Abstract
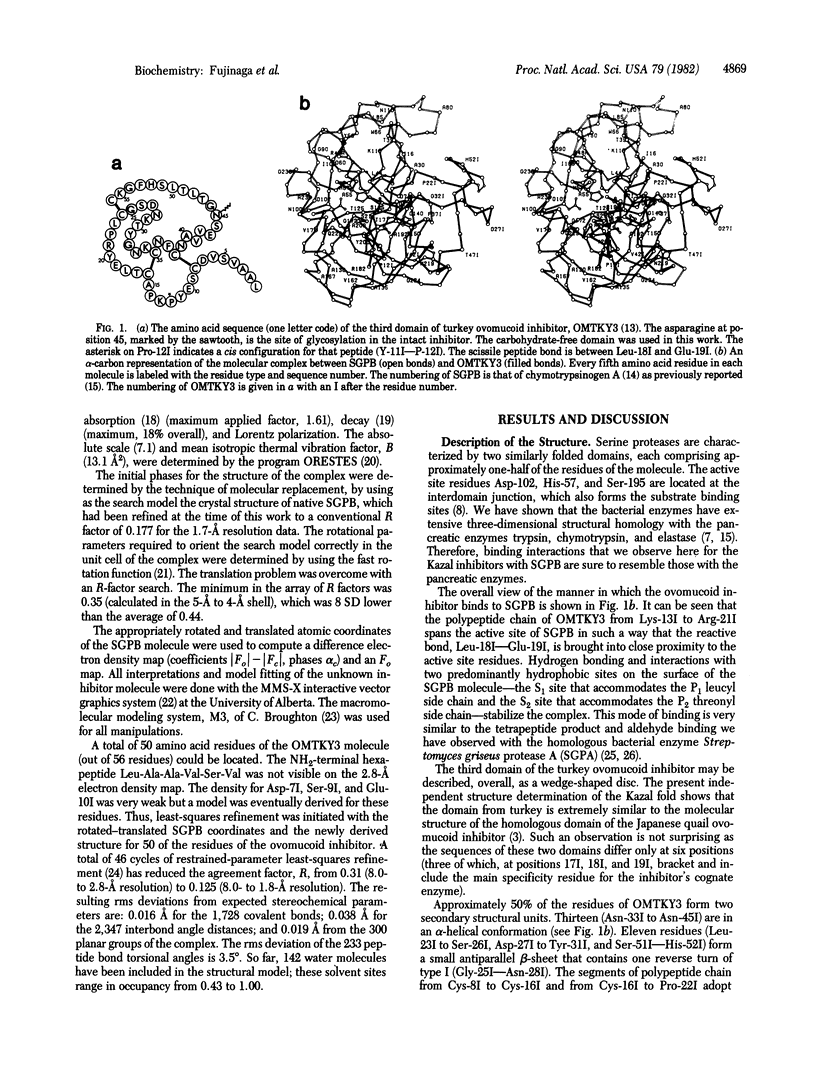
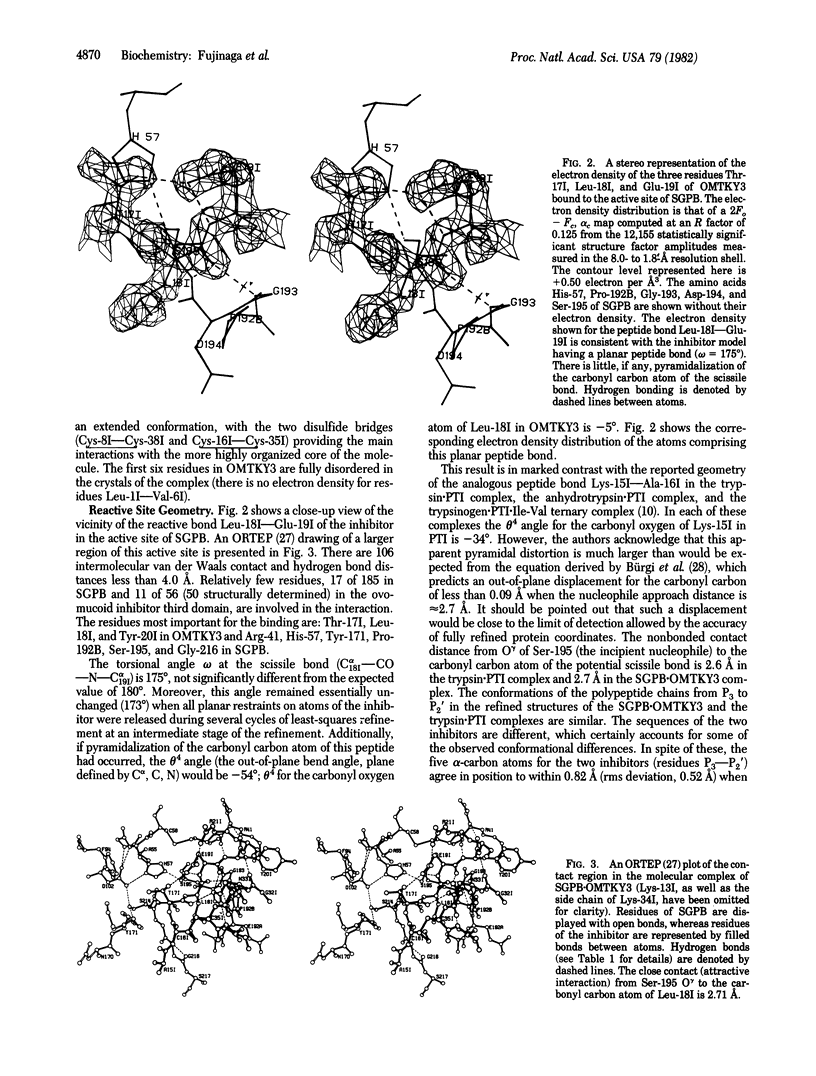
We have determined the crystal structure of the molecular complex between Streptomyces griseus protease B (SGPB), a bacterial serine protease, and the third domain of the ovomucoid inhibitor from turkey. Restrained-parameter least-squares refinement of the structure with the 1.8-A intensity data set has resulted in an R factor of 0.125. The carbonyl carbon atom of the reactive bond between Leu-18 and Glu-19 in the inhibitor lies at a distance of 2.71 A from the O gamma atom of the nucleophilic Ser-195 in SGPB; this distance is 0.5 A shorter than a normal van der Waals contact. Unlike the reactive bond in the pancreatic trypsin inhibitor complexed with bovine trypsin, the Leu--Glu bond of the ovomucoid inhibitor is not distorted from planarity towards a pyramidal configuration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer C. A. Active centers of Streptomyces griseus protease 1, Streptomyces griseus protease 3, and alpha-chymotrypsin: enzyme-substrate interactions. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):375–380. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizzozero S. A., Zweifel B. O. The importance of the conformation of the tetrahedral intermediate for the alpha-chymotrypsin-catalyzed hydrolysis of peptide substrates. FEBS Lett. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogard W. C., Jr, Kato I., Laskowski M., Jr A Ser162/Gly162 polymorphism in Japanese quail ovomucoid. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6569–6574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbaere L. T., Hutcheon W. L., James M. N., Thiessen W. E. Tertiary structural differences between microbial serine proteases and pancreatic serine enzymes. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):758–763. doi: 10.1038/257758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S., Kauffman D. L. Corrections to the amino acid sequence of bovine chymotrypsinogen A. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):229–231. doi: 10.1042/bj1010229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A. Radiation damage in protein crystallography. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):889–893. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirono S., Nakamura K. T., Iitaka Y., Mitsui Y. Crystal structure of the complex of subtilisin BPN' with its protein inhibitor Streptomyces subtilisin inhibitor. The structure at 4.3 Angstroms resolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):855–869. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Kukla D., Bode W., Schwager P., Bartels K., Deisenhofer J., Steigemann W. Structure of the complex formed by bovine trypsin and bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. II. Crystallographic refinement at 1.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):73–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. N., Brayer G. D., Delbaere L. T., Sielecki A. R., Gertler A. Crystal structure studies and inhibition kinetics of tripeptide chloromethyl ketone inhibitors with Streptomyces griseus protease B. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):423–438. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. N., Delbaere L. T., Brayer G. D. Amino acid sequence alignment of bacterial and mammalian pancreatic serine proteases based on topological equivalences. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jun;56(6):396–402. doi: 10.1139/o78-062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. N., Sielecki A. R., Brayer G. D., Delbaere L. T., Bauer C. A. Structures of product and inhibitor complexes of Streptomyces griseus protease A at 1.8 A resolution. A model for serine protease catalysis. J Mol Biol. 1980 Nov 25;144(1):43–88. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurásek J., Johnson P., Olafson R. W., Smillie L. B. An improved fractionation system for pronase on CM-sephadex. Can J Biochem. 1971 Nov;49(11):1195–1201. doi: 10.1139/o71-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurásek L., Carpenter M. R., Smillie L. B., Gertler A., Levy S., Ericsson L. H. Amino acid sequence of Streptomyces griseus protease B, A MAJOR COMPONENT OF Pronase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1095–1100. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80396-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Argos P. The taxonomy of protein structure. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 5;109(1):99–129. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sielecki A. R., Hendrickson W. A., Broughton C. G., Delbaere L. T., Brayer G. D., James M. N. Protein structure refinement: Streptomyces griseus serine protease A at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):781–804. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90486-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. M., Wright H. T., Janin J., Chothia C. H., Blow D. M. Crystal structure of the complex of porcine trypsin with soybean trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz) at 2.6-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 24;13(20):4212–4228. doi: 10.1021/bi00717a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Papamokos E., Bode W., Huber R., Kato I., Laskowski M., Jr Crystallization, crystal structure analysis and molecular model of the third domain of Japanese quail ovomucoid, a Kazal type inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):109–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


