Abstract
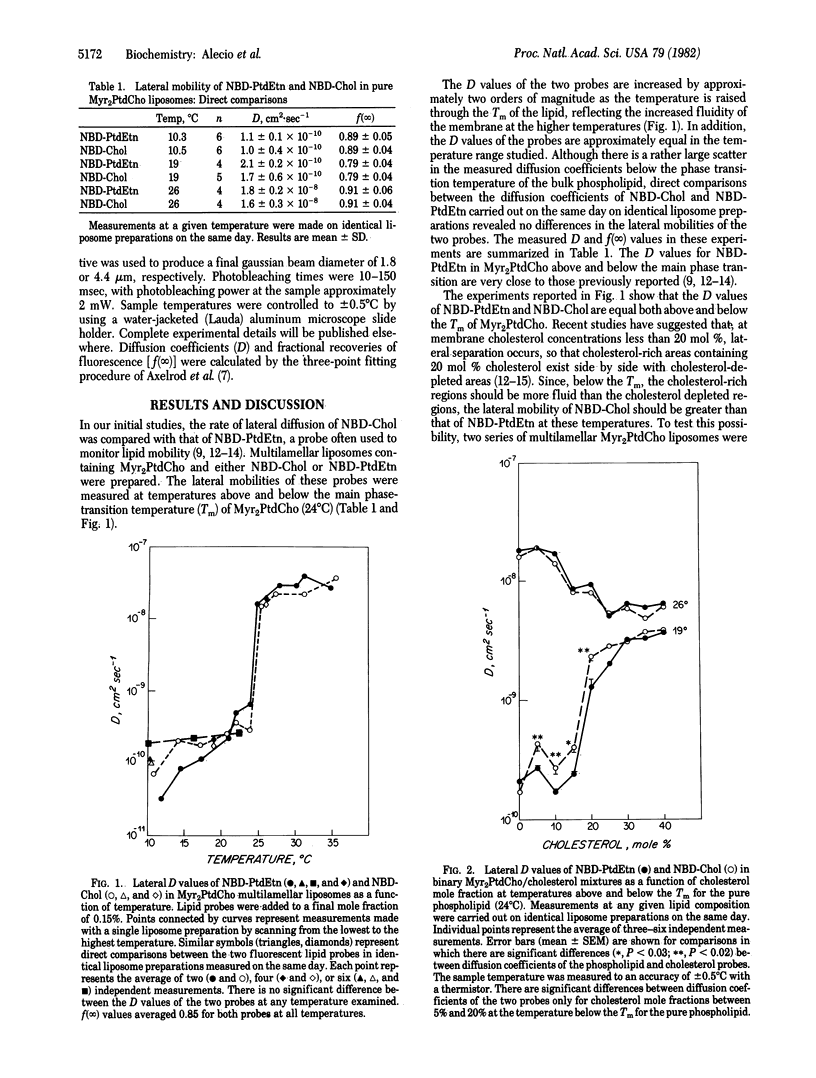
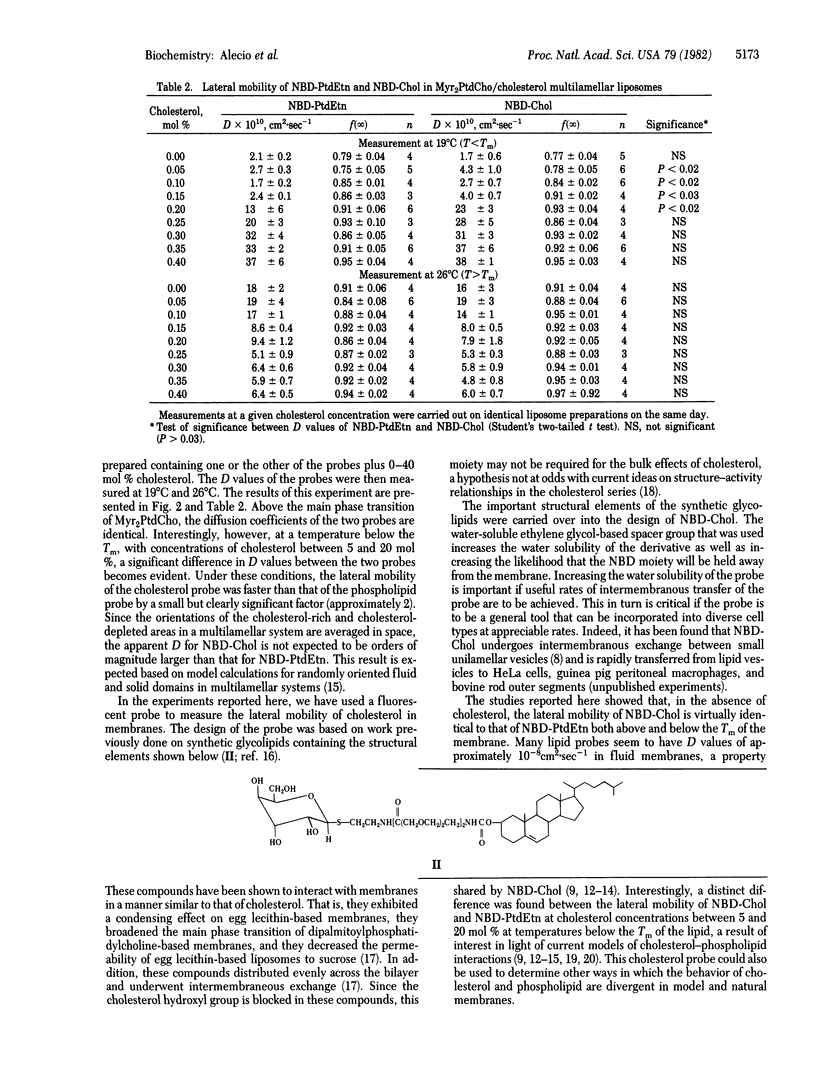
N1-Cholesterylcarbamoyl-N8-(4-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole)-3,6-dioxaoctyl-1,8-diamine (NBD-Chol), a new fluorescent derivative of cholesterol, was incorporated into L-alpha-dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (Myr2PtdCho)-based liposomes. The lateral mobility of this derivative, as well as that of N-(4-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole)phosphatidylethanolamine (NBD-PtdEtn), was measured by fluorescence recovery after photobleaching techniques. In Myr2PtdCho liposomes, the diffusion coefficients (D) of the two probes are the same within experimental error below (D, approximately equal to 2 X 10(-10) cm2 X sec-1) and above (D, approximately equal to 2 X 10(-8) cm2 X sec-1) the main phase transition temperature of the bulk lipid (Tm). There is, however, a distinct difference between the mobilities of the derivatives at concentrations of added cholesterol between 5 and 20 mol % at temperatures below the main phase transition. Under these conditions, the diffusion coefficient of NBD-Chol is approximately twice that of NBD-PtdCho, a result consistent with the idea that cholesterol undergoes a lateral phase separation in these membranes at concentrations less than 20 mol %. At cholesterol concentrations greater than 20 mol % or temperatures above the Tm, the D values of the two probes are identical. The lateral mobility of a cholesterol derivative has thus been monitored directly in cholesterol-containing membranes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Dawidowicz E. A. Mechanism of cholesterol exchange between phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3805–3810. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Dawidowicz E. A. Transmembrane movement of cholesterol in small unilamellar vesicles detected by cholesterol oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):586–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., De Kruyff B. The function of sterols in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):109–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estep T. N., Mountcastle D. B., Biltonen R. L., Thompson T. E. Studies on the anomalous thermotropic behavior of aqueous dispersions of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine-cholesterol mixtures. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1984–1989. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P. Structural analysis of hydrated egg lecithin and cholesterol bilayers. I. X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 25;100(3):345–358. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golan D. E., Veatch W. Lateral mobility of band 3 in the human erythrocyte membrane studied by fluorescence photobleaching recovery: evidence for control by cytoskeletal interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2537–2541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppel D. E. Fluorescence redistribution after photobleaching. A new multipoint analysis of membrane translational dynamics. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85176-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., McConnell H. M. Lateral diffusion in inhomogeneous membranes. Model membranes containing cholesterol. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):383–397. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85103-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R., Bangerter F. W. Threshold effects on the lectin-mediated aggregation of synthetic glycolipid-containing liposomes. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(3):295–309. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R., Slama J., Bangerter F. W. Functional incorporation of synthetic glycolipids into cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2510–2513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. L., Smith B. A., McConnell H. M. Lateral diffusion in binary mixtures of cholesterol and phosphatidylcholines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):15–18. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimshick E. J., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separations in binary mixtures of cholesterol and phospholipids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 17;53(2):446–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90682-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. A., McConnell H. M. Determination of molecular motion in membranes using periodic pattern photobleaching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2759–2763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Rubenstein J. L., Parce J. W., McConnell H. M. Lateral diffusion of M-13 coat protein in mixtures of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5907–5911. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder B., Freire E. Compositional domain structure in phosphatidylcholine--cholesterol and sphingomyelin--cholesterol bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4055–4059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcester D. L., Franks N. P. Structural analysis of hydrated egg lecithin and cholesterol bilayers. II. Neutrol diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 25;100(3):359–378. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



