Abstract
In the title compound, C9H8N2O2S, the sulfamoyl NH2 group is involved in intramolecular N—H⋯N and intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonding. In the crystal, molecules are linked via pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming inversion dimers, which are further associated through π–π stacking interactions between the quinoline benzene rings [centroid–centroid distance = 3.649 (1) Å] into a one-dimensional polymeric structure extending along the a axis.
Related literature
For the use of the quinolinesulfamoyl unit in medicinal chemistry, see: Borras et al. (1999 ▶); Eveloch et al. (1981 ▶); Zajdel et al. (2011 ▶, 2012 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Maślankiewicz et al. (2007 ▶). For hydrogen-bonding motifs in sufonamides, see: Adsmond & Grant (2001 ▶). For graph-set notation of hydrgen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).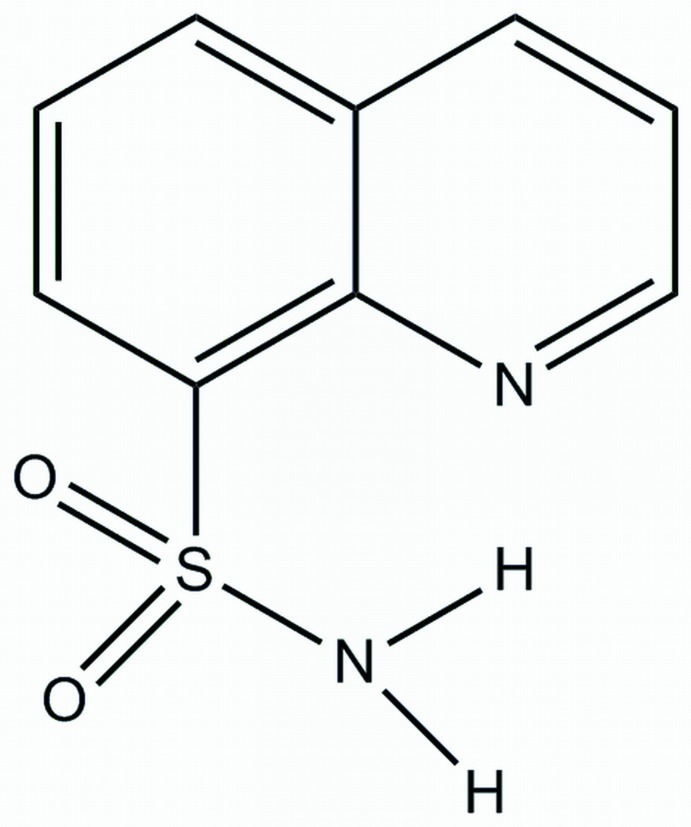
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H8N2O2S
M r = 208.23
Monoclinic,

a = 8.9431 (3) Å
b = 10.4542 (2) Å
c = 10.4648 (2) Å
β = 109.313 (2)°
V = 923.33 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.32 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.34 × 0.21 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire3 CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.898, T max = 0.944
5936 measured reflections
1636 independent reflections
1446 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.014
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.095
S = 0.97
1636 reflections
135 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.36 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis CCD; data reduction: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: Jmol (Hanson, 2010 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036963/gk2515sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036963/gk2515Isup2.mol
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036963/gk2515Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036963/gk2515Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H1N⋯O2i | 0.87 (2) | 2.15 (3) | 3.013 (2) | 169 (2) |
| N2—H2N⋯N1 | 0.83 (2) | 2.33 (2) | 2.921 (2) | 129 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Medical University of Silesia, grant No. KNW-1–073/P/1/0.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Quinolinesulfamoyl moiety is being more and more frequently incorporated into molecules of biologically active compounds such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (Borras et al., 1999) and 5-HT receptors ligands (Zajdel et al., 2011; Zajdel et al., 2012). Since the quinoline drugs as well as sulfonamides strongly interact with enzymatic receptors via their nitrogen atoms (Eveloch et al., 1981) we studied the crystal structure of the title compound, to evaluate the spatial environment of the nitrogen atoms.
The molecular conformation of quinoline-8-sulfonamide with the adopted atomic numbering is presented in Fig.1. The sulfonamide group participates in both intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The H2 atom of the sulfamoyl group shows an intramolecular contact with the N1 atom of the quinoline ring system (Table 1) resulting in the graph-set motif of S(6) (Bernstein et al., 1995). In the crystal, the molecules form dimers through N2—H1···O2 hydrogen bonds (Table 1). It is interesting to note that the most commonly observed hydrogen bonding in sulfonamides in the studies reported by Adsmond &Grant (2001) consing of S=O···H—N chains (50 occurrences in 39 different sulfonamide structures) is absent in the title compound.
A π-π stacking interaction is observed between the benzene C4A/C5—C8/C8A rings of neighboring dimers with the centroid-to-centroid distance, Cg···Cg (1 - x, 2 - y, -z) of 3.649 (1) Å and interplanar spacing of 3.373 (1) Å (Fig. 2). The π–π stacking interaction connects the dimers along the [100] direction forming one-dimesional polymeric structure.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by the reaction of 8-quinolinesulfonylchloride with an excess ammonia at temperature of 45°C according to the procedure reported by Maślankiewicz et al. (2007). Single crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray structure determination were obtained by recrystallization from an ethanolic solution.
Refinement
The hydrogen atoms participating in hydrogen bonding were located in a difference Fourier map and freely refined. Other hydrogen atoms were introduced in geometrically idealized positions and refined using a riding-model approximation with C—H distances of 0.93 Å and with Uiso(H)= 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
π-π stacking interactions (green dashed line) and hydrogen bonds (black dashed lines) in the title crystal structure. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Fig. 3.
Crystal packing of the title compound along the c axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C9H8N2O2S | F(000) = 432 |
| Mr = 208.23 | Dx = 1.498 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Melting point: 457.2 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.9431 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 5251 reflections |
| b = 10.4542 (2) Å | θ = 3.1–34.5° |
| c = 10.4648 (2) Å | µ = 0.32 mm−1 |
| β = 109.313 (2)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 923.33 (4) Å3 | Polyhedron, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.34 × 0.21 × 0.18 mm |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire3 CCD diffractometer | 1636 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1446 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.014 |
| Detector resolution: 16.0328 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.1°, θmin = 3.1° |
| ω–scan | h = −8→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2008) | k = −12→11 |
| Tmin = 0.898, Tmax = 0.944 | l = −12→10 |
| 5936 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.095 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.97 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.075P)2 + 0.1368P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1636 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 135 parameters | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.36 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.66396 (4) | 0.87959 (4) | 0.17318 (4) | 0.03962 (18) | |
| O1 | 0.69562 (15) | 0.80754 (13) | 0.29483 (13) | 0.0560 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.52811 (14) | 0.84522 (13) | 0.05984 (13) | 0.0542 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.98319 (16) | 0.98818 (14) | 0.31765 (14) | 0.0438 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.6409 (2) | 1.02696 (16) | 0.2070 (2) | 0.0501 (4) | |
| C2 | 1.1202 (2) | 1.03811 (18) | 0.3911 (2) | 0.0556 (5) | |
| H2 | 1.1242 | 1.0848 | 0.4678 | 0.067* | |
| C3 | 1.2598 (2) | 1.0245 (2) | 0.3596 (2) | 0.0637 (6) | |
| H3 | 1.3541 | 1.0596 | 0.4160 | 0.076* | |
| C4 | 1.2566 (2) | 0.96016 (18) | 0.2470 (2) | 0.0568 (5) | |
| H4 | 1.3485 | 0.9520 | 0.2245 | 0.068* | |
| C4A | 1.1134 (2) | 0.90515 (16) | 0.16339 (19) | 0.0430 (4) | |
| C5 | 1.0985 (2) | 0.83950 (17) | 0.0427 (2) | 0.0513 (5) | |
| H5 | 1.1871 | 0.8287 | 0.0161 | 0.062* | |
| C6 | 0.9568 (2) | 0.79162 (18) | −0.0357 (2) | 0.0540 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.9487 | 0.7495 | −0.1161 | 0.065* | |
| C7 | 0.8221 (2) | 0.80560 (16) | 0.00428 (17) | 0.0448 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.7254 | 0.7722 | −0.0494 | 0.054* | |
| C8 | 0.83294 (17) | 0.86792 (14) | 0.12156 (15) | 0.0341 (4) | |
| C8A | 0.97904 (17) | 0.92153 (14) | 0.20522 (15) | 0.0351 (3) | |
| H1N | 0.603 (3) | 1.071 (2) | 0.133 (3) | 0.059 (6)* | |
| H2N | 0.722 (3) | 1.057 (2) | 0.263 (3) | 0.065 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0313 (3) | 0.0447 (3) | 0.0465 (3) | −0.00383 (16) | 0.01779 (19) | 0.00320 (17) |
| O1 | 0.0532 (8) | 0.0673 (9) | 0.0553 (8) | −0.0052 (6) | 0.0284 (6) | 0.0151 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0352 (6) | 0.0582 (8) | 0.0648 (8) | −0.0102 (5) | 0.0106 (6) | −0.0017 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0371 (7) | 0.0500 (8) | 0.0436 (8) | −0.0022 (6) | 0.0122 (6) | −0.0040 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0378 (8) | 0.0549 (10) | 0.0613 (10) | 0.0023 (7) | 0.0215 (8) | −0.0066 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0484 (10) | 0.0542 (11) | 0.0545 (11) | −0.0042 (8) | 0.0039 (8) | −0.0058 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0357 (10) | 0.0557 (12) | 0.0876 (16) | −0.0070 (8) | 0.0040 (10) | 0.0055 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0326 (8) | 0.0488 (10) | 0.0919 (15) | 0.0036 (7) | 0.0247 (9) | 0.0119 (10) |
| C4A | 0.0367 (9) | 0.0358 (8) | 0.0629 (11) | 0.0066 (7) | 0.0250 (8) | 0.0120 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0562 (11) | 0.0431 (9) | 0.0718 (12) | 0.0111 (8) | 0.0443 (10) | 0.0076 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0732 (13) | 0.0457 (10) | 0.0560 (10) | 0.0069 (9) | 0.0389 (10) | −0.0030 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0509 (10) | 0.0404 (9) | 0.0448 (9) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0181 (8) | −0.0018 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0337 (8) | 0.0322 (8) | 0.0396 (8) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0166 (6) | 0.0045 (6) |
| C8A | 0.0333 (8) | 0.0328 (8) | 0.0418 (8) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0161 (7) | 0.0047 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—O1 | 1.4247 (13) | C4—C4A | 1.413 (3) |
| S1—O2 | 1.4348 (12) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| S1—N2 | 1.6092 (17) | C4A—C5 | 1.405 (3) |
| S1—C8 | 1.7693 (15) | C4A—C8A | 1.419 (2) |
| N1—C2 | 1.320 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.357 (3) |
| N1—C8A | 1.357 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N2—H1N | 0.87 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.407 (2) |
| N2—H2N | 0.83 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.400 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.364 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.349 (3) | C8—C8A | 1.425 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | ||
| O1—S1—O2 | 118.03 (8) | C5—C4A—C4 | 123.55 (17) |
| O1—S1—N2 | 108.14 (10) | C5—C4A—C8A | 119.89 (16) |
| O2—S1—N2 | 106.66 (9) | C4—C4A—C8A | 116.54 (17) |
| O1—S1—C8 | 107.39 (7) | C6—C5—C4A | 121.06 (15) |
| O2—S1—C8 | 107.79 (8) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 |
| N2—S1—C8 | 108.52 (7) | C4A—C5—H5 | 119.5 |
| C2—N1—C8A | 117.50 (15) | C5—C6—C7 | 120.09 (16) |
| S1—N2—H1N | 110.7 (15) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.0 |
| S1—N2—H2N | 112.0 (16) | C7—C6—H6 | 120.0 |
| H1N—N2—H2N | 115 (2) | C8—C7—C6 | 120.29 (16) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 123.47 (19) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.9 |
| N1—C2—H2 | 118.3 | C6—C7—H7 | 119.9 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 118.3 | C7—C8—C8A | 121.20 (14) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.58 (17) | C7—C8—S1 | 119.61 (12) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.2 | C8A—C8—S1 | 119.17 (12) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.2 | N1—C8A—C4A | 123.12 (15) |
| C3—C4—C4A | 119.77 (17) | N1—C8A—C8 | 119.41 (13) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C4A—C8A—C8 | 117.45 (15) |
| C4A—C4—H4 | 120.1 | ||
| C8A—N1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (3) | O1—S1—C8—C8A | −64.59 (13) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.7 (3) | O2—S1—C8—C8A | 167.26 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4—C4A | −1.2 (3) | N2—S1—C8—C8A | 52.10 (15) |
| C3—C4—C4A—C5 | 178.30 (18) | C2—N1—C8A—C4A | −0.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—C4A—C8A | −0.2 (3) | C2—N1—C8A—C8 | −178.87 (15) |
| C4—C4A—C5—C6 | −178.12 (17) | C5—C4A—C8A—N1 | −177.31 (15) |
| C8A—C4A—C5—C6 | 0.4 (3) | C4—C4A—C8A—N1 | 1.3 (2) |
| C4A—C5—C6—C7 | −1.0 (3) | C5—C4A—C8A—C8 | 0.8 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.4 (3) | C4—C4A—C8A—C8 | 179.37 (14) |
| C6—C7—C8—C8A | 0.8 (2) | C7—C8—C8A—N1 | 176.81 (15) |
| C6—C7—C8—S1 | −177.78 (13) | S1—C8—C8A—N1 | −4.61 (19) |
| O1—S1—C8—C7 | 114.02 (14) | C7—C8—C8A—C4A | −1.4 (2) |
| O2—S1—C8—C7 | −14.14 (15) | S1—C8—C8A—C4A | 177.22 (11) |
| N2—S1—C8—C7 | −129.30 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H1N···O2i | 0.87 (2) | 2.15 (3) | 3.013 (2) | 169 (2) |
| N2—H2N···N1 | 0.83 (2) | 2.33 (2) | 2.921 (2) | 129 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z.
Footnotes
Part CXXXII in the series of Azinyl Sulfides.
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GK2515).
References
- Adsmond, D. A. & Grant, D. J. W. (2001). J. Pharm. Sci. 90, 2058–2077. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Borras, J., Scozzafava, A., Menabuoni, L., Mincione, F., Briganti, F., Mincione, G. & Supuran, C. T. (1999). Bioorg. Med. Chem. pp. 2397–2406. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Eveloch, J. L., Bocian, D. F. & Sudmeier, J. L. (1981). Biochemistry, 20, 4951–4954. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hanson, R. M. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 1250–1260.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Maślankiewicz, A., Marciniec, K., Pawłowski, M. & Zajdel, P. (2007). Heterocycles, 71, 1975–1990.
- Oxford Diffraction (2008). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abington, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zajdel, P., Marciniec, K., Maślankiewicz, A., Paluchowska, M. H., Satała, G., Partyka, A., Jastrzębska-Więsek, M., Wróbel, D., Wesołowska, A., Duszyńska, B., Bojarski, A. J. & Pawłowski, M. (2011). Bioorg. Med. Chem. pp. 6750–6759. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zajdel, P., Marciniec, K., Maślankiewicz, A., Satała, G., Duszyńska, B., Bojarski, A. J., Partyka, A., Jastrzębska-Więsek, M., Wróbel, D., Wesołowska, A. & Pawłowski, M. (2012). Bioorg. Med. Chem. pp. 1545–1556. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036963/gk2515sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036963/gk2515Isup2.mol
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036963/gk2515Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036963/gk2515Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





