Abstract
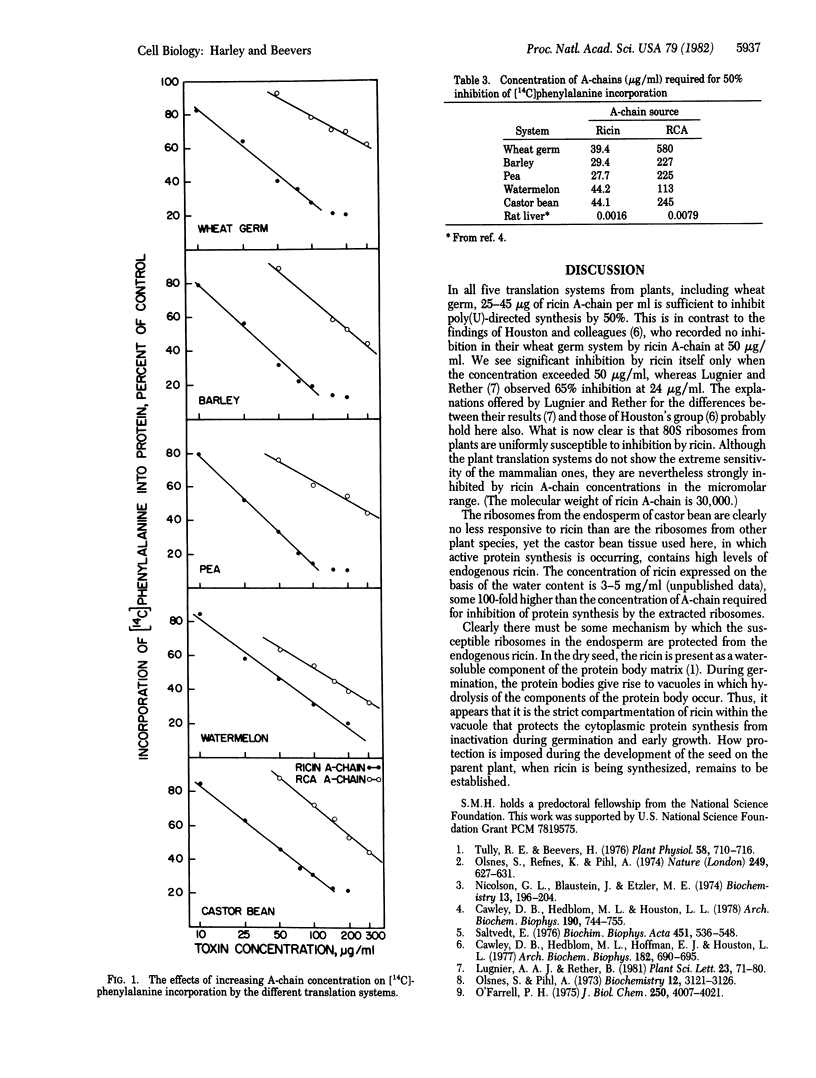
In vitro translation systems were prepared with supernatant factors from wheat germ and 80S ribosomes from wheat germ, barley embryos, watermelon cotyledons, pea cotyledons, and castor bean endosperm. Ricin A-chain, which strongly inhibits protein synthesis by mammalian ribosomes, inhibited all of the plant ribosomal systems by 50% when present at 25-45 μg/ml—≈23,000 times the concentration needed to inhibit mammalian systems. Ricinus communis agglutinin A-chain, a protein similar to ricin A-chain, inhibited translation by the plant systems 50% at concentrations 5-10 times those of the ricin A-chain. Ribosomes from castor bean endosperm, the source of ricin and the agglutinin, were just as susceptible to the inhibitors as were ribosomes from the other four plants. Compartmentation of the inhibitors within vacuoles derived from protein bodies of the endosperm appears to be responsible for protecting cytoplasmic protein synthesis during germination of castor beans.
Keywords: Ricinus communis agglutinin, castor bean, wheat germ
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almog R., Shirey T. L. A modified orcinol test for the specific determination of RNA. Anal Biochem. 1978 Nov;91(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90823-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawley D. B., Hedblom M. L., Hoffman E. J., Houston L. L. Differential ricin sensitivity of rat liver and wheat germ ribosomes in polyuridylic acid translation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):690–695. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90550-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawley D. B., Hedblom M. L., Houston L. L. Homology between ricin and Ricinus communis agglutinin: amino terminal sequence analysis and protein synthesis inhibition studies. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):744–755. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwódź E. A., Bewley J. D. Plant desiccation and protein synthesis: an in vitro system from dry and hydrated mosses using endogenous and synthetic messenger ribonucleic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1975 Feb;55(2):340–345. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A., Efron D., Weeks D. P. The wheat embryo cell-free system. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:749–754. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J., Etzler M. E. Characterization of two plant lectins from Ricinus communis and their quantitative interaction with a murine lymphoma. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):196–204. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Pihl A. Different biological properties of the two constituent peptide chains of ricin, a toxic protein inhibiting protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3121–3126. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Refsnes K., Christensen T. B., Pihl A. Studies on the structure and properties of the lectins from Abrus precatorius and Ricinus communis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 9;405(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Refsnes K., Pihl A. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectins abrin and ricin. Nature. 1974 Jun 14;249(458):627–631. doi: 10.1038/249627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltvedt E. Structure and toxicity of pure ricinus agglutinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 21;451(2):536–548. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


