Abstract
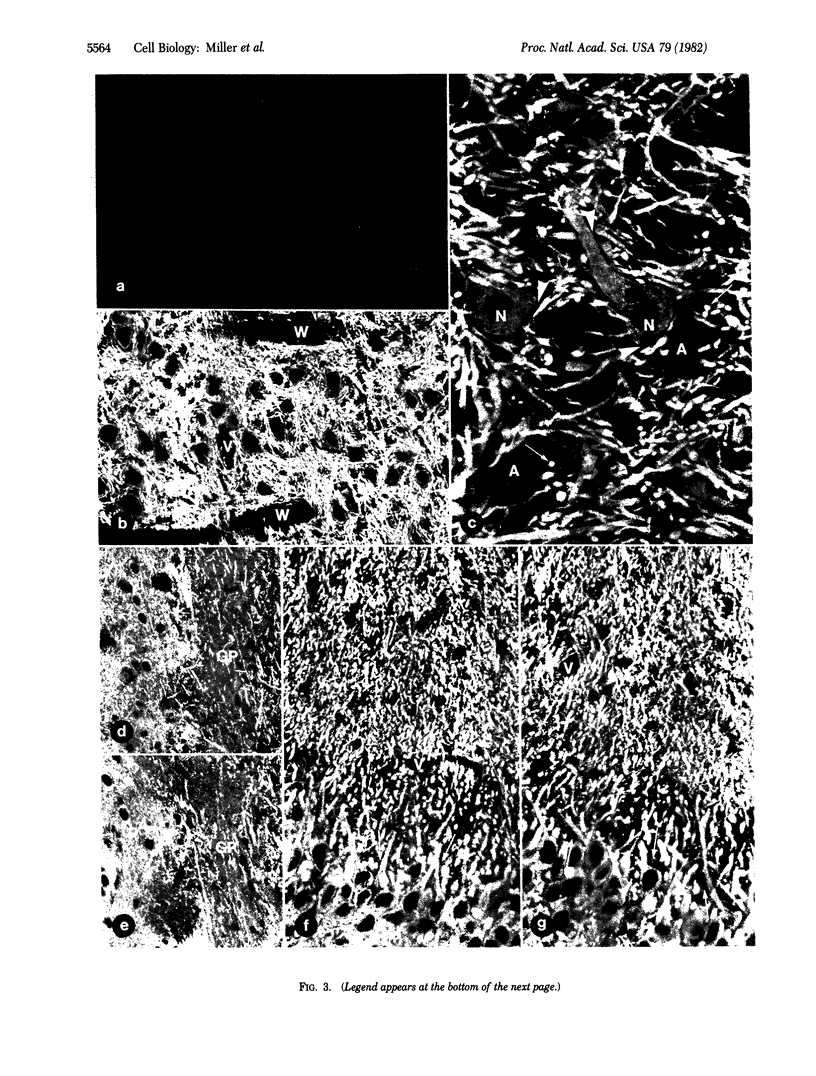
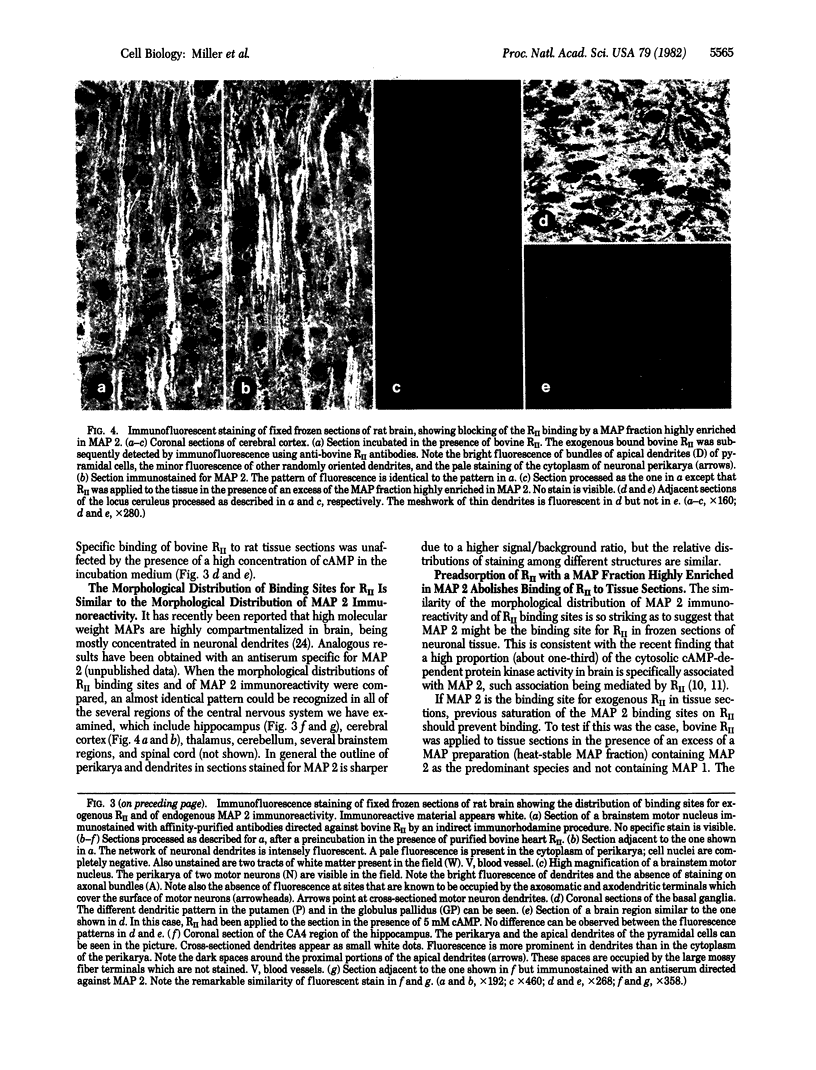
Specific binding sites for the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase (RII) were revealed in neurons by an immunohistochemical approach. Fixed frozen sections of several regions of the rat central nervous system were incubated in the presence of bovine RII. Bound bovine RII was subsequently detected by an immunofluorescence procedure using antibodies that recognize bovine but not rat RII. The results indicate that RII binds with high affinity to neurons. Binding is prominent in dendrites and almost undetectable in axons and axon terminals. The morphological distribution of the RII binding sites is almost identical to that of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP 2) immunoreactivity. Preadsorption of RII with a MAP preparation highly enriched in MAP 2 completely abolished binding of RII to tissue sections, suggesting that the binding is mediated by MAP 2. Our results indicate that frozen sections of fixed tissues are a suitable experimental system for study of specific interactions of cellular macromolecules at a morphological level.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., Lincoln T. M., Keely S. L. Compartmentalization of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in heart tissue. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3854–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Ueda T., Bloom F. E., Battenberg E., Greengard P. Widespread distribution of protein I in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5977–5981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous A., Francon J., Lennon A. M., Nunez J. Microtubule assembly in vitro. Purification of assembly-promoting factors. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. R., Adelstein R. S., Klee C. B. Interaction of calmodulin with myosin light chain kinase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase in bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog W., Weber K. Fractionation of brain microtubule-associated proteins. Isolation of two different proteins which stimulate tubulin polymerization in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Concentrations of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in various tissues. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1441–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Greengard P. Dopamine-sensitive adenyl cyclase: possible role in synaptic transmission. Science. 1971 Dec 24;174(4016):1346–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4016.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Binder L. I., Rosenbaum J. L. The periodic association of MAP2 with brain microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):266–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire S., Pelletier G., Labrie F. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine anterior pituitary gland. II. Subcellular distribution. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7303–7310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Greengard P. Identification of endogenous substrate proteins for cAMP-dependent protein kinase in bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9985–9992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Miller P. E., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Immunohistochemical localization of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A., Bernhardt R., Hugh-Jones T. High molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins are preferentially associated with dendritic microtubules in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Erlichman J., Rosen O. M. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase of human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6135–6139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rangel-Aldao R., Sarkar D., Erlichman J., Fleischer N. Characterization and comparison of membrane-associated and cytosolic cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Physicochemical and immunological studies on bovine cerebral cortex protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3797–3805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda R. D., Rudolph S. A., Rosenbaum J. L., Greengard P. Cyclic AMP-dependent endogenous phosphorylation of a microtubule-associated protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., DiBartolomeis M. J., Theurkauf W. E. A protein kinase bound to the projection portion of MAP 2 (microtubule-associated protein 2). J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):568–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. Structure and phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP 2). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3206–3210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Kanof P., Schulman H., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate receptor proteins in mammalian brain. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6275–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Miller P., Wilson F., Menkes D., Greengard P. Immunological distinction between guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3757–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H., Kumon A., Nishizuka Y. Cross-reactions of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase systems from rat liver and rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1544–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]