Abstract
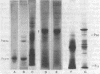
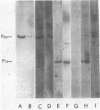
Patients affected with systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease produce antibodies directed against two nuclear antigens, Sm and nuclear ribonucleoprotein (nRNP), respectively. The two antigens exhibit a relationship of partial identity in serologic assays, but the molecular basis of this relationship was not understood. This report describes the isolation of a nRNP particle containing both nRNP and Sm antigens. The particle was isolated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation of a rat liver nuclear extract followed by anti-nRNP affinity chromatography of a 14S gradient fraction. The protein moiety of the isolated particle consisted primarily of two polypeptides, P13 (Mr, 13,000) and P30 (Mr, 30,000). The immunoreactivity of P13 and P30 was demonstrated directly by transfer of these proteins from gels to nitrocellulose paper, followed by immunoautoradiography. Anti-nRNP sera reacted only with P30, whereas anti-Sm sera reacted with P13. Anti-nRNP sera were previously found to react with P13, but only in the presence of RNA [Douvas, A. S., Stumph, W. E., Reyes, P. R. & Tan, E. M. (1979) J. Biol. Chem. 254, 3608--3616]. From these observations it was concluded that P13 is the Sm antigen. The precipitating nRNP antigen is composed of P30--RNA complexes or P13--RNA complexes, with a RNA-independent reaction occurring with P30. The partial identity between Sm and nRNP antigens can be explained on the basis of a common reactivity to the P30--P13--RNA particle, with anti-Sm sera capable of binding additionally to RNA-free P13.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barque J. P., Yeni P., Peraudeau L., Danon F., Larsen C. J. Nuclear ribonucleoproteins recognized by human antinuclear antibodies in retrovirus-infected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 16;99(1):284–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91743-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas A. S., Achten M., Tan E. M. Identification of a nuclear protein (Scl-70) as a unique target of human antinuclear antibodies in scleroderma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10514–10522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas A. S., Stumph W. E., Reyes P., Tan E. M. Isolation and characterization of nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes using human anti-nuclear ribonucleoprotein antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3608–3616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata N., Tan E. M. Identification of antibodies to nuclear acidic antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19(3):574–580. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notman D. D., Kurata N., Tan E. M. Profiles of antinuclear antibodies in systemic rheumatic diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Oct;83(4):464–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-4-464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. D. Ribonucleoprotein antibodies: frequency and clinical significance in systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and mixed connective tissue disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Nov;82(5):769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., May C. M., Holman H. R., McDuffie F. C., Hess E. V., Schmid F. R. Association of antibodies to ribonucleoprotein and Sm antigens with mixed connective-tissue disease, systematic lupus erythematosus and other rheumatic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1976 Nov 18;295(21):1149–1154. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197611182952101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TS'O P. O., SATO C. S. Synthesis of ribonucleic acid in plants. I. Distribution of ribonucleic acid and of protein among subcellular components of pea epicotyls. Exp Cell Res. 1959 May;17(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(59)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Palter K., Van Lente F. Histones H2a, H2b, H3, and H4 form a tetrameric complex in solutions of high salt. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):85–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Gardner W. D., Hoch S. O. Identification of the immunogenically active components of the Sm and RNP antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):626–630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]