Abstract
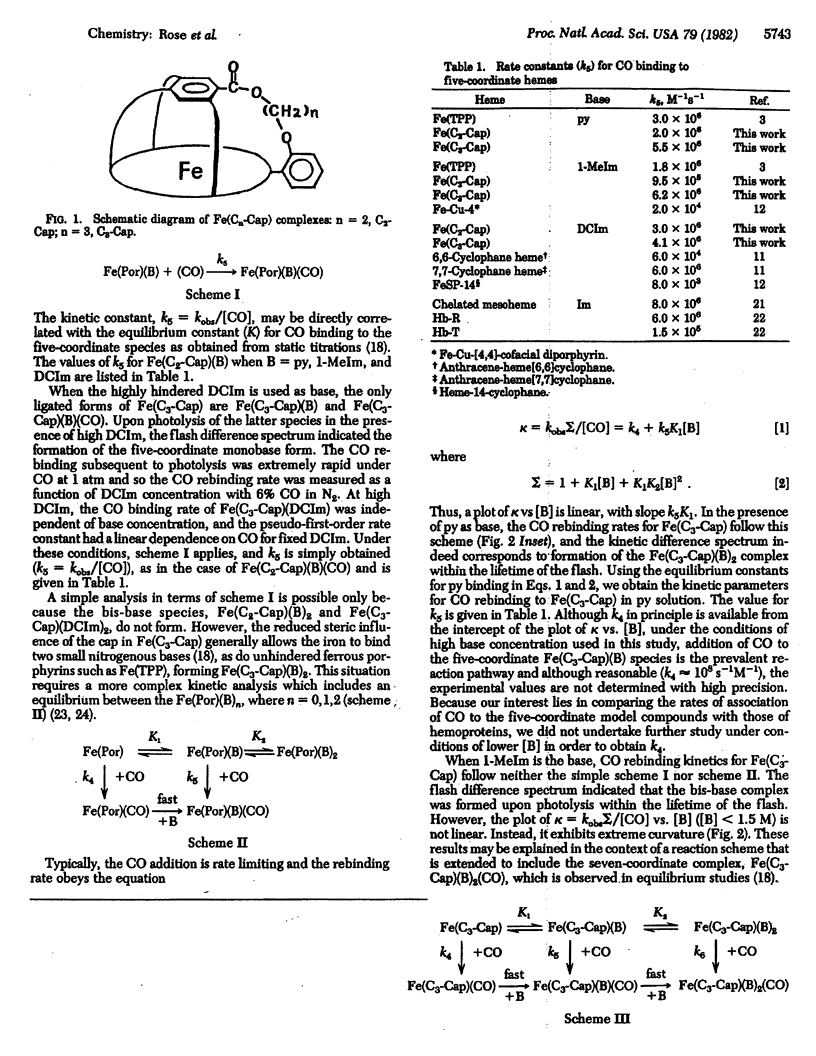
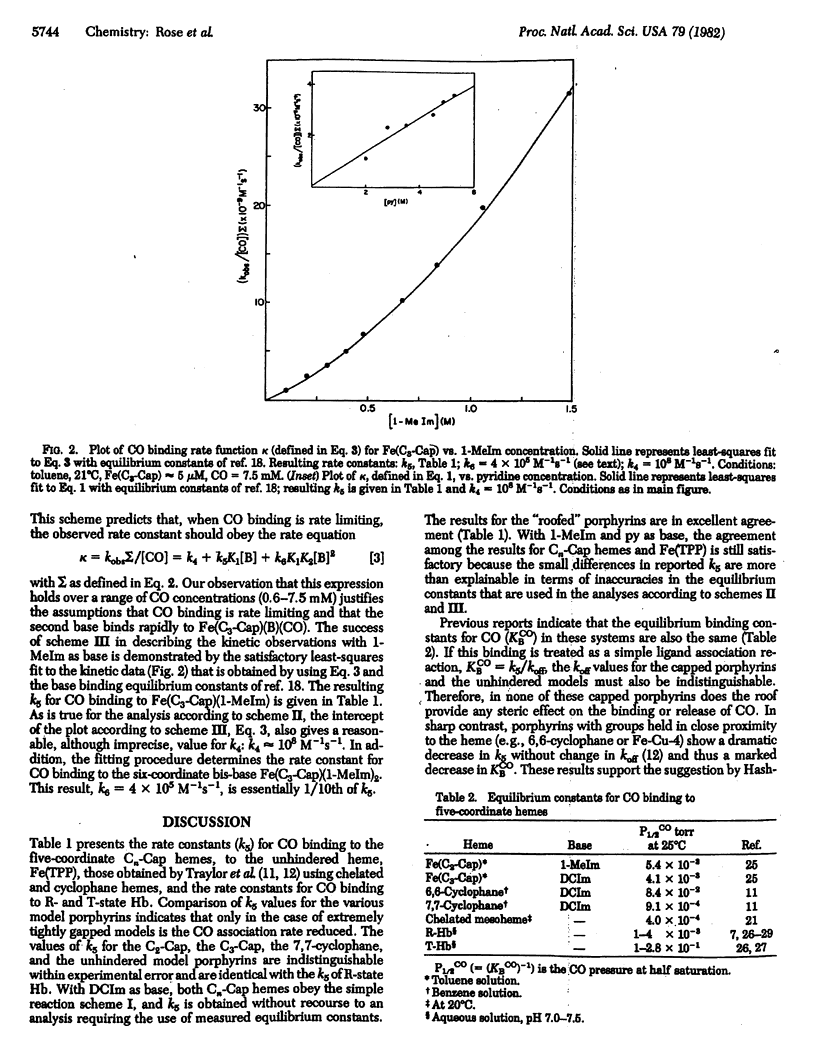
The rate constants for CO binding to the five-coordinate ferrous iron complexes of 5,10,15,20-[pyromellitoyl(tetrakis-o-oxyoxyphenyl)]porphyrin and 5,10,15,20-[pyromellitoyl(tetrakis-o-oxypropoxyphenyl)]porphyrin have been measured and compared with the corresponding rate constants for other hemes and hemoproteins. The second-order rate constant is independent of cap size and is comparable to that of high-affinity state hemoglobin (k5 approximately 4 X 10(6) M-1s-1). Therefore, these capped porphyrins provide no steric hindrance to CO binding. In addition, a kinetic scheme involving an unusual seven-coordinate porphyrin species is described.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbot E. H., Rafson P. A. Letter: Enhancement of ligand binding by iron (III) deuteroporphyrin (IX) dimethyl ester via interaction with 1,10-phenanthroline at a site remote from the metal ion. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Nov 13;96(23):7378–7379. doi: 10.1021/ja00830a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch D. H., Zimmer L. L., Grzybowski J. J., Olszanski D. J., Jackels S. C., Callahan R. C., Christoph G. G. Steric control of CO binding in a totally synthetic heme protein model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):5919–5923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.5919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey W. S. Carbon monoxide bonding in hemeproteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 5;174(1):148–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb49781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huestis W. H., Raftery M. A. Conformation and cooperativity in hemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1975 May 6;14(9):1886–1892. doi: 10.1021/bi00680a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacQuarrie R., Gibson Q. H. Use of a fluorescent analogue of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate as a probe of human hemoglobin conformation during carbon monoxide binding. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5832–5835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUGHTON F. J. The equilibrium between carbon monoxide and sheep haemoglobin at very high percentage saturations. J Physiol. 1954 Nov 29;126(2):359–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma V. S., Schmidt M. R., Ranney H. M. Dissociation of CO from carboxyhemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4267–4272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace W. J., Volpe J. A., Maxwell J. C., Caughey W. S. Properties of hemoglobin A and hemoglobin Zurich (beta63 histidine replaced by arginine): quantitative evaluation of functional abnormalities in hemoglobins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1379–1386. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



