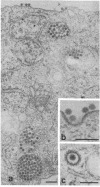
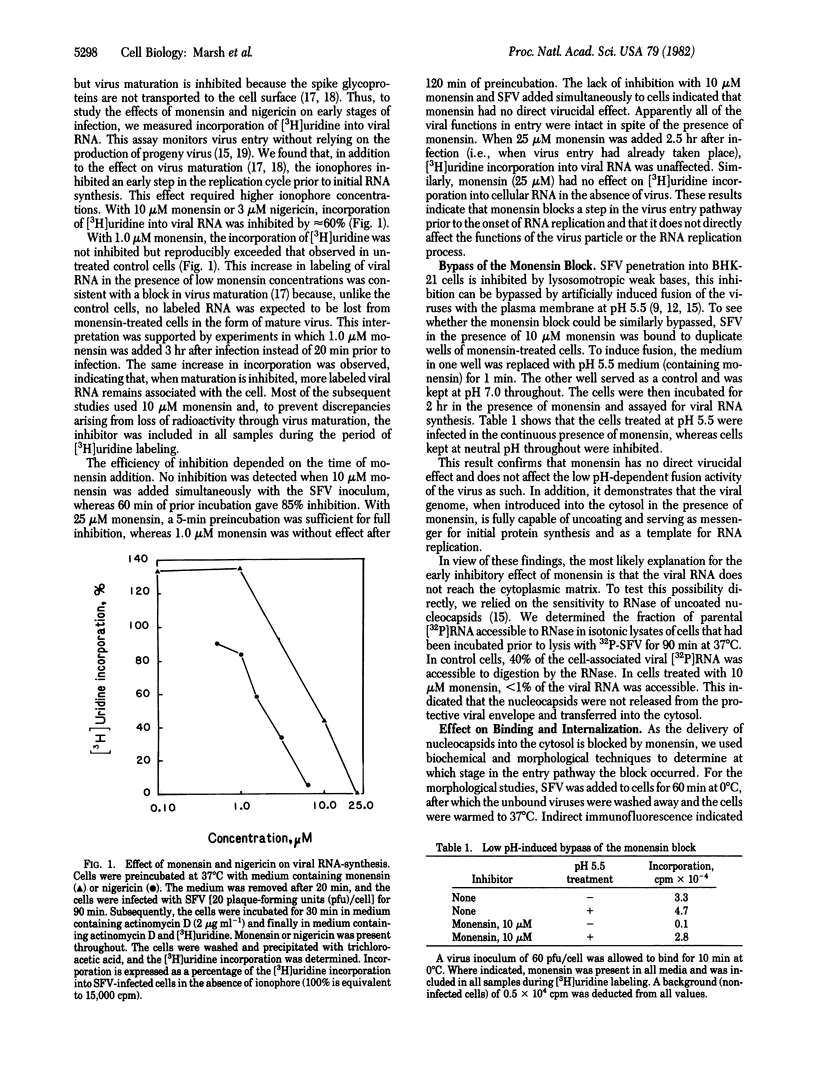
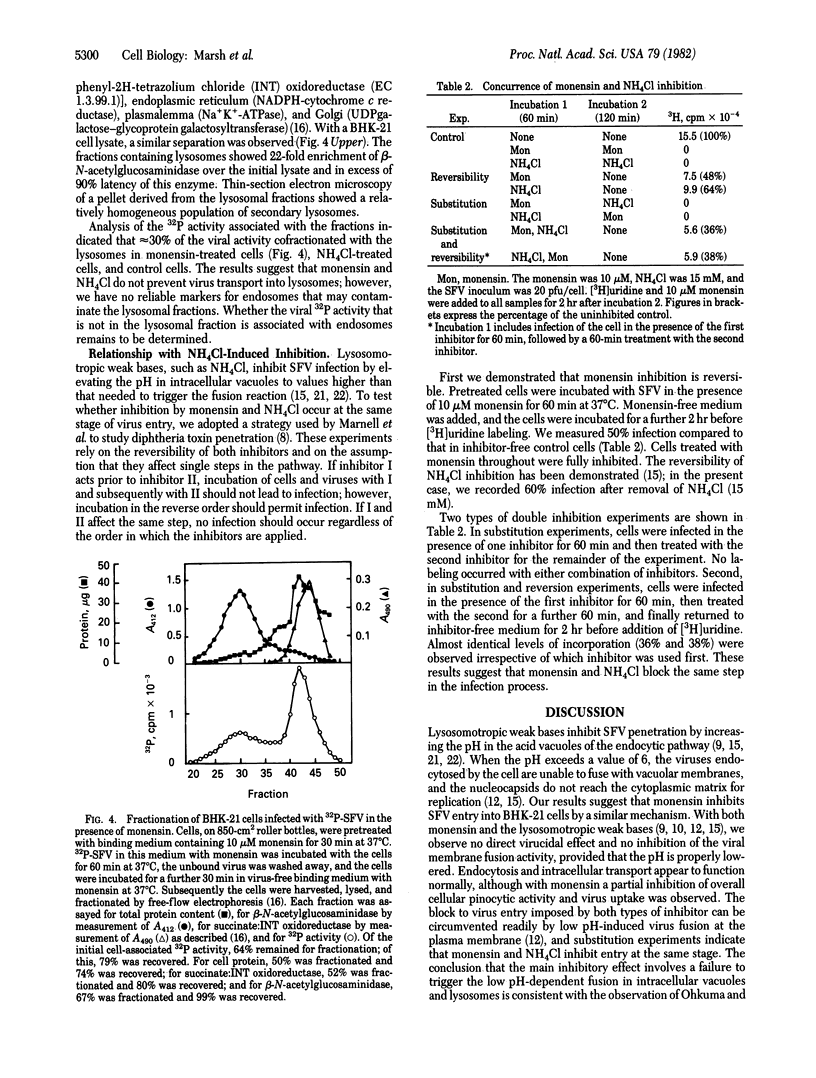
Abstract
The carboxylic ionophores monensin and nigericin, at concentrations higher than 10 and 6 muM, respectively, prevent the penetration of the Semliki Forest virus (SFV) genome into the cytosol of baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells and thereby inhibit viral replication. In the absence of inhibitors, the entry of SFV is known to proceed by adsorptive endocytosis in coated vesicles, followed by acid-triggered membrane fusion in intracellular vacuoles or lysosomes. The results show that binding of the virus to the cell surface, adsorptive endocytosis, and intracellular transport of viruses to the lysosomes are only marginally affected by the ionophores. No direct virucidal effect is observed, nor is the membrane fusion activity of the virus at low pH directly affected. Sequential addition of monensin and ammonium chloride (a non-related lysosomotropic inhibitor of SFV entry) indicates that both inhibitors affect the same step in the entry pathway. On the basis of these data and the known effects of carboxylic ionophores and lysosomotropic weak bases on cellular pH gradients, we conclude that monensin inhibits penetration by increasing the pH in endocytic vacuoles and lysosomes above pH 6, which is the pH threshold for the viral membrane fusion activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Monensin interrupts the recycling of low density lipoprotein receptors in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Simon M. I. The entry of diphtheria toxin into the mammalian cell cytoplasm: evidence for lysosomal involvement. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):849–854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms E., Kern H., Schneider J. A. Human lysosomes can be purified from diploid skin fibroblasts by free-flow electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Marsh M., White J. Inhibition of Semliki forest virus penetration by lysosomotropic weak bases. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jan;58(Pt 1):47–61. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Söderlund H. Stepwise dissociation of the Semliki Forest Virus membrane with trition X-100. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):287–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Schlesinger M. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus and sindbis virus glycoprotein transport to the cell surface is inhibited by ionophores. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Hashimoto K., Saraste J., Virtanen I., Penttinen K. Monensin and FCCP inhibit the intracellular transport of alphavirus membrane glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):783–791. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Simons K., von Bonsdorff C. H. Studies in subviral components of Semliki Forest virus. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(4):235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marnell M. H., Stookey M., Draper R. K. Monensin blocks the transport of diphtheria toxin to the cell cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):57–62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Adsorptive endocytosis of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Pathway of vesicular stomatitis virus entry leading to infection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):609–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. K., Feuer B. I., Vanderoef R., Lenard J. Reconstituted G protein-lipid vesicles from vesicular stomatitis virus and their inhibition of VSV infection. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):421–429. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. K., Lenard J. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus infection by spike glycoprotein. Evidence for an intracellular, G protein-requiring step. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):430–437. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole B., Ohkuma S. Effect of weak bases on the intralysosomal pH in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):665–669. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Diphtheria toxin entry into cells is facilitated by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):828–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Willingham M., Pastan I. Monensin blocks endocytosis of vesicular stomatitis virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 15;102(3):992–998. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91636-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Yamamoto S., Homma M., Ishida N. Effect of chloroquine on the growth of animal viruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;36(1):93–104. doi: 10.1007/BF01250299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. The interaction of soluble horseradish peroxidase with mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1972 Oct;55(1):186–204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Lodish H. F. Intracellular transport of secretory and membrane proteins in hepatoma cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Vassalli P. Plasma cell immunoglobulin secretion: arrest is accompanied by alterations of the golgi complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1332–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida N., Smilowitz H., Ledger P. W., Tanzer M. L. Kinetic studies of the intracellular transport of procollagen and fibronectin in human fibroblasts. Effects of the monovalent ionophore, monensin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8638–8644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A. pH-dependent fusion between the Semliki Forest virus membrane and liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Fusion of Semliki forest virus with the plasma membrane can be induced by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):264–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox D. K., Kitson R. P., Widnell C. C. Inhibition of pinocytosis in rat embryo fibroblasts treated with monensin. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):859–864. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]