Abstract
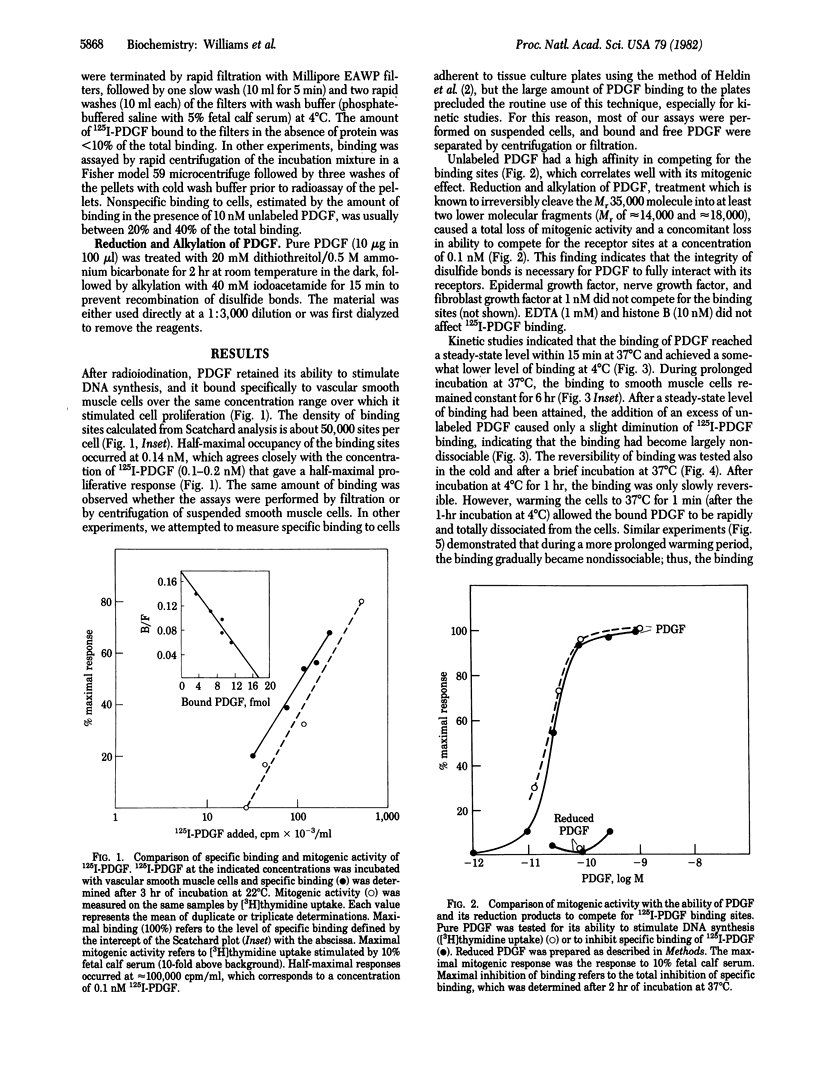
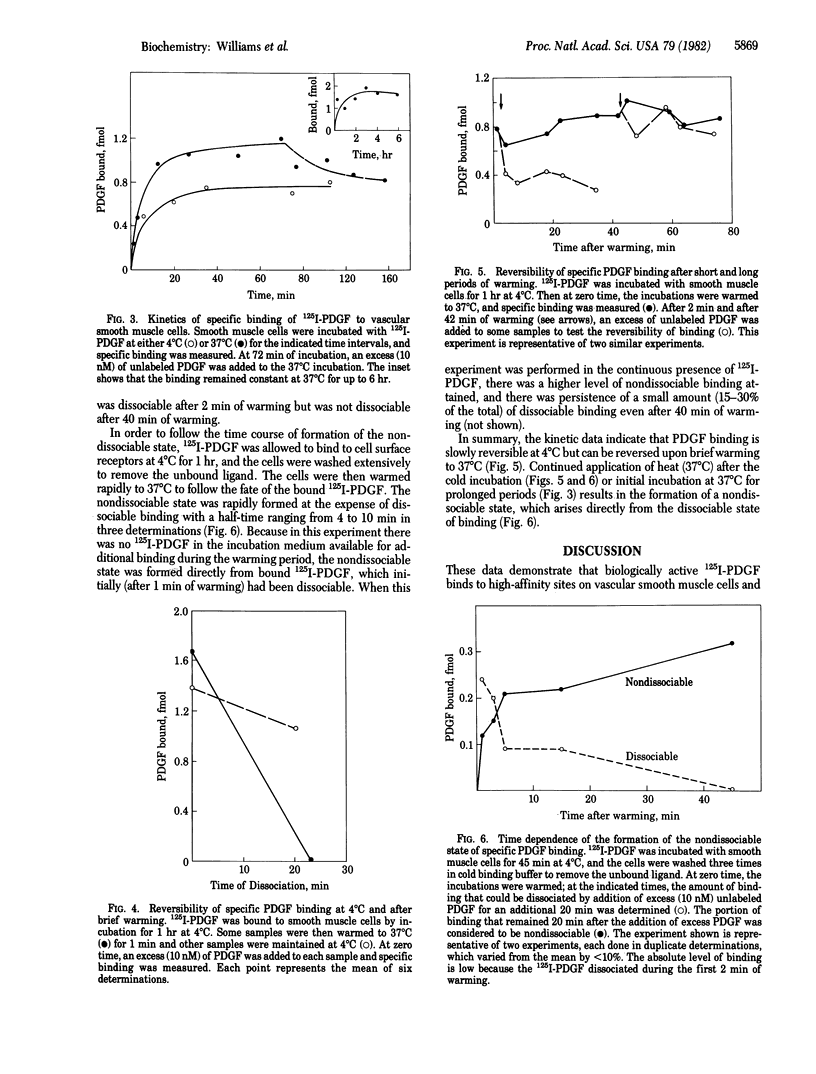
Radioiodinated platelet-derived growth factor (125I-PDGF) was used in studies of PDGF binding sites on vascular smooth muscle cells. There was an excellent correlation between the ability of 125I-PDGF to stimulate cell proliferation and to bind specifically to cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. The half-maximal concentration for both processes was 0.1 nM. There were 50,000 binding sites per cell. Reduced PDGF, prepared by treatment of PDGF with 20 mM dithiothreitol, had neither the ability to bind to smooth muscle cells nor to stimulate cellular proliferation. Epidermal growth factor, nerve growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, and histone B did not compete for the binding sites at a concentration of 10 nM. 125I-PDGF binding was slowly reversible at 4 degrees C and was rapidly and totally reversible after a 1-min incubation at 37 degrees C. After continued incubation at 37 degrees C, the binding became irreversible. The half-time for formation of the nondissociable state of 125I-PDGF binding was approximately equal to 5 min at 37 degrees C. The nondissociable state of binding was not formed at 4 degrees C even after 1 hr of incubation. These data suggest that the sites we labeled are the PDGF receptors that mediate PDGF's mitogenic action and that a nondissociable state of PDGF binding is formed at 37 degrees C. It is likely that nondissociable PDGF represents internalized ligand or binding to sites that are converted to a high-affinity state after the ligand binds.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson H. T., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Uncoupling of RNA and DNA synthesis after plasma stimulation of G0-arrested BALB/C-3T3 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 27;561(2):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Role of the coated endocytic vesicle in the uptake of receptor-bound low density lipoprotein in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N. Human platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF): purification of PDGF-I and PDGF-II and separation of their reduced subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7314–7317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. II. Specific binding to cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5161–5171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corin R. E., Donner D. B. Insulin receptors convert to a higher affinity state subsequent to hormone binding. A two-state model for the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Moskowitz M. A., Antoniades H. N., Levine L. Serotonin receptor-mediated stimulation of bovine smooth muscle cell prostacyclin synthesis and its modulation by platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7134–7138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner D. B., Martin D. W., Sonenberg M. Accumulation of a slowly dissociable peptide hormone binding component by isolated target cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorland R. B., Middlebrook J. L., Leppla S. H. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of diphtheria toxin by monkey kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11337–11342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Smith G. J., Wong K. Y., Jones A. L. Cellular uptake and nuclear binding of insulin in human cultured lymphocytes: evidence for potential intracellular sites of insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1368–1372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Specific receptors for platelet-derived growth factor on cells derived from connective tissue and glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Kennedy B., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor. Specific binding to target cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8130–8136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Resolution of high and low affinity epidermal growth factor receptors. Inhibition of high affinity component by low temperature, cycloheximide, and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3053–3060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreth G. E., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells: ligand-induced conversion from low- to high-affinity states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4751–4755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. An ordered sequence of events is required before BALB/c-3T3 cells become committed to DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 12;295(7):369–377. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608122950707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Nilsson M., Norum K. R. Uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled asialo-fetuin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



