Abstract
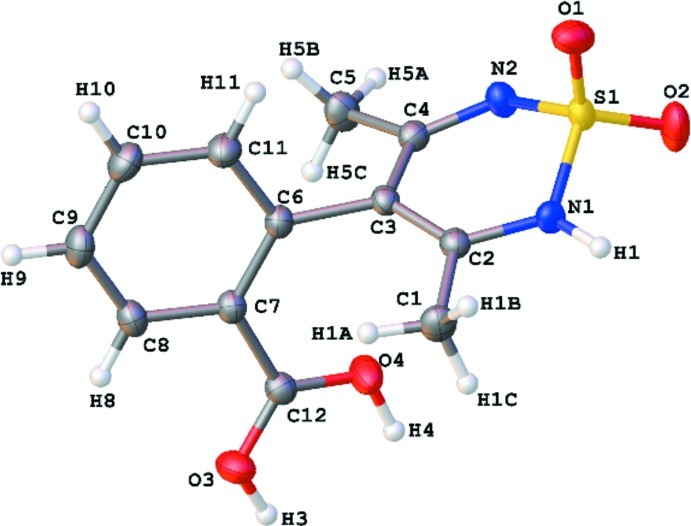
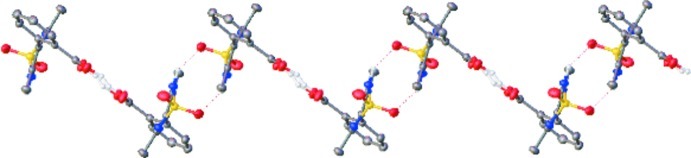
In the title molecule, C12H12N2O4S, the S atom of the thiadiazine ring deviates by 0.5104 (4) Å from the mean plane of the other five atoms [largest deviation = 0.0623 (15) Å] giving a slightly distorted sofa conformation. The carboxy H atom was refined as disordered over two sets of sites with refined occupancies of 0.58 (2) and 0.48 (2). This corresponds to rotational disorder of the C=O and O—H groups about the attached C—C bond. In the crystal, O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds connect the molecules into chains along [110].
Related literature
The title compound is a phenyl acid thiadiazine derivative. For synthetic background and applications of 1,2,6-thiadiazine-1,1-dioxide derivatives, see: Wright (1964 ▶); Breining et al. (1995 ▶). For a related structure, see: Bhatt et al. (2012 ▶)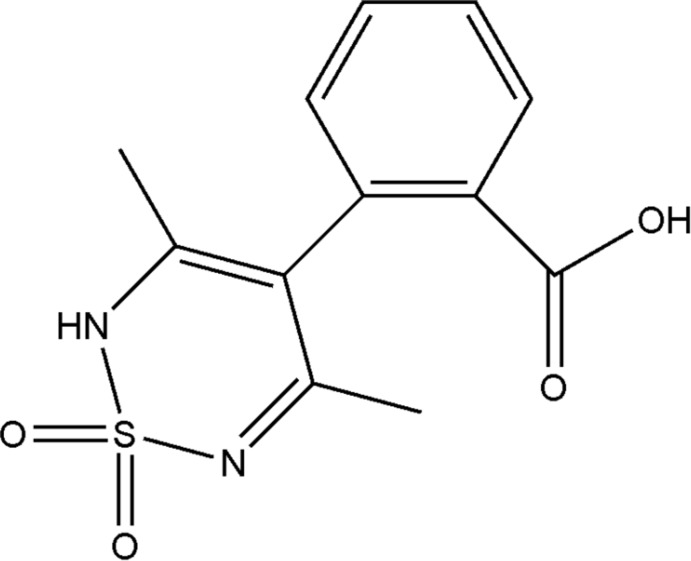
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H12N2O4S
M r = 280.30
Monoclinic,
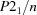
a = 10.5048 (14) Å
b = 10.4254 (13) Å
c = 11.1294 (14) Å
β = 92.772 (4)°
V = 1217.4 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.28 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.24 × 0.19 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa DUO APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2006 ▶) T min = 0.936, T max = 0.952
5724 measured reflections
3030 independent reflections
2573 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.020
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.103
S = 1.05
3030 reflections
187 parameters
3 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.42 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2006 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812037026/lh5507sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812037026/lh5507Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812037026/lh5507Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.97 (1) | 2.09 (2) | 2.9699 (18) | 151 (2) |
| O4—H4⋯O3ii | 0.97 (3) | 1.64 (3) | 2.6103 (19) | 177 (3) |
| O3—H3⋯O4ii | 0.97 (3) | 1.67 (3) | 2.6103 (19) | 161 (5) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 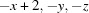 ; (ii)
; (ii) 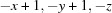 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr Hong Su from the University of Cape Town for assistance with the data collection and refinement.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The synthesis of 1,2,6-thiadiazine-1,1-dioxides derivatives was first reported using sulfamide with alpha and beta diketones (Wright, 1964). Anti-HIV-1 activity for this family of structures was also reported (Breining et al., 1995). For this reason we are interested in this class of compounds as potential agents in other diseases. The crystal structure of the title compound is described herein.
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. It is the second 3,5-dimethyl based structure reported with an aromatic ring at position 4 of the thiadiazine ring. Previously we have reported the phenyl ethyl and methyl ester (Bhatt et al., 2012). It is the first containing an acid functional group in the broader family of 1,2,6-thiadiazine-1,1-dioxides. The S atom of the thiadiazine ring deviates by 0.5104 (4) Å from the plane of the other five atoms [largest deviation 0.0623 (15) Å] giving a slightly distorted sofa conformation. The carboxylic acid H atom was refined as disordered over two sets of sites with refined occupancies 0.58 (2) and 0.48 (2). This corresponds to roational disorder of the C═O and O—H groups about the attached C—C bond. In the crystal, O—H···O and N—H···O hydrogen bonds connect molecules into chains along [110] (Fig. 2).
Experimental
2-(2, 4-dioxopentan-3-yl) benzoic acid (0.072 mol) and sulfamide (0.072 mol) were dissolved in methanol (70 ml). Anhydrous hydrogen chloride gas was bubbled into the mixture until the temperature increased to 323 K. The contents of the reaction were then refluxed for 3hrs. The reaction mixture was cooled, filtered and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The residual solid was treated with NaOH (0.138 mol) in water (200 ml), the contents were heated at 343 K for 2.5 hrs. The reaction progress was monitored by TLC ethyl acetate/hexane (80:20 Rf = 1/2). The reaction mixture was cooled and acidified using concentrated HCl to get the crude acid as an oil. To this oily residue was added a solution of methanol/ethyl acetate (10 ml) (10/90) which yielded a white colourless solid (79%). M.p.= 523 K. Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were grown in dioxane/water at room temprature.
Refinement
All hydrogen atoms, except H1, H3 and H4, were placed in idealized positions and refined with geometric constraints [C—H = 0.95 - 0.98 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(Cmethyl). The hydrogen atom H1 was located in a difference Fourier map and refined with O—H distance restraint to the value of 0.97 (1) Å. The carboxy hydroxyl hydrogen is distributed over two sites: H3 and H4, were both located in a difference Fourier map and refined with a O—H distance restraint to the value of 0.97 (1) Å. The site occupancy factors refined to 0.48 (8) for H3 and 0.52 (8) for H4.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at 40% probability. Atoms H3 and H4 are disorder components.
Fig. 2.
The hydrogen bonding interactions of the title compound along [110]. All H atoms except those involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C12H12N2O4S | F(000) = 584 |
| Mr = 280.30 | Dx = 1.529 Mg m−3Dm = 0 Mg m−3Dm measured by not measured |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Melting point: 523 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.5048 (14) Å | Cell parameters from 5724 reflections |
| b = 10.4254 (13) Å | θ = 2.6–28.4° |
| c = 11.1294 (14) Å | µ = 0.28 mm−1 |
| β = 92.772 (4)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 1217.4 (3) Å3 | 0, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.24 × 0.19 × 0.18 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa DUO APEXII diffractometer | 3030 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2573 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.020 |
| 0.5° φ scans and ω scans | θmax = 28.4°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2006) | h = −12→14 |
| Tmin = 0.936, Tmax = 0.952 | k = −13→12 |
| 5724 measured reflections | l = −11→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.103 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0518P)2 + 0.4988P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3030 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 187 parameters | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 3 restraints | Δρmin = −0.42 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| S1 | 0.98957 (3) | 0.13712 (4) | 0.12970 (3) | 0.02250 (12) | |
| O1 | 1.01274 (12) | 0.00736 (13) | 0.16838 (11) | 0.0344 (3) | |
| O2 | 1.09339 (11) | 0.20118 (15) | 0.07866 (12) | 0.0395 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.39308 (11) | 0.41036 (12) | 0.06653 (11) | 0.0311 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.60472 (11) | 0.39428 (13) | 0.08005 (13) | 0.0353 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.87045 (12) | 0.13786 (13) | 0.02772 (11) | 0.0231 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.93605 (12) | 0.21970 (13) | 0.23740 (12) | 0.0241 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.65248 (16) | 0.09799 (18) | −0.03955 (14) | 0.0285 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.5677 | 0.0883 | −0.0076 | 0.043* | |
| H1B | 0.6784 | 0.0168 | −0.0754 | 0.043* | |
| H1C | 0.6500 | 0.1653 | −0.1010 | 0.043* | |
| C2 | 0.74610 (14) | 0.13394 (14) | 0.06012 (13) | 0.0201 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.71616 (13) | 0.16832 (14) | 0.17403 (13) | 0.0192 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.81280 (14) | 0.22158 (14) | 0.25478 (13) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.77422 (16) | 0.29238 (17) | 0.36412 (15) | 0.0293 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.8483 | 0.3374 | 0.4007 | 0.044* | |
| H5B | 0.7416 | 0.2314 | 0.4222 | 0.044* | |
| H5C | 0.7076 | 0.3547 | 0.3412 | 0.044* | |
| C6 | 0.58294 (14) | 0.15746 (14) | 0.21603 (13) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.48160 (14) | 0.24135 (14) | 0.18462 (13) | 0.0206 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.36101 (15) | 0.21905 (16) | 0.22911 (14) | 0.0252 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.2925 | 0.2749 | 0.2067 | 0.030* | |
| C9 | 0.34023 (16) | 0.11711 (17) | 0.30514 (15) | 0.0292 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.2581 | 0.1035 | 0.3349 | 0.035* | |
| C10 | 0.43933 (16) | 0.03505 (17) | 0.33774 (15) | 0.0296 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.4257 | −0.0349 | 0.3903 | 0.036* | |
| C11 | 0.55916 (16) | 0.05546 (15) | 0.29322 (14) | 0.0263 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.6267 | −0.0015 | 0.3159 | 0.032* | |
| C12 | 0.49362 (14) | 0.35576 (14) | 0.10521 (14) | 0.0217 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.606 (4) | 0.469 (2) | 0.028 (3) | 0.030 (16)* | 0.52 (8) |
| H3 | 0.406 (6) | 0.491 (3) | 0.025 (5) | 0.06 (2)* | 0.48 (8) |
| H1 | 0.892 (2) | 0.113 (2) | −0.0528 (8) | 0.047 (6)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.01708 (18) | 0.0281 (2) | 0.02257 (19) | 0.00231 (14) | 0.00382 (13) | −0.00124 (14) |
| O1 | 0.0401 (7) | 0.0339 (7) | 0.0292 (6) | 0.0161 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0019 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0237 (6) | 0.0582 (9) | 0.0374 (7) | −0.0106 (6) | 0.0105 (5) | −0.0040 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0259 (6) | 0.0294 (6) | 0.0376 (7) | 0.0023 (5) | −0.0030 (5) | 0.0086 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0255 (6) | 0.0308 (6) | 0.0503 (8) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0102 (5) | 0.0165 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0207 (6) | 0.0306 (7) | 0.0182 (6) | 0.0028 (5) | 0.0029 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0201 (6) | 0.0278 (7) | 0.0246 (6) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0017 (5) | −0.0048 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0275 (8) | 0.0347 (9) | 0.0231 (7) | −0.0019 (7) | −0.0012 (6) | −0.0041 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0201 (7) | 0.0183 (7) | 0.0219 (7) | 0.0013 (5) | 0.0018 (5) | 0.0012 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0182 (6) | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0218 (7) | 0.0022 (5) | 0.0030 (5) | 0.0010 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0228 (7) | 0.0193 (7) | 0.0204 (6) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0026 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0275 (8) | 0.0350 (9) | 0.0256 (7) | 0.0028 (7) | 0.0024 (6) | −0.0096 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0196 (7) | 0.0211 (7) | 0.0207 (6) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0035 (5) | −0.0006 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0191 (7) | 0.0206 (7) | 0.0222 (7) | −0.0010 (6) | 0.0027 (5) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0191 (7) | 0.0281 (8) | 0.0285 (7) | 0.0005 (6) | 0.0031 (6) | −0.0019 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0242 (8) | 0.0326 (9) | 0.0313 (8) | −0.0066 (7) | 0.0081 (6) | −0.0011 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0338 (9) | 0.0278 (8) | 0.0279 (8) | −0.0048 (7) | 0.0071 (6) | 0.0039 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0233 (8) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0024 (6) | 0.0038 (6) | 0.0036 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0212 (7) | 0.0202 (7) | 0.0236 (7) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0016 (5) | −0.0014 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—O2 | 1.4206 (12) | C3—C6 | 1.5011 (19) |
| S1—O1 | 1.4368 (13) | C4—C5 | 1.496 (2) |
| S1—N2 | 1.5998 (13) | C5—H5A | 0.9800 |
| S1—N1 | 1.6483 (13) | C5—H5B | 0.9800 |
| O3—C12 | 1.2573 (19) | C5—H5C | 0.9800 |
| O3—H3 | 0.9699 (10) | C6—C11 | 1.397 (2) |
| O4—C12 | 1.2781 (18) | C6—C7 | 1.409 (2) |
| O4—H4 | 0.9699 (10) | C7—C8 | 1.402 (2) |
| N1—C2 | 1.3724 (19) | C7—C12 | 1.493 (2) |
| N1—H1 | 0.9698 (10) | C8—C9 | 1.382 (2) |
| N2—C4 | 1.3185 (19) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.494 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.382 (2) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9800 | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9800 | C10—C11 | 1.391 (2) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9800 | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.369 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.435 (2) | ||
| O2—S1—O1 | 116.12 (8) | C4—C5—H5A | 109.5 |
| O2—S1—N2 | 110.55 (8) | C4—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| O1—S1—N2 | 110.05 (7) | H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| O2—S1—N1 | 107.12 (8) | C4—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O1—S1—N1 | 108.82 (8) | H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| N2—S1—N1 | 103.34 (7) | H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| C12—O3—H3 | 115 (4) | C11—C6—C7 | 118.02 (13) |
| C12—O4—H4 | 115 (2) | C11—C6—C3 | 116.49 (13) |
| C2—N1—S1 | 121.29 (10) | C7—C6—C3 | 125.49 (13) |
| C2—N1—H1 | 120.0 (14) | C8—C7—C6 | 119.63 (14) |
| S1—N1—H1 | 115.7 (14) | C8—C7—C12 | 116.44 (13) |
| C4—N2—S1 | 120.07 (11) | C6—C7—C12 | 123.94 (13) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C9—C8—C7 | 121.06 (15) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.5 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.5 |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C10—C9—C8 | 119.82 (15) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C10—C9—H9 | 120.1 |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C8—C9—H9 | 120.1 |
| C3—C2—N1 | 119.99 (14) | C9—C10—C11 | 119.65 (15) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 125.51 (14) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 114.40 (13) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.62 (13) | C10—C11—C6 | 121.82 (15) |
| C2—C3—C6 | 121.88 (13) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| C4—C3—C6 | 118.44 (12) | C6—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| N2—C4—C3 | 124.92 (13) | O3—C12—O4 | 122.93 (14) |
| N2—C4—C5 | 115.67 (13) | O3—C12—C7 | 118.07 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.29 (13) | O4—C12—C7 | 119.00 (13) |
| O2—S1—N1—C2 | −152.60 (12) | C4—C3—C6—C11 | −78.20 (18) |
| O1—S1—N1—C2 | 81.12 (13) | C2—C3—C6—C7 | −75.8 (2) |
| N2—S1—N1—C2 | −35.82 (14) | C4—C3—C6—C7 | 101.44 (18) |
| O2—S1—N2—C4 | 143.83 (13) | C11—C6—C7—C8 | −1.2 (2) |
| O1—S1—N2—C4 | −86.58 (14) | C3—C6—C7—C8 | 179.14 (14) |
| N1—S1—N2—C4 | 29.49 (14) | C11—C6—C7—C12 | 178.69 (14) |
| S1—N1—C2—C3 | 20.0 (2) | C3—C6—C7—C12 | −0.9 (2) |
| S1—N1—C2—C1 | −163.46 (12) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 1.1 (2) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 6.8 (2) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −178.81 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −169.34 (15) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.3 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3—C6 | −175.96 (13) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.3 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C6 | 7.9 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C6 | 0.2 (3) |
| S1—N2—C4—C3 | −9.0 (2) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | 0.6 (2) |
| S1—N2—C4—C5 | 174.88 (12) | C3—C6—C11—C10 | −179.72 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | −13.2 (2) | C8—C7—C12—O3 | −12.3 (2) |
| C6—C3—C4—N2 | 169.49 (14) | C6—C7—C12—O3 | 167.81 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 162.84 (15) | C8—C7—C12—O4 | 167.35 (15) |
| C6—C3—C4—C5 | −14.5 (2) | C6—C7—C12—O4 | −12.6 (2) |
| C2—C3—C6—C11 | 104.52 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.97 (1) | 2.09 (2) | 2.9699 (18) | 151 (2) |
| O4—H4···O3ii | 0.97 (3) | 1.64 (3) | 2.6103 (19) | 177 (3) |
| O3—H3···O4ii | 0.97 (3) | 1.67 (3) | 2.6103 (19) | 161 (5) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y, −z; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5507).
References
- Bhatt, N., Bhatt, P., Vyas, K. B., Nimavat, K., Govender, T., Kruger, H. G. & Maguire, G. E. M. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Breining, T., Cimpoia, A. R., Mansour, T. S., Cammack, N., Hopewell, P. & Ashman, C. (1995). Heterocycles, 41, 87–94.
- Bruker (2006). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS, Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wright, J. B. (1964). J. Org. Chem. 29, 1905–1909.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812037026/lh5507sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812037026/lh5507Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812037026/lh5507Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report