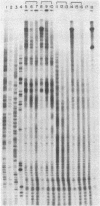
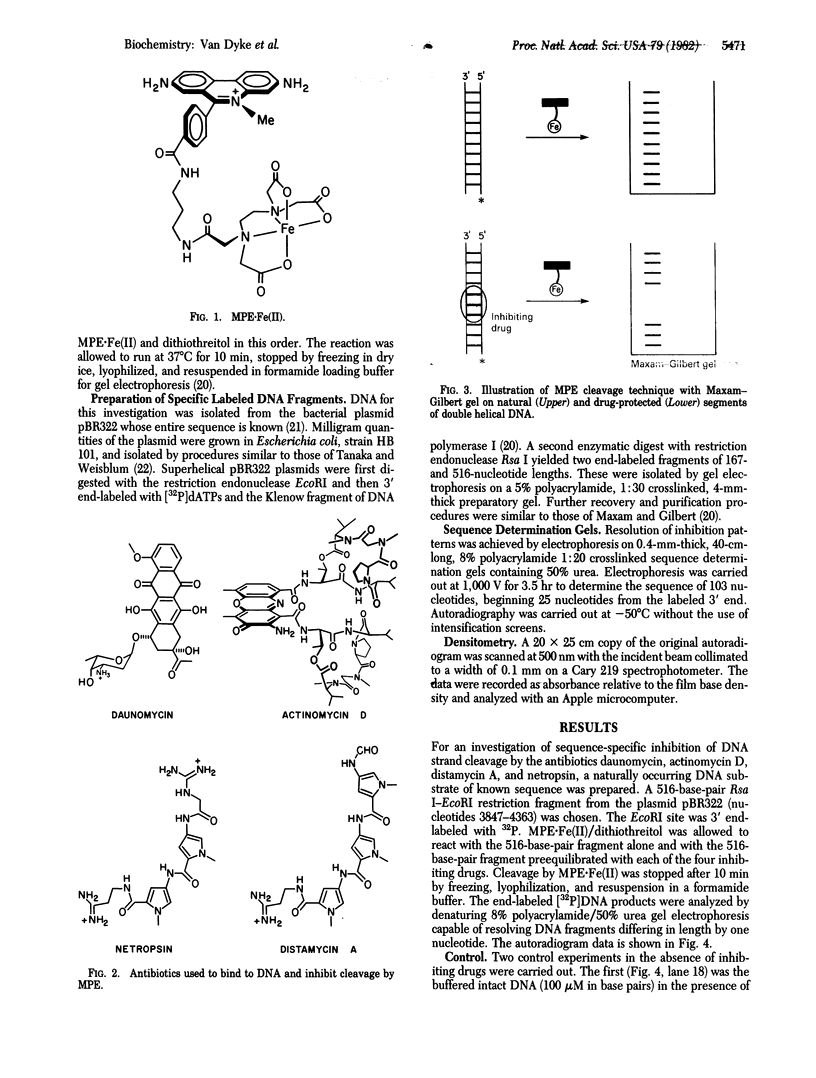
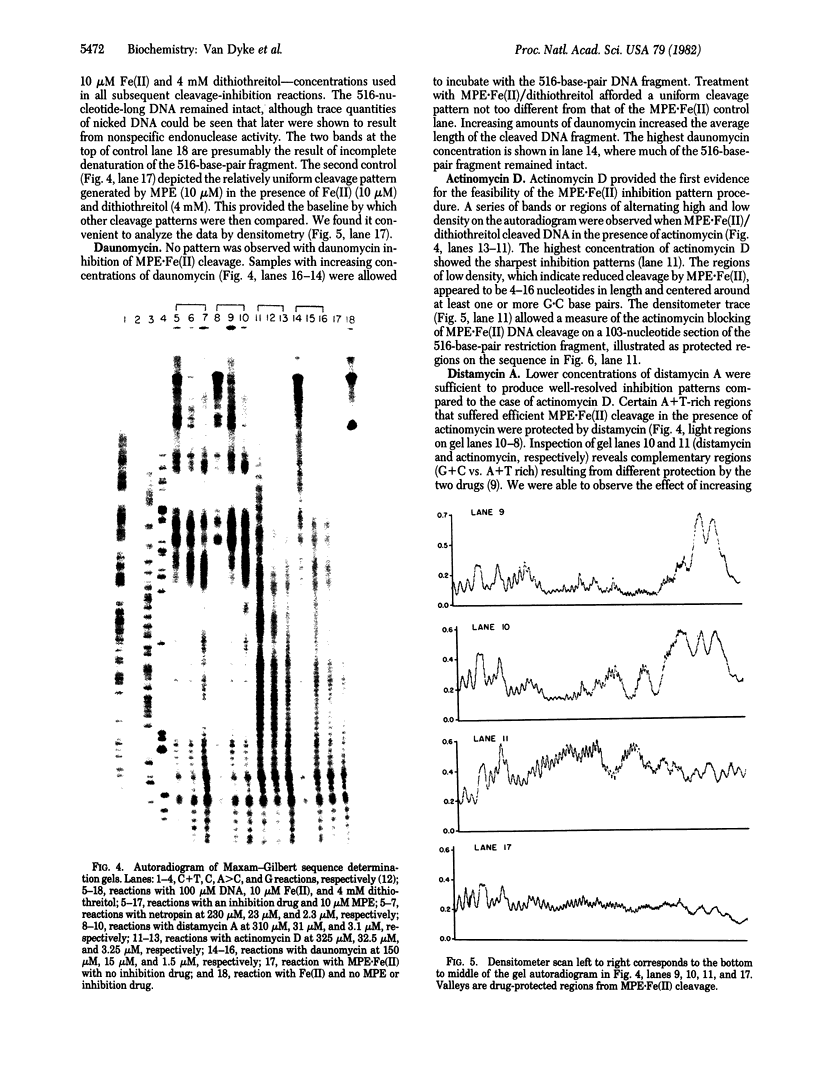
Abstract
We report a direct technique for determining the binding sites of small molecules on naturally occurring heterogeneous DNA. Methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II) [MPE.Fe(II) cleaves double helical DNA with low sequence specificity. Using a combination of MPE.Fe(II) cleavage of drug-protected DNA fragments and Maxam-Gilbert gel methods of sequence analysis, we have determined the preferred binding sites on a Rsa I-EcoRI restriction fragment from pBR322 for the intercalator actinomycin D and the minor groove binders netropsin and distamycin A. Netropsin and distamycin A gave identical DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns and bound preferentially to A+T-rich regions with a minimal protected site of four base pairs. We were able to observe the effect of increasing concentration on site selection by netropsin and distamycin A. Actinomycin D afforded a completely different cleavage-inhibition pattern, with 4- to 16-base-pair-long protected regions centered around one or more G.C base pairs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berlin V., Haseltine W. A. Reduction of adriamycin to a semiquinone-free radical by NADPH cytochrome P-450 reductase produces DNA cleavage in a reaction mediated by molecular oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4747–4756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman H. M., Neidle S., Zimmer C., Thrum H. Netropsin, a DNA-binding oligopeptide structural and binding studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 26;561(1):124–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90496-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresloff J. L., Crothers D. M. Equilibrium studies of ethidium--polynucleotide interactions. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3547–3553. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. M., Peisach J., Horwitz S. B. Mechanism of bleomycin action: in vitro studies. Life Sci. 1981 Feb 16;28(7):715–727. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Haseltine W. A. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by the antitumor antibiotics neocarzinostatin and bleomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG I. H., RABINOWITZ M., REICH E. Basis of actinomycin action. I. DNA binding and inhibition of RNA-polymerase synthetic reactions by actinomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2094–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastrup R. V., Young M. A., Krugh T. R. Ethidium bromide complexes with self-complementary deoxytetranucleotides. Demonstration and discussion of sequence preferences in the intercalative binding of ethidium bromide. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4855–4865. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krylov A. S., Grokhovsky S. L., Zasedatelev A. S., Zhuze A. L., Gursky G. V., Gottikh B. P. Quantitative estimation of the contribution of pyrrolcarboxamide groups of the antibiotic distamycin A into specificity of its binding to DNA AT pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):289–304. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck G., Triebel H., Waring M., Zimmer C. Conformation dependent binding of netropsin and distamycin to DNA and DNA model polymers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):503–530. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Crothers D. M. Interactions of heteroaromatic compounds with nucleic acids. 1. The influence of heteroatoms and polarizability on the base specificity of intercalating ligands. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):267–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Crothers D. M. Studies of the binding of actinomycin and related compounds to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 28;35(2):251–290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Rice J. A., Broka C., Itakura K. Mutual interaction between adjacent dG . dC actinomycin binding sites and dA . dT netropsin binding sites on the self-complementary d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G) duplex in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7281–7284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Rice J. A. Hydrogen bonding, overlap geometry, and sequence specificity in anthracycline antitumor antibiotic.DNA complexes in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3333–3337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Wang A. H., Ughetto G., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of an anticancer drug-DNA complex: daunomycin plus d(CpGpTpApCpG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7204–7208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. The stereochemistry of actinomycin binding to DNA and its implications in molecular biology. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1973;13:153–190. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita M., Grollman A. P., Ohtsubo E., Ohtsubo H. Interaction of bleomycin with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5983–5987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takusagawa F., Dabrow M., Neidle S., Berman H. M. The structure of a pseudo intercalated complex between actinomycin and the DNA binding sequence d(GpC). Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):466–469. doi: 10.1038/296466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Weisblum B. Construction of a colicin E1-R factor composite plasmid in vitro: means for amplification of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):354–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.354-362.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. Complex formation between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):269–282. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M., Larson J. E., Wells R. D. Netropsin. A specific probe for A-T regions of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6719–6731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Larson J. E. Studies on the binding of actinomycin D to DNA and DNA model polymers. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):319–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90248-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C. Effects of the antibiotics netropsin and distamycin A on the structure and function of nucleic acids. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1975;15(0):285–318. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]