Abstract
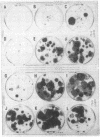
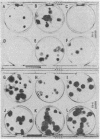
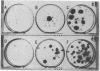
A new supplemented medium has been developed to improve human amniotic fluid cell growth and to reduce the dependence on exogenously added serum. The medium consists of a mixture of Ham's F12 medium and Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium supplemented with Hepes, antibiotics, and 10 growth-promoting factors at 4% fetal bovine serum. Good clonal growth is achieved consistently in 8--13 days and is associated with large numbers of metaphase cells. Primary clones may be analyzed directly, thereby reducing difficulty with interpretation of chromosomal mosaicism. This medium could also be used for cultivation of fetal solid tissues and peripheral blood cultures of lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D., Sato G. Serum-free cell culture: a unifying approach. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. C., Jones O. W., Bradshaw C., Sarkar S., Porreco R. P. Enhancement of human amniotic cell growth by Ficoll-Paque gradient fractionation. In Vitro. 1981 Jan;17(1):81–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02618035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chettur L., Christensen E., Philip J. Stimulation of amniotic fluid cells by fibroblast growth factor. Clin Genet. 1978 Oct;14(4):223–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1978.tb02135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Crandall B. F. Thyroid hormones and thyrotropin in amniotic fluid. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 9;293(15):740–743. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510092931503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon H. G., Weiss M. C. A quantitative comparison of formation of spontaneous and virus-produced viable hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):852–859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawood M. Y. Hormones in amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Jul 1;128(5):576–583. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(77)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmore E., Swift M. Growth of human skin fibroblasts in dialyzed fetal bovine serum. In Vitro. 1977;13(12):837–842. doi: 10.1007/BF02615132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esber H. J., Payne I. J., Bogden A. Variability of hormone concentrations and ratios in commercial sera used for tissue culture. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):559–562. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix J. S., Doherty R. A., Davis H. T., Ridge S. C. Amniotic fluid cell culture. I. Experimental design for evaluating cell culture variables: determination of optimal fetal calf serum concentration. Pediatr Res. 1974 Nov;8(11):870–874. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197411000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golbus M. S., Djalali M., Klagsbrun M., Kaback M. M., Levenson R. M., Epstein C. J. Stimulation of amniotic fluid cell growth by cartilage growth factor. Am J Med Genet. 1980;6(2):107–111. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320060203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J. S., Owashi N. D. Effects of fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor on the rate of growth of amniotic fluid-derived cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Apr;44(4):651–659. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-4-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht F., Peakman D. C., Kaiser-McCaw B., Robinson A. Amniocyte clones for prenatal cytogenetics. Am J Med Genet. 1981;10(1):51–54. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320100107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. Y., Yahr F., Kim H. J., Kerenyi T., Hirschhorn K. 550 cases of prenatal cytogenetic diagnosis: experience and prospects. Mt Sinai J Med. 1978 Jan-Feb;45(1):135–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler H. L., Gerbie A. B. Role of amniocentesis in the intrauterine detection of genetic disorders. N Engl J Med. 1970 Mar 12;282(11):596–599. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197003122821105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peakman D. C., Moreton M. F., Robinson A. Prenatal diagnosis: techniques used to help in ruling out maternal cell contamination. J Med Genet. 1977 Feb;14(1):37–39. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porreco R. P., Bradshaw C., Sarkar S., Jones O. W. Enhanced Growth of amniotic fluid cells in presence of fibroblast growth factor. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Jan;55(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy J. A., Chen A. T. Reducing use of fetal-calf serum in culturing of amniotic-fluid cells. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 18;303(12):704–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009183031222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Stanbridge E. J., Epstein C. J., Golbus M., Abbo-Halbasch G., Rodgers G. Mycoplasma contamination of cultured amniotic fluid cells: potential hazard to prenatal chromosomal diagnosis. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):477–480. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanners C. P., Eliceiri G. L., Green H. Two types of ribosome in mouse-hamster hybrid cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 10;230(10):52–54. doi: 10.1038/newbio230052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele M. W., Breg W. R., Jr Chromosome analysis of human amniotic-fluid cells. Lancet. 1966 Feb 19;1(7434):383–385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91387-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]