Abstract
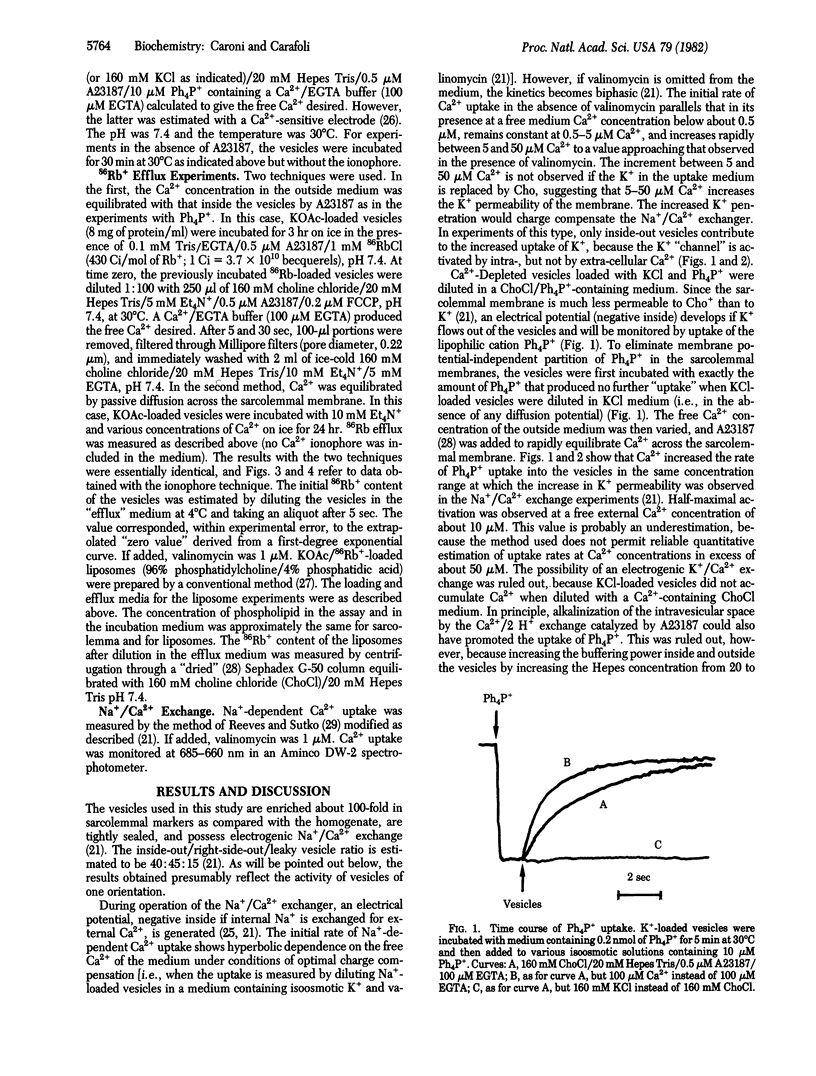
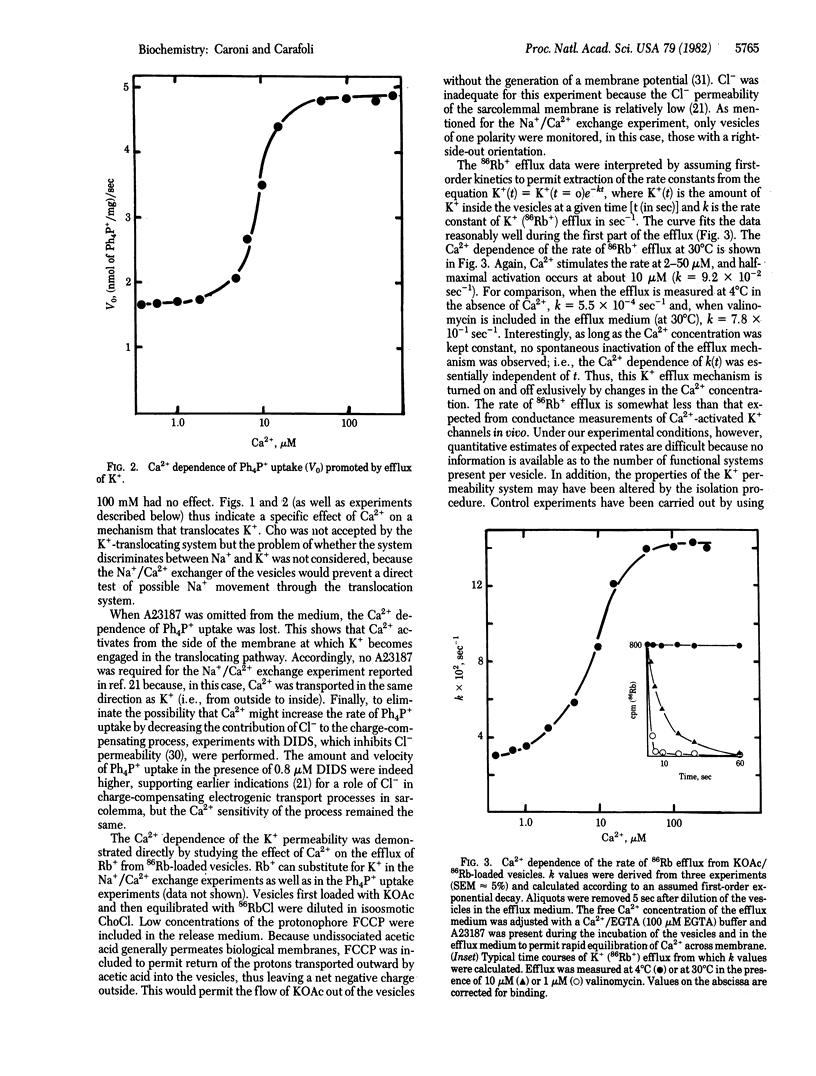
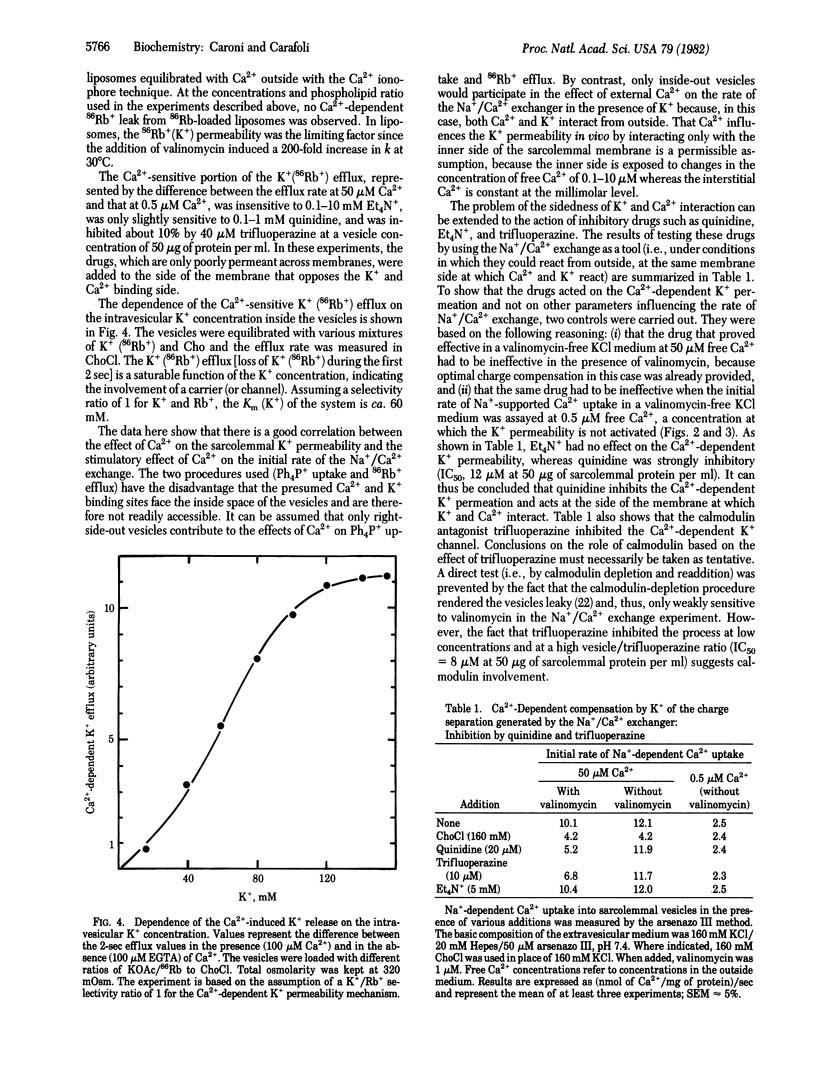
The movement of K+ in heart sarcolemmal vesicles has been followed through the opposing movement of the tetraphenylphosphonium ion. Ca2+ (5-50 microM) stimulates the efflux of K+ from K+-loaded vesicles [Km(Ca2+) approximately equal to 10 microM]. and the activation requires that Ca2+ be present inside the vesicles together with K+. The efflux of 86Rb+ from K+-, Rb+-loaded vesicles is similarly stimulated by 5-50 microM Ca2+ [Km(Ca2+) approximately equal to 10 microM]. The Ca2+-induced increase of K+ permeability does not become spontaneously inactivated. The effects of some inhibitors have been tested under conditions in which Ca2+ promotes the entry of K+ into vesicles. In this system, direct interaction of the drug with the Ca2+ and K+ membrane binding site(s) was therefore studied. Tetraethylammonium ion, which inhibits the potential-dependent K+ channel, does not interfere with the effect of Ca2+ whereas quinidine (IC50 = 12 microM) and trifluoperazine (IC50 = 8 microM at 50 micrograms of sarcolemmal protein per ml) inhibit.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armando-Hardy M., Ellory J. C., Ferreira H. G., Fleminger S., Lew V. L. Inhibition of the calcium-induced increase in the potassium permeability of human red blood cells by quinine. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):32P–33P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassingthwaighte J. B., Fry C. H., McGuigan J. A. Relationship between internal calcium and outward current in mammalian ventricular muscle; a mechanism for the control of the action potential duration? J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):15–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler G. W., Reuter H. Reconstruction of the action potential of ventricular myocardial fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):177–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T., Lynch C. Effects of internal divalent cations on voltage-clamped squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jun;63(6):675–689. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.6.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. The nature of the membrane sites controlling anion permeability of human red blood cells as determined by studies with disulfonic stilbene derivatives. J Membr Biol. 1972 Dec 29;10(3):311–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01867863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Carafoli E. The Ca2+-pumping ATPase of heart sarcolemma. Characterization, calmodulin dependence, and partial purification. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3263–3270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Reinlib L., Carafoli E. Charge movements during the Na+-Ca2+ exchange in heart sarcolemmal vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clusin W., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Activation of a voltage-insensitive conductance by inward calcium current. Nature. 1975 Jul 31;256(5516):425–427. doi: 10.1038/256425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDOS G. The function of calcium in the potassium permeability of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Dec;30(3):653–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isnberg G. Is potassium conductance of cardiac Purkinje fibres controlled by (Ca2+)? Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):273–274. doi: 10.1038/253273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. R., Besch H. R., Jr, Fleming J. W., McConnaughey M. M., Watanabe A. M. Separation of vesicles of cardiac sarcolemma from vesicles of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Comparative biochemical analysis of component activities. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):530–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamo N., Muratsugu M., Hongoh R., Kobatake Y. Membrane potential of mitochondria measured with an electrode sensitive to tetraphenyl phosphonium and relationship between proton electrochemical potential and phosphorylation potential in steady state. J Membr Biol. 1979 Aug;49(2):105–121. doi: 10.1007/BF01868720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Tsien R. W. Control of action potential duration by calcium ions in cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 May;67(5):599–617. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.5.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon J. L., Gibbons W. R. 4-Aminopyridine and the early outward current of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Feb;73(2):139–157. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackington I., Orrego F. Inhibition of calcium-activated potassium conductance of human erythrocytes by calmodulin inhibitory drugs. FEBS Lett. 1981 Oct 12;133(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80481-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L. Effect of intracellular calcium on the potassium permeability of human red cells. J Physiol. 1970 Feb;206(2):35P–36P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Ferreira H. G. Variable Ca sensitivity of a K-selective channel in intact red-cell membranes. Nature. 1976 Sep 23;263(5575):336–338. doi: 10.1038/263336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marban E., Rink T. J., Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium in heart muscle at rest and during contraction measured with Ca2+ -sensitive microelectrodes. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):845–850. doi: 10.1038/286845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Oliva J., Williams A. J., Nayler W. G. Two orientations of isolated cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles separated by affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):222–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. A centrifuged-column procedure for the measurement of ligand binding by beef heart F1. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:527–530. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer D. R., Hutson S. M., Kauffman R. F., Lardy H. A. Some effects of ionophore A23187 on energy utilization and the distribution of cations and anions in mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 15;15(12):2690–2697. doi: 10.1021/bi00657a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Sutko J. L. Sodium-calcium ion exchange in cardiac membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinlib L., Caroni P., Carafoli E. Studies on heart sarcolemma: vesicles of opposite orientation and the effect of ATP on the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 6;126(1):74–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal M. S., Hoffman B. F. Effects of calcium on canine Purkinje fiber action potential duration in the presence of agents affecting potassium permeability. Circ Res. 1980 Feb;46(2):227–236. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Tsien R. W. Calcium-activated transient outward current in calf cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:485–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam R. Control of membrane permeability to potassium in red blood cells. Nature. 1968 Aug 10;219(5154):610–610. doi: 10.1038/219610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


