Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, [Li4(C6H2N2O4)2(H2O)6]n, comprises two Li+ ions bridged by a completely deprotonated pyrimidine-3,6-dicarboxylate ligand and coordinated by two water molecules; the asymmetric units related by an inversion operation create a structural unit which forms part of a two-dimensional polymeric structure parallel to (10-1). One of the Li+ ions shows a distorted tetrahedral arrangement involving two symmetry-related coordinating water molecules and two carboxylate O atoms. The other Li+ ion is in distorted trigonal–bipyramidal geometry defined by N and O atoms of the ligands and a water molecule. Water O atoms are proton donors to carboxylate O atoms forming hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For the crystal structures of pyrimidine-3,6-dicarboxylic acid dihydrate and two K+ complexes with pyrimidine-3,6-dicarboxylate and aqua ligands, see: Beobide et al. (2007 ▶). For the structures of Li+ complexes with a pyrimidine-2-carboxylato ligand, see: Starosta & Leciejewicz (2011 ▶) and with a pyrimidine-4-carboxylate ligand, see: Starosta & Leciejewicz (2012 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[Li4(C6H2N2O4)2(H2O)6]
M r = 234.02
Monoclinic,

a = 6.7014 (13) Å
b = 11.755 (2) Å
c = 12.251 (3) Å
β = 98.38 (3)°
V = 954.8 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.15 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.48 × 0.20 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Kuma KM-4 four-cricle diffractometer
Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.960, T max = 0.988
3009 measured reflections
2792 independent reflections
2094 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.023
3 standard reflections every 200 reflections intensity decay: 0.4%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.126
S = 0.95
2792 reflections
178 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.47 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.41 e Å−3
Data collection: KM-4 Software (Kuma, 1996 ▶); cell refinement: KM-4 Software; data reduction: DATAPROC (Kuma, 2001 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812038755/kp2437sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812038755/kp2437Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Li1—O5 | 2.081 (3) |
| Li1—O3i | 2.100 (2) |
| Li1—N3i | 2.153 (2) |
| Li1—O1 | 2.030 (2) |
| Li1—N1 | 2.156 (2) |
| Li2—O4ii | 1.967 (2) |
| Li2—O7 | 1.898 (3) |
| Li2—O6 | 1.990 (3) |
| Li2—O3 | 1.949 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O7—H71⋯O6iii | 0.85 (3) | 2.19 (3) | 3.0409 (18) | 175 (2) |
| O7—H72⋯O1iv | 0.96 (3) | 1.75 (3) | 2.6920 (15) | 168 (2) |
| O6—H62⋯O2v | 0.91 (3) | 1.85 (3) | 2.7518 (15) | 172 (2) |
| O6—H61⋯O5vi | 0.88 (3) | 1.98 (3) | 2.7889 (16) | 151 (2) |
| O5—H51⋯O2vii | 0.87 (3) | 1.89 (3) | 2.7594 (14) | 172 (3) |
| O5—H52⋯O4viii | 0.85 (3) | 2.02 (3) | 2.8670 (14) | 178 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  ; (vi)
; (vi)  ; (vii)
; (vii)  ; (viii)
; (viii)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
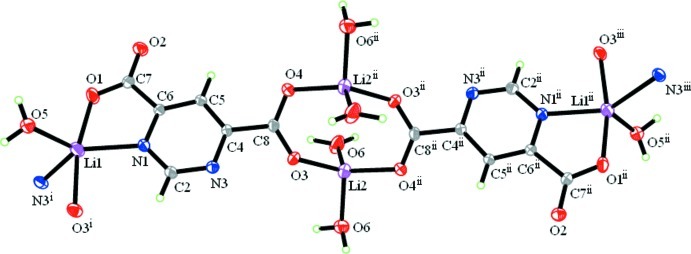
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains two symmetry independent LiI ions, one with distorted trigonal bipyramidal, the other with distorted tetrahedral coordination geometry, a deprotonated ligand molecule acting in µ4 bridging mode and two independent water molecules coordinated to metal ions. The structural unit is built of asymmetric units related by an inversion centre. The ligand N1,O1 bonding group chelates the Li1 ion leaving the carboxylato O2 atom coordination inactive while its carboxylato O3 and O4 atoms bridge, related by an inversion centre, Li2 and Li2ii ions. The latter are also coordinated by O4ii and O3ii atoms donated by the adjacent one related by the same inversion center ligand forming a dimeric bonding loop which constitutes a core of a centrosymmetric structural unit composed of the Li1 ion, the ligand, the dimeric loop, the ligandii and the Li1ii ion (Fig. 1). Symmetry code; i -x + 1/2, y + 1/2, -z + 1/2; ii -x + 1, -y + 1,-z + 1; iiix + 1/2, -y + 1/2, z + 1/2; iv -x + 1/2, y - 1/2, -z + 1/2; vx - 1/2, -y + 1/2, z - 1/2. The plane of the loop [r.m.s. 0.2647 (5) Å] makes a dihedral angle of 24.0 (2)° with the ligand ring plane. This unit, terminated on both sides by Li1 and Li1ii ions linked to adjacent units via N3i,O3i and N3iii,O3iii bonding groups and via N3,O3 and N3ii,O3ii bonding groups to Li1v and Liivions in adjacent units, generate a two-dimensional layer with Li1 ions as its nodes (Fig. 2). The arrangement of the layers in the unit cell is shown in Fig. 3. The coordination polyhedron of the Li1 ion, composed of the bridging N1,O1 and N3i),O3(i) bonding groups and the aqua O5 atom is a distorted trigonal bipyramid. Its equatorial plane is formed by N1, N3i and O5 atoms. The Li1 ion is 0.0908 (2) Å out of this plane, O1 and O3i atoms are at apical positions. The Li2 ion chelated by carboxylato O3,O4ii atoms and aqua O6 with inversion related atoms shows a distorted tetrahedral coordination geometry. The Li—O and Li—N bond lengths (Table 1) fit well to those observed in the structures of Li complexes with other pyrimidine carboxylate ligands (Starosta & Leciejewicz, 2011, 2012). The pyrimidine ring is planar with r.m.s. of 0.0121 (2) A°, C7/O1/O2 and C8/O3/O4 carboxylate groups make with it dihedral angles of 4.0 (1)° and 24.0 (2)°, respectively. Bond distances and bond angles are close to those observed in the structure of the parent acid and its two potassium complexes (Beobide et al., 2007). A network of hydrogen bonds (Table 2), in which coordinated water molecules act as donors and carboxylato O atoms are acceptors maintains the stability of the structure.
Experimental
1 mmol of pyrimidine-3,6-dicarboxylic acid dihydrate and 2 mmol s of lithium hydroxide were dissolved in 50 mL of hot, doubly distilled water and boiled under reflux with stirring for six hours. Left to crystallize at room temperature, colourless single-crystal blocks deposited after a week. They were washed with cold methanol and dried in the air.
Refinement
Hydrogen atoms attached to water molecules were located in a difference map and refined isotropically, while two H atoms attached to pyrimidine C atoms were located at a calculated positions and treated as riding on the parent atoms with C—H=0.93 Å and Uiso(H)=1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
A structural unit of the title compound with atom labelling scheme and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids. Symmetry code: i -x + 1/2, y + 1/2, -z + 1/2; ii -x + 1, -y + 1,-z + 1; iiix + 1/2, -y + 1/2, z + 1/2.
Fig. 2.
The orientation of a fragment of a single molecular layer in the unit cell of the title structure.
Fig. 3.
The arrangement of molecular layers in the structure of a LiI complex with pyrimidine-4-carboxylate and aqua molecules.
Crystal data
| [Li4(C6H2N2O4)2(H2O)6] | F(000) = 480 |
| Mr = 234.02 | Dx = 1.628 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| a = 6.7014 (13) Å | θ = 6–15° |
| b = 11.755 (2) Å | µ = 0.15 mm−1 |
| c = 12.251 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 98.38 (3)° | Blocks, colourless |
| V = 954.8 (3) Å3 | 0.48 × 0.20 × 0.13 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Kuma KM-4 four-cricle diffractometer | 2094 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.023 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 30.1°, θmin = 2.4° |
| profile data from ω/2θ scans | h = −9→0 |
| Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2008) | k = 0→16 |
| Tmin = 0.960, Tmax = 0.988 | l = −17→17 |
| 3009 measured reflections | 3 standard reflections every 200 reflections |
| 2792 independent reflections | intensity decay: 0.4% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.126 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.95 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0949P)2 + 0.1908P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2792 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 178 parameters | Δρmax = 0.47 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.41 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O2 | 0.24613 (17) | 1.10050 (8) | 0.59876 (7) | 0.0279 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.44978 (14) | 0.61780 (7) | 0.39479 (7) | 0.0225 (2) | |
| O4 | 0.34896 (15) | 0.65464 (8) | 0.55698 (7) | 0.0244 (2) | |
| N3 | 0.26576 (17) | 0.80458 (9) | 0.30736 (8) | 0.0208 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.16917 (19) | 1.18808 (8) | 0.43666 (8) | 0.0321 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.37372 (17) | 0.67999 (9) | 0.46084 (9) | 0.0174 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.18480 (16) | 1.00000 (8) | 0.32426 (8) | 0.0205 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.21347 (17) | 1.10298 (9) | 0.49612 (9) | 0.0181 (2) | |
| O6 | 0.82841 (18) | 0.51649 (10) | 0.29471 (8) | 0.0315 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.30347 (16) | 0.79650 (9) | 0.41748 (9) | 0.0162 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.22823 (16) | 0.99180 (9) | 0.43410 (9) | 0.0157 (2) | |
| O7 | 0.85977 (18) | 0.58692 (9) | 0.52784 (9) | 0.0345 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.28409 (18) | 0.88905 (9) | 0.48558 (9) | 0.0172 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.3074 | 0.8825 | 0.5620 | 0.021* | |
| C2 | 0.2031 (2) | 0.90580 (10) | 0.26635 (9) | 0.0235 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.1691 | 0.9109 | 0.1902 | 0.028* | |
| Li1 | 0.0920 (4) | 1.16918 (19) | 0.27116 (17) | 0.0257 (5) | |
| Li2 | 0.6732 (4) | 0.51046 (19) | 0.4213 (2) | 0.0259 (4) | |
| H71 | 0.951 (5) | 0.556 (2) | 0.574 (2) | 0.070 (8)* | |
| H72 | 0.848 (4) | 0.668 (2) | 0.530 (2) | 0.056 (7)* | |
| H62 | 0.789 (4) | 0.481 (2) | 0.229 (2) | 0.058 (7)* | |
| H61 | 0.832 (4) | 0.589 (2) | 0.279 (2) | 0.055 (7)* | |
| O5 | −0.19709 (17) | 1.23656 (9) | 0.26248 (8) | 0.0291 (2) | |
| H51 | −0.223 (4) | 1.284 (2) | 0.207 (2) | 0.066 (7)* | |
| H52 | −0.239 (4) | 1.268 (2) | 0.317 (2) | 0.055 (6)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O2 | 0.0469 (6) | 0.0212 (4) | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0015 (4) | 0.0028 (4) | −0.0020 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0321 (5) | 0.0169 (4) | 0.0189 (4) | 0.0065 (3) | 0.0052 (3) | −0.0018 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0391 (5) | 0.0177 (4) | 0.0176 (4) | 0.0048 (3) | 0.0080 (3) | 0.0036 (3) |
| N3 | 0.0309 (5) | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0046 (4) | 0.0021 (4) | −0.0008 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0598 (7) | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0214 (4) | 0.0058 (4) | 0.0022 (4) | 0.0013 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0217 (5) | 0.0126 (4) | 0.0174 (5) | 0.0013 (4) | 0.0013 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0310 (5) | 0.0162 (4) | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0049 (4) | 0.0029 (4) | 0.0017 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0229 (5) | 0.0142 (5) | 0.0175 (5) | 0.0005 (4) | 0.0037 (4) | −0.0018 (4) |
| O6 | 0.0486 (6) | 0.0248 (5) | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0005 (4) | 0.0090 (4) | −0.0011 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0205 (5) | 0.0134 (4) | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0031 (4) | 0.0011 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0200 (5) | 0.0134 (5) | 0.0142 (5) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0040 (4) | −0.0001 (4) |
| O7 | 0.0406 (6) | 0.0243 (5) | 0.0359 (6) | 0.0057 (4) | −0.0034 (4) | −0.0093 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0249 (5) | 0.0147 (5) | 0.0123 (4) | 0.0024 (4) | 0.0035 (4) | 0.0007 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0374 (7) | 0.0195 (5) | 0.0128 (5) | 0.0065 (5) | 0.0013 (4) | 0.0002 (4) |
| Li1 | 0.0381 (12) | 0.0196 (10) | 0.0195 (10) | −0.0007 (8) | 0.0042 (9) | 0.0028 (8) |
| Li2 | 0.0334 (11) | 0.0186 (10) | 0.0261 (10) | 0.0034 (8) | 0.0053 (8) | 0.0000 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0445 (6) | 0.0217 (4) | 0.0228 (4) | 0.0065 (4) | 0.0102 (4) | 0.0028 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O2—C7 | 1.2449 (14) | C8—Li2ii | 2.707 (3) |
| O3—C8 | 1.2527 (14) | N1—C2 | 1.3305 (15) |
| Li1—O5 | 2.081 (3) | N1—C6 | 1.3382 (14) |
| Li1—O3i | 2.100 (2) | C7—C6 | 1.5222 (15) |
| Li1—N3i | 2.153 (2) | O6—H62 | 0.91 (3) |
| Li1—O1 | 2.030 (2) | O6—H61 | 0.88 (3) |
| Li1—N1 | 2.156 (2) | C4—C5 | 1.3886 (15) |
| Li2—O4ii | 1.967 (2) | C6—C5 | 1.3885 (15) |
| Li2—O7 | 1.898 (3) | O7—H71 | 0.85 (3) |
| Li2—O6 | 1.990 (3) | O7—H72 | 0.96 (3) |
| Li2—O3 | 1.949 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O3—Li1iii | 2.100 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| O4—C8 | 1.2492 (14) | Li1—Li2i | 3.313 (3) |
| O4—Li2ii | 1.968 (2) | Li2—C8ii | 2.707 (3) |
| N3—C2 | 1.3352 (15) | Li2—Li2ii | 3.237 (5) |
| N3—C4 | 1.3393 (14) | Li2—Li1iii | 3.313 (3) |
| N3—Li1iii | 2.153 (2) | O5—H51 | 0.87 (3) |
| O1—C7 | 1.2476 (14) | O5—H52 | 0.85 (3) |
| C8—C4 | 1.5187 (15) | ||
| C8—O3—Li2 | 130.20 (11) | O1—Li1—O3i | 167.65 (14) |
| C8—O3—Li1iii | 116.62 (10) | O5—Li1—O3i | 93.91 (10) |
| Li2—O3—Li1iii | 109.76 (11) | O1—Li1—N1 | 77.25 (8) |
| C8—O4—Li2ii | 112.72 (10) | O5—Li1—N1 | 126.29 (12) |
| C2—N3—C4 | 116.43 (10) | O3i—Li1—N1 | 91.07 (10) |
| C2—N3—Li1iii | 128.76 (10) | O1—Li1—N3i | 107.48 (11) |
| C4—N3—Li1iii | 111.52 (9) | O5—Li1—N3i | 99.51 (10) |
| C7—O1—Li1 | 119.98 (10) | O3i—Li1—N3i | 77.60 (8) |
| O4—C8—O3 | 126.32 (11) | N1—Li1—N3i | 133.62 (12) |
| O4—C8—C4 | 117.91 (10) | O1—Li1—Li2i | 143.55 (11) |
| O3—C8—C4 | 115.77 (10) | O5—Li1—Li2i | 77.24 (9) |
| O4—C8—Li2ii | 42.09 (7) | O3i—Li1—Li2i | 33.61 (6) |
| O3—C8—Li2ii | 87.24 (8) | N1—Li1—Li2i | 78.26 (8) |
| C4—C8—Li2ii | 151.42 (9) | N3i—Li1—Li2i | 108.96 (9) |
| C2—N1—C6 | 116.92 (10) | O7—Li2—O3 | 102.77 (12) |
| C2—N1—Li1 | 130.69 (10) | O7—Li2—O4ii | 115.41 (13) |
| C6—N1—Li1 | 112.39 (9) | O3—Li2—O4ii | 126.15 (14) |
| O1—C7—O2 | 126.90 (11) | O7—Li2—O6 | 98.77 (12) |
| O1—C7—C6 | 115.10 (10) | O3—Li2—O6 | 108.87 (12) |
| O2—C7—C6 | 118.00 (10) | O4ii—Li2—O6 | 101.48 (11) |
| Li2—O6—H62 | 124.0 (15) | O7—Li2—C8ii | 98.08 (10) |
| Li2—O6—H61 | 104.1 (16) | O3—Li2—C8ii | 118.56 (11) |
| H62—O6—H61 | 105 (2) | O4ii—Li2—C8ii | 25.19 (5) |
| N3—C4—C5 | 121.96 (10) | O6—Li2—C8ii | 124.03 (11) |
| N3—C4—C8 | 114.82 (9) | O7—Li2—Li2ii | 94.80 (12) |
| C5—C4—C8 | 123.20 (10) | O3—Li2—Li2ii | 63.13 (9) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 121.62 (10) | O4ii—Li2—Li2ii | 76.67 (10) |
| N1—C6—C7 | 114.81 (9) | O6—Li2—Li2ii | 165.63 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 123.56 (10) | C8ii—Li2—Li2ii | 58.00 (7) |
| Li2—O7—H71 | 126.2 (19) | O7—Li2—Li1iii | 117.02 (11) |
| Li2—O7—H72 | 116.1 (14) | O3—Li2—Li1iii | 36.62 (6) |
| H71—O7—H72 | 118 (2) | O4ii—Li2—Li1iii | 127.50 (11) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 116.82 (10) | O6—Li2—Li1iii | 73.31 (8) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 121.6 | C8ii—Li2—Li1iii | 138.88 (10) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 121.6 | Li2ii—Li2—Li1iii | 96.31 (11) |
| N1—C2—N3 | 126.12 (10) | Li1—O5—H51 | 111.2 (18) |
| N1—C2—H2 | 116.9 | Li1—O5—H52 | 122.7 (17) |
| N3—C2—H2 | 116.9 | H51—O5—H52 | 106 (2) |
| O1—Li1—O5 | 96.27 (11) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O7—H71···O6iv | 0.85 (3) | 2.19 (3) | 3.0409 (18) | 175 (2) |
| O7—H72···O1v | 0.96 (3) | 1.75 (3) | 2.6920 (15) | 168 (2) |
| O6—H62···O2vi | 0.91 (3) | 1.85 (3) | 2.7518 (15) | 172 (2) |
| O6—H61···O5iii | 0.88 (3) | 1.98 (3) | 2.7889 (16) | 151 (2) |
| O5—H51···O2vii | 0.87 (3) | 1.89 (3) | 2.7594 (14) | 172 (3) |
| O5—H52···O4viii | 0.85 (3) | 2.02 (3) | 2.8670 (14) | 178 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (iii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iv) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (v) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1; (vi) x+1/2, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (vii) x−1/2, −y+5/2, z−1/2; (viii) −x, −y+2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: KP2437).
References
- Beobide, G., Castillo, O., Luque, A., Garcia-Couceiro, U., Garcia-Teran, J. P. & Roman, P. (2007). Dalton Trans. pp. 2668–2680. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kuma (1996). KM-4 Software Kuma Diffraction Ltd, Wrocław, Poland.
- Kuma (2001). DATAPROC Kuma Diffraction Ltd, Wrocław, Poland.
- Oxford Diffraction (2008). CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Starosta, W. & Leciejewicz, J. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, m818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Starosta, W. & Leciejewicz, J. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, m1065–m1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812038755/kp2437sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812038755/kp2437Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report