Abstract
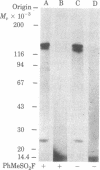
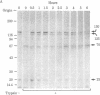
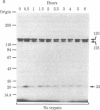
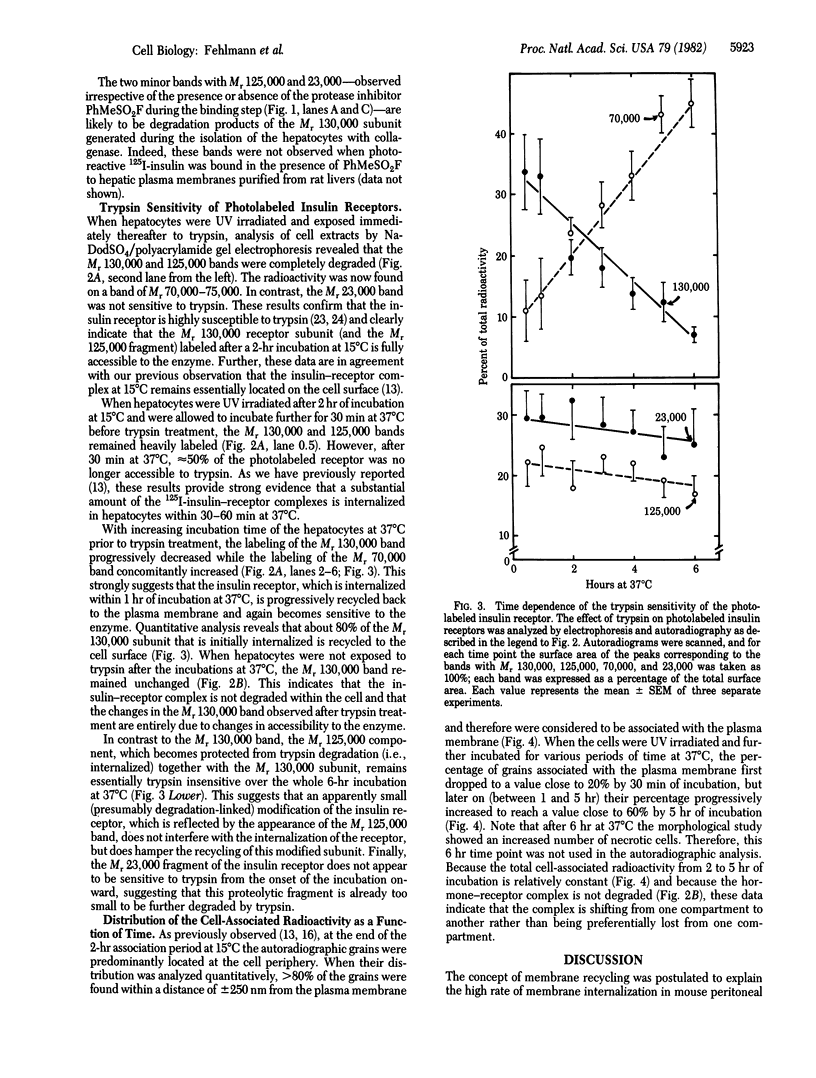
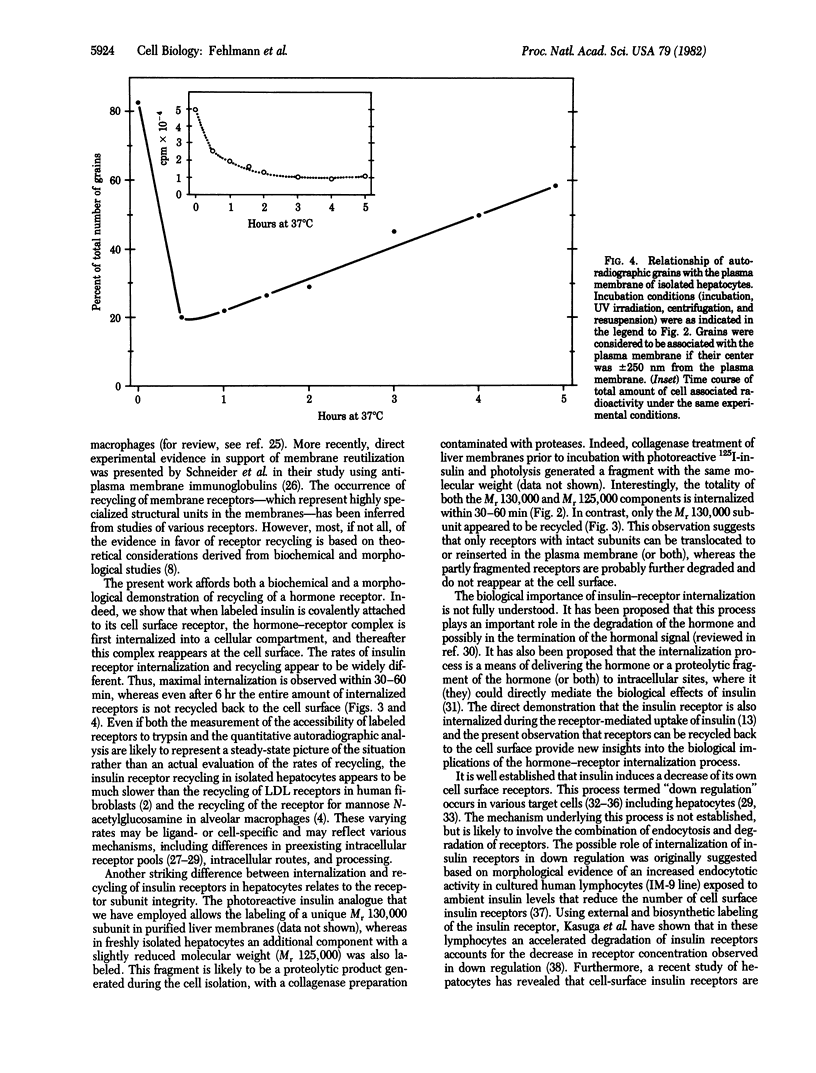
We have followed the fate of cell surface insulin receptors in isolated rat hepatocytes by both a biochemical and a morphological approach. Hepatocytes were labeled with the photoreactive and biologically active 125I-labeled insulin analogue, [2-nitro-4-azidophenylacetylB2]des-PheB1-insulin, under conditions that allow for minimal internalization (2 hr at 15 degrees C). Analysis of the cell-associated radioactivity by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions followed by autoradiography revealed the specific labeling of a major insulin receptor subunit with Mr 130,000 and a minor degradation product with Mr 125,000. When the cells were exposed at 15 degrees C to trypsin at the end of the association period, these two bands were no longer observed, indicating that the labeled receptors were at the cell surface. This trypsin sensitivity of the receptor disappeared within 30-60 min of incubation of the cells at 37 degrees C, reflecting the internalization of the hormone-receptor complexes. Over the subsequent 4 hr of incubation, this was followed by a progressive reappearance of the receptor complexes at the cell surface, as indicated by the recovery of trypsin sensitivity of the labeled insulin receptors. An identical (both chronologically and quantitatively) journey of the insulin receptors was observed when the labeled material was studied by quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography. Thus, when the cells were incubated at 37 degrees C there was a rapid decrease (30-60 min) in the percentage of autoradiographic grains associated with the plasma membrane, followed by a progressive increase in this percentage over the subsequent 4 hr of incubation. In conclusion, using a biochemical and morphological approach to trace the photoaffinity-labeled insulin receptor, we have shown that the internalized hormone-receptor complex is recycled back to the cell surface.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. A mutation that impairs the ability of lipoprotein receptors to localise in coated pits on the cell surface of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):695–699. doi: 10.1038/270695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D., Jr, Prince M., Marshall S., Davies P., Olefsky J. M. Regulation of insulin receptors: evidence for involvement of an endocytotic internalization pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5975–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Monensin interrupts the recycling of low density lipoprotein receptors in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Characterization of the low density lipoprotein receptor in membranes prepared from human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3852–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Guzelian P. S., Small M. E. Down regulation of insulin receptors in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes in monolayer. Endocrinology. 1978 Aug;103(2):548–553. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-2-548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Amherdt M., Van Obberghen E., Kahn C. R., Orci L. 125I-insulin binding to cultured human lymphocytes. Initial localization and fate of hormone determined by quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1057–1070. doi: 10.1172/JCI109005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Freychet P., Canivet B., Orci L. The fate of [125I]iodoepidermal growth factor in isolated hepatocytes: a quantitative electron microscopic autoradiographic study. Endocrinology. 1981 Sep;109(3):768–775. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-3-768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Freychet P., Le Cam A., Orci L. Lysosomal association of internalized 125I-insulin in isolated rat hepatocytes. Direct demonstration by quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1249–1261. doi: 10.1172/JCI109420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlmann M., Carpentier J. L., Le Cam A., Thamm P., Saunders D., Brandenburg D., Orci L., Freychet P. Biochemical and morphological evidence that the insulin receptor is internalized with insulin in hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):82–87. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlmann M., Le Cam A., Freychet P. Insulin and glucagon stimulation of amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Synthesis of a high affinity component of transport. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10431–10437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. M., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptor degradation measured by density labeling: effects of cholinergic ligands and evidence against recycling. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):661–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Noriega A., Grubb J. H., Talkad V., Sly W. S. Chloroquine inhibits lysosomal enzyme pinocytosis and enhances lysosomal enzyme secretion by impairing receptor recycling. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):839–852. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Carpentier J. L., Freychet P. O., Orci L. Internalization of polypeptide hormones: mechanism, intracellular localization and significance. Diabetologia. 1980 Apr;18(4):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00251003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon P., Carpentier J. L., Van Obberghen E., Barazzone P., Roth J., Orci L. Insulin-induced receptor loss in the cultured human lymphocyte: quantitative morphological perturbations in the cell and plasma membrane. J Cell Sci. 1979 Oct;39:77–88. doi: 10.1242/jcs.39.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. Evidence for reutilization of surface receptors for alpha-macroglobulin.protease complexes in rabbit alveolar macrophages. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. Polypeptide-binding membrane receptors: analysis and classification. Science. 1981 Apr 3;212(4490):14–20. doi: 10.1126/science.6259730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Kahn C. R., Hedo J. A., Van Obberghen E., Yamada K. M. Insulin-induced receptor loss in cultured human lymphocytes is due to accelerated receptor degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6917–6921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., van Obberghen E., Yamada K. M., Harrison L. C. Autoantibodies against the insulin receptor recognize the insulin binding subunits of an oligomeric receptor. Diabetes. 1981 Apr;30(4):354–357. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.4.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Willis R. A., Cuatrecasas P. Accumulation of epidermal growth factor within cells does not depend on receptor recycling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 16;97(3):840–845. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91453-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Barham F. W. The relationship between the insulin-binding capacity of fat cells and the cellular response to insulin. Studies with intact and trypsin-treated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6210–6216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmakos F. C., Roth J. Insulin-induced loss of the insulin receptor in IM-9 lymphocytes. A biological process mediated through the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9860–9869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M., Lane M. D. On the mechanism of ligand-induced down-regulation of insulin receptor level in the liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1689–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Olefsky J. M. Effects of insulin incubation on insulin binding, glucose transport, and insulin degradation by isolated rat adipocytes. Evidence for hormone-induced desensitization at the receptor and postreceptor level. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):763–772. doi: 10.1172/JCI109914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Hormone binding alters the conformation of the insulin receptor. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1152–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.7003712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Hirsch A., Fung C., Rosen O. M. Development of hormone receptors and hormonal responsiveness in vitro. Insulin receptors and insulin sensitivity in the preadipocyte and adipocyte forms of 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7570–7578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Basu S. K., McPhaul M. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Solubilization of the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5577–5581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider Y. J., Tulkens P., de Duve C., Trouet A. Fate of plasma membrane during endocytosis. II. Evidence for recycling (shuttle) of plasma membrane constituents. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):466–474. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Schlesinger P. H., Sigardson E., Rodman J. S., Lee Y. C. Receptor-mediated pinocytosis of mannose glycoconjugates by macrophages: characterization and evidence for receptor recycling. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer C. J., Ashwell G. Studies on a mammalian hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. Evidence for receptor recycling in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3008–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F. The Banting Memorial Lecture 1976. Insulin today. Diabetes. 1977 Apr;26(4):322–340. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.4.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Van Den Berghe H. Primary amines inhibit recycling of alpha 2M receptors in fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Ksauga M., Le Cam A., Hedo J. A., Itin A., Harrison L. C. Biosynthetic labeling of insulin receptor: studies of subunits in cultured human IM-9 lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor of rat adiopocyte plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1743–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]