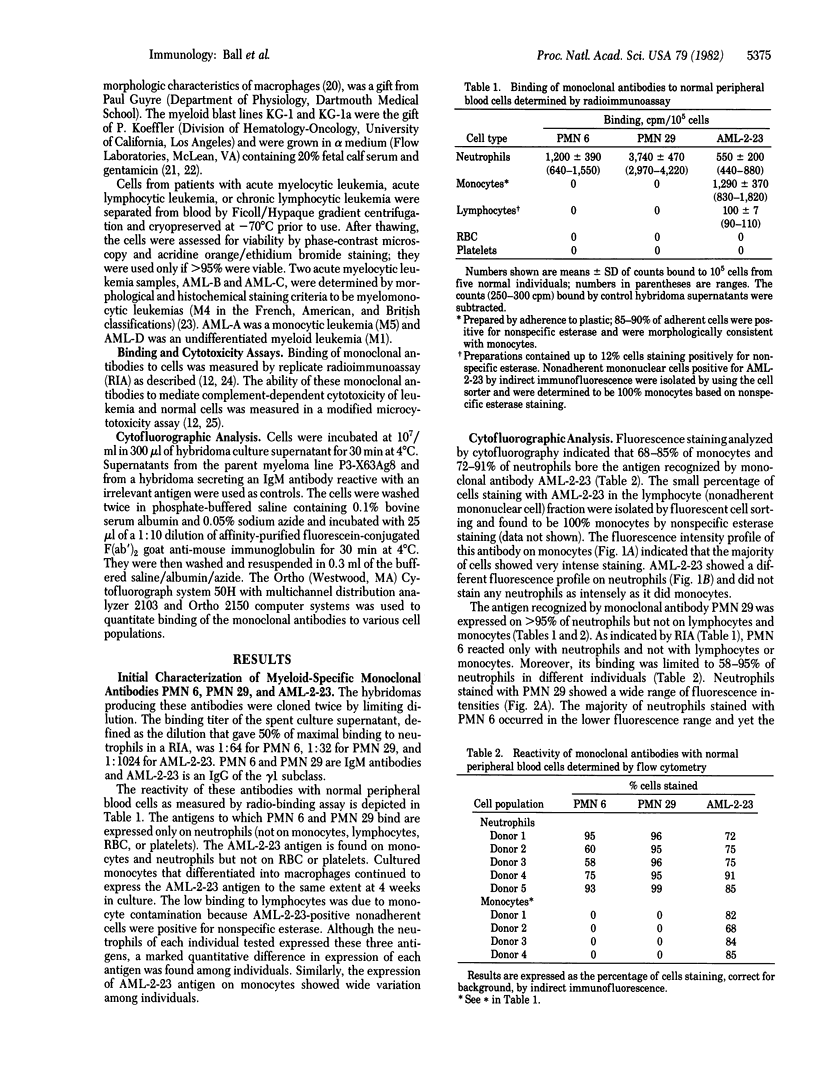
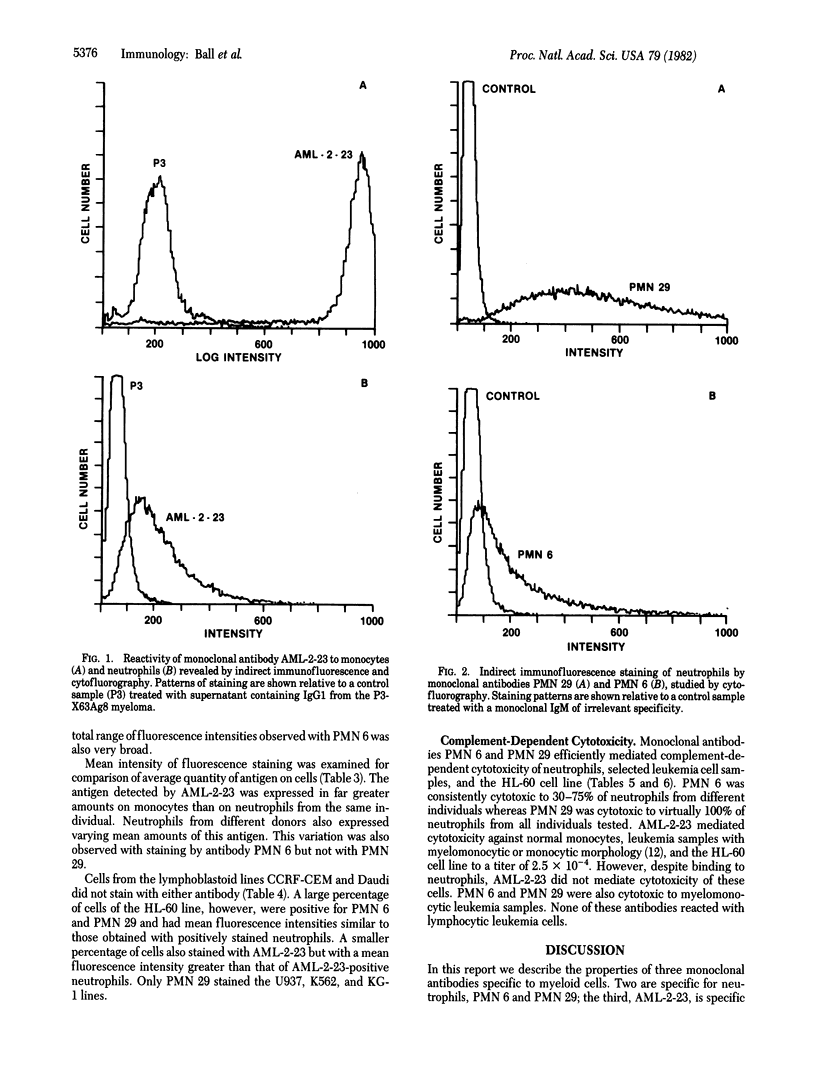
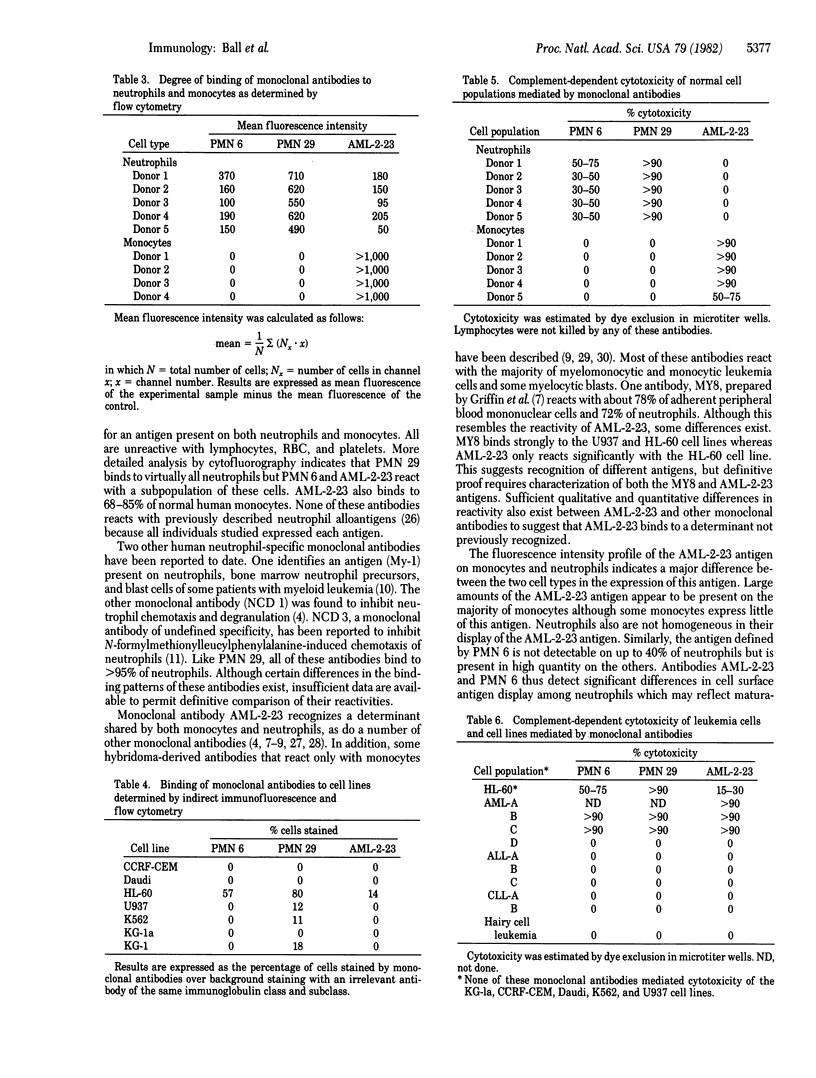
Abstract
Three cytotoxic murine monoclonal antibodies that recognize myeloid-specific antigens have been produced by immunization with normal human neutrophils or myeloblasts from a patient with acute myelomonocytic leukemia. Two of these, PMN 6 and PMN 29, are specific for neutrophils; the third monoclonal antibody, AML-2-23, is reactive with the majority of normal monocytes as well as a subpopulation of mature neutrophils. Although neutrophils from all individuals tested expressed these antigens, cytofluorographic analysis revealed that the percentage of cells bearing the PMN 6 and AML-2-23 antigens varied among individuals. Significant additional heterogeneity in the density of each antigen among antigen-bearing cells was also observed. All three antibodies efficiently mediated complement-dependent cytotoxicity of acute myelocytic leukemia cells yet were unreactive with lymphocytic leukemia cells. Neutrophil cytotoxicity was mediated by PMN 6 and PMN 29 but not by AML-2-23. On the other hand, AML-2-23, but not PMN 6 or PMN 29, was cytotoxic for normal monocytes and macrophages. These monoclonal antibodies may be of value in the study of normal neutrophil function and differentiation and may have clinical utility in diagnosis and therapy of myeloid leukemia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball E. D., Fanger M. W. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with human myeloid leukaemia cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):655–665. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball E. D., Kadushin J. M., Schacter B., Fanger M. W. Studies on the ability of monoclonal antibodies to selectively mediate complement-dependent cytotoxicity of human myelogenous leukemia blast cells. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1476–1481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breard J., Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1943–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Ralph P., Bognacki J., Kincade P. W., Desousa M. A subpopulation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils contains an active form of lactoferrin capable of binding to human monocytes and inhibiting production of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulatory activities. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):903–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civin C. I., Mirro J., Banquerigo M. L. My-1, new myeloid-specific antigen identified by a mouse monoclonal antibody. Blood. 1981 May;57(5):842–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claas F. H., Langerak J., Sabbe L. J., van Rood J. J. NE1: a new neutrophil specific antigen. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Feb;13(2):129–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb01148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Classification of acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Dec;87(6):740–753. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-6-740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter T. G., Keeling P. J., Henson P. M. A monoclonal antibody-inhibiting FMLP-induced chemotaxis of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2241–2245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter T. G., Spears P., Henson P. M. A monoclonal antibody inhibiting human neutrophil chemotaxis and degranulation. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1355–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY G. E., LAZARUS H., FARBER S., UZMAN B. G., BOONE B. A., MCCARTHY R. E. CONTINUOUS CULTURE OF HUMAN LYMPHOBLASTS FROM PERIPHERAL BLOOD OF A CHILD WITH ACUTE LEUKEMIA. Cancer. 1965 Apr;18:522–529. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196504)18:4<522::aid-cncr2820180418>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana J. A., Colbert D. A., Deisseroth A. B. Identification of a population of bipotent stem cells in the HL60 human promyelocytic leukemia cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3863–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Roos D., Kaplan H. B., Weissmann G. Complement and immunoglobulins stimulate superoxide production by human leukocytes independently of phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1155–1163. doi: 10.1172/JCI108191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Ritz J., Nadler L. M., Schlossman S. F. Expression of myeloid differentiation antigens on normal and malignant myeloid cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):932–941. doi: 10.1172/JCI110348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Oades Z. G. Stimulation of human neutrophils by soluble and insoluble immunoglobulin aggregates. Secretion of granule constituents and increased oxidation of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1053–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI108152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Gallin J. I. Separation and functional characterization of human neutrophil subpopulations. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):659–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Billing R., Lusis A. J., Sparkes R., Golde D. W. An undifferentiated variant derived from the human acute myelogenous leukemia cell line (KG-1). Blood. 1980 Aug;56(2):265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Golde D. W. Acute myelogenous leukemia: a human cell line responsive to colony-stimulating activity. Science. 1978 Jun 9;200(4346):1153–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.306682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Lebman D., Ip S. H., Rovera G., Trinchieri G. Terminal differentiation surface antigens of myelomonocytic cells are expressed in human promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL60) treated with chemical inducers. Blood. 1981 Oct;58(4):836–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H. V., Picker L. J., Stobo J. D. Macrophage heterogeneity in man. A subpopulation of HLA-DR-bearing macrophages required for antigen-induced T cell activation also contains stimulators for autologous-reactive T cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):581–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfré G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):301–306. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd R. F., 3rd, Nadler L. M., Schlossman S. F. Antigens on human monocytes identified by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1435–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugolini V., Nunez G., Smith R. G., Stastny P., Capra J. D. Initial characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6764–6768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



