Abstract
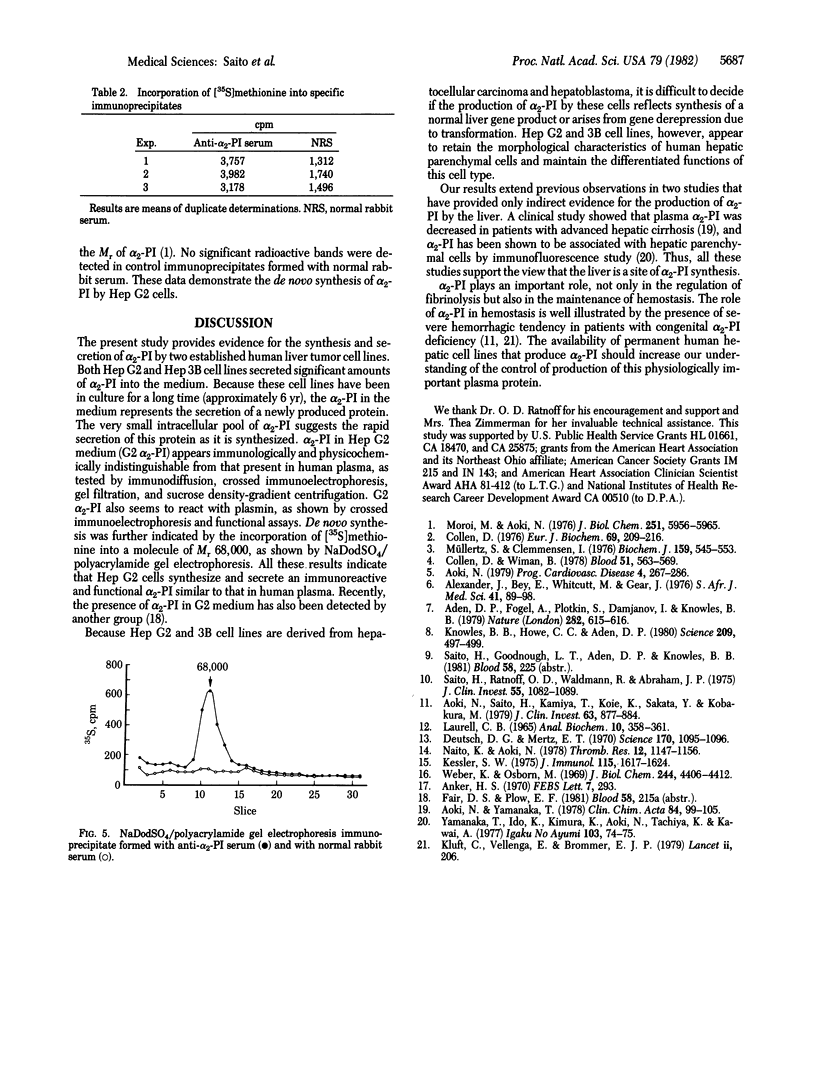
The site of synthesis of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor (alpha 2-PI), a physiologic inhibitor of plasmin, is not known with certainty. We have studied the production and secretion of alpha 2-PI by three established human liver cell lines derived from hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatoblastoma (Hep G2, Hep 3B, and PLC/PRF/5). As measured by a specific radioimmunoassay, the titer of alpha 2-PI increased in the medium of Hep G2 and Hep 3B cells with time, but no significant amount of alpha 2-PI was found in the medium of PLC/PRF/5. There was no evidence for a significant intracellular pool of this protein. On immunodiffusion against anti-alpha 2-PI serum, alpha 2-PI secreted by Hep G2 (G2 alpha 2-PI) formed a simple precipitin line of complete identity with the alpha 2-PI present in plasma (plasma alpha 2-PI). G2 alpha 2-PI behaved similarly to plasma alpha 2-PI in Sephadex G-150 gel filtration, sucrose density-gradient centrifugation, and crossed immunoelectrophoresis. G2 alpha 2-PI inhibited plasmin activity instantaneously in a functional assay and formed a complex with plasmin demonstrable by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. De novo synthesis of alpha 2-PI was shown by the presence of specific immunoprecipitable radioactivity in the medium after 5 hr of labeling of the cells with [35S]methionine. Analysis of the immunoprecipitates by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed a single peak of radioactivity corresponding to Mr 68,000. These results indicate that the liver is a site of alpha 2-PI production.
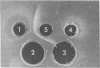
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aden D. P., Fogel A., Plotkin S., Damjanov I., Knowles B. B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):615–616. doi: 10.1038/282615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J., Bey E., Whitcutt J. M., Gear J. H. Adaptation of cells derived from human malignant tumours to growth in vitro. S Afr J Med Sci. 1976;41(2):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anker H. S. A solubilizable acrylamide gel for electrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 16;7(3):293–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N. Natural inhibitors of fibrinolysis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1979 Jan-Feb;21(4):267–286. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(79)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Saito H., Kamiya T., Koie K., Sakata Y., Kobakura M. Congenital deficiency of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor associated with severe hemorrhagic tendency. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):877–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI109387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Yamanaka T. The alpha2-plasmin inhibitor levels in liver diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Mar 1;84(1-2):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. Identification and some properties of a new fast-reacting plasmin inhibitor in human plasma. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Wiman B. Fast-acting plasmin inhibitor in human plasma. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):563–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluft C., Vellenga E., Brommer E. J. Homozygous alpha 2-antiplasmin deficiency. Lancet. 1979 Jul 28;2(8135):206–206. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91481-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. Isolation and characterization of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor from human plasma. A novel proteinase inhibitor which inhibits activator-induced clot lysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5956–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllertz S., Clemmensen I. The primary inhibitor of plasmin in human plasma. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):545–553. doi: 10.1042/bj1590545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito K., Aoki N. Assay of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor activity by means of a plasmin specific tripeptide substrate. Thromb Res. 1978 Jun;12(6):1147–1156. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Ratnoff O. D., Waldmann R., Abraham J. P. Fitzgerald Trait: Deficiency of a Hitherto Unrecognized Agent, Fitzgerald Factor, Participating in Surface-Mediated Reactions of Clotting, Fibrinolysis, Generation of Kinins, and the Property of Diluted Plasma Enhancing Vascular Permeability (PF/Dil). J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1082–1089. doi: 10.1172/JCI108009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]