Abstract
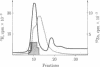
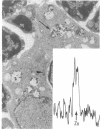
The serum thymic factor (FTS) utilized in its synthetic or natural form loses its biological activity in a rosette assay after treatment with a metal ion-chelating agent, Chelex 100. This activity is restored by the addition of Zn salts and, to a lesser extent, certain other metal salts. FTS activation is secondary to the binding of the metal to the peptide. The metal-to-peptide molar ratio of 1:1 provides the best activation. These data indicate the existence of two forms of FTS. The first one lacks Zn and is biologically inactive; the second one contains Zn and is biologically active, for which we propose the name of "thymulin" (FTS-Zn). The presence of Zn in synthetic FTS was confirmed by atomic absorption spectrometry. The interaction between Zn and FTS was further suggested by microanalysis demonstrating the presence of this metal in thymic reticuloepithelial cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach J. F., Carnaud C. Thymic factors. Prog Allergy. 1976;21:342–408. doi: 10.1159/000399402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F., Dardenne M., Pleau J. M., Bach M. A. Isolation, biochemical characteristics, and biological activity of a circulating thymic hormone in the mouse and in the human. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:186–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F., Dardenne M. Studies on thymus products. II. Demonstration and characterization of a circulating thymic hormone. Immunology. 1973 Sep;25(3):353–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J., Bardenne M., Pleau J., Rosa J. Biochemical characterisation of a serum thymic factor. Nature. 1977 Mar 3;266(5597):55–57. doi: 10.1038/266055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra R. K., Heresi G., Au B. Serum thymic factor activity in deficiencies of calories, zinc, vitamin A and pyridoxine. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):332–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardenne M., Pleau J. M., Savino W., Bach J. F. Monoclonal antibody against the serum thymic factor (FTS). Immunol Lett. 1982 Feb;4(2):79–83. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(82)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardenne M., Pléau J. M., Blouquit J. Y., Bach J. F. Characterization of facteur thymique sérique (FTS) in the thymus. II. Direct demonstration of the presence of FTS in thymosin fraction V. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):477–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLE P. MISE AU POINT D'UNE M'ETHODE DE MICROANALYSE DES TISSUS BIOLOGIQUES AU MOYEN DE LA MICROSONDE DE CASTAING. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1964 Feb;9:203–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata T., Incefy G. S., Tanaka T., Fernandes G., Menendez-Botet C. J., Pih K., Good R. A. Circulating thymic hormone levels in zinc deficiency. Cell Immunol. 1979 Sep 15;47(1):100–105. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. Thermolysin: a zinc metalloenzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 8;37(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90739-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier J. C., Dardenne M., Pléau J. M., Schmitt D., Deschaux P., Bach J. F. Characterization of facteur thymique sérique (FTS) in the thymus. I. Fixation of anti-FTS antibodies on thymic reticulo-epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):470–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pléau J. M., Fuentes V., Morgat J. L., Bach J. F. Specific receptors for the serum thymic factor (FTS) in lymphoblastoid cultured cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2861–2865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Kemmler W., Tager H. S., Peterson J. D. Proteolytic processing in the biosynthesis of insulin and other proteins. Fed Proc. 1974 Oct;33(10):2105–2115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]