. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):700–701. doi: 10.1038/295700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cande W. Z., Wolniak S. M. Chromosome movement in lysed mitotic cells is inhibited by vanadate. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):573–580. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark T. G., Rosenbaum J. L. An actin filament matrix in hand-isolated nuclei of X. laevis oocytes. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1101–1108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons B. H., Gibbons I. R. The effect of partial extraction of dynein arms on the movement of reactivated sea-urchin sperm. J Cell Sci. 1973 Sep;13(2):337–357. doi: 10.1242/jcs.13.2.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Cosson M. P., Evans J. A., Gibbons B. H., Houck B., Martinson K. H., Sale W. S., Tang W. J. Potent inhibition of dynein adenosinetriphosphatase and of the motility of cilia and sperm flagella by vanadate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2220–2224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN-BERLING H. Geisselmodelle und Adenosintriphosphat (ATP). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jan;16(1):146–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Martensen T., Nath J., Flavin M. Inhibition of dynein ATPase by vanadate, and its possible use as a probe for the role of dynein in cytoplasmic motility. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1313–1318. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91279-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Tilney L. G. The role of microtubules in the movement of pigment granules in teleost melanophores. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jun;61(3):757–779. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obika M., Menter D. G., Tchen T. T., Taylor J. D. Actin microfilaments in melanophores of Fundulus heteroclitus. Their possible involvement in melanosome migration. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Oct 30;193(3):387–397. doi: 10.1007/BF00225337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obika M., Turner W. A., Jr, Negishi S., Menter D. G., Tchen T. T., Taylor J. D. The effects of lumicolchicine, colchicine and vinblastine on pigment migration in fish chromatophores. J Exp Zool. 1978 Jul;205(1):95–110. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402050112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penningroth S. M., Cheung A., Bouchard P., Gagnon C., Bardin C. W. Dynein ATPase is inhibited selectively in vitro by erythro-9-[3-2-(hydroxynonyl)]adenine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):234–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. C., Kredich N. M., Snyderman R. Requirement of S-adenosyl-L-methionine-mediated methylation for human monocyte chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3928–3932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K. R. Microtubules in intracellular locomotion. Ciba Found Symp. 1973;14:149–169. doi: 10.1002/9780470719978.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt M. M., Otter T., Salmon E. D. Dynein-like Mg2+-ATPase in mitotic spindles isolated from sea urchin embryos (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis). J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):738–745. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebhun L. I. Polarized intracellular particle transport: saltatory movements and cytoplasmic streaming. Int Rev Cytol. 1972;32:93–137. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Schwender C. F. Enzyme inhibitors. 26. Bridging hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions on adenosine deaminase with some 9-(2-hydroxy-3-alkyl)adenines. J Med Chem. 1974 Jan;17(1):6–8. doi: 10.1021/jm00247a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M., Euteneuer U. A microtuble-independent component may be involved in granule transport in pigment cells. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):556–558. doi: 10.1038/273556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M., Weber K., Porter K. R. Localization and organization of actin in melanophores. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):267–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E. The contractile ring. I. Fine structure of dividing mammalian (HeLa) cells and the effects of cytochalasin B. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;109(4):431–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. Vanadate--a new tool for biologists. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):337–338. doi: 10.1038/281337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers K. E., Gibbons I. R. Adenosine triphosphate-induced sliding of tubules in trypsin-treated flagella of sea-urchin sperm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Spooner B. S., Ash J. F., Bradley M. O., Luduena M. A., Taylor E. L., Wrenn J. T., Yamada K. Microfilaments in cellular and developmental processes. Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):135–143. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., NcIntosh J. R. A probe for flagellar dynein in the mammalian mitotic apparatus. J Cell Sci. 1981 Apr;48:241–257. doi: 10.1242/jcs.48.1.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]