Abstract
Recombination-defective mutants at two loci that are known to decrease drastically the frequency of meiotic crossing-over do not decrease the frequency of gene conversion at the rosy locus. mei-9 mutant alleles produce frequent postmeiotic segregants manifested as mosaic progeny whereas controls and mei-218 mutants produce none. It is concluded that (i) recombination in Drosophila involves a biparental DNA intermediate and (ii) correction of heteroduplex DNA or recognition of biparental DNA or both is necessary, but not sufficient, for this intermediate to result in crossing-over of flanking markers. It is therefore likely, at least in Drosophila, that the isomerization step in Meselson-Radding type molecular models of recombination is under genetic control.
Full text
PDF

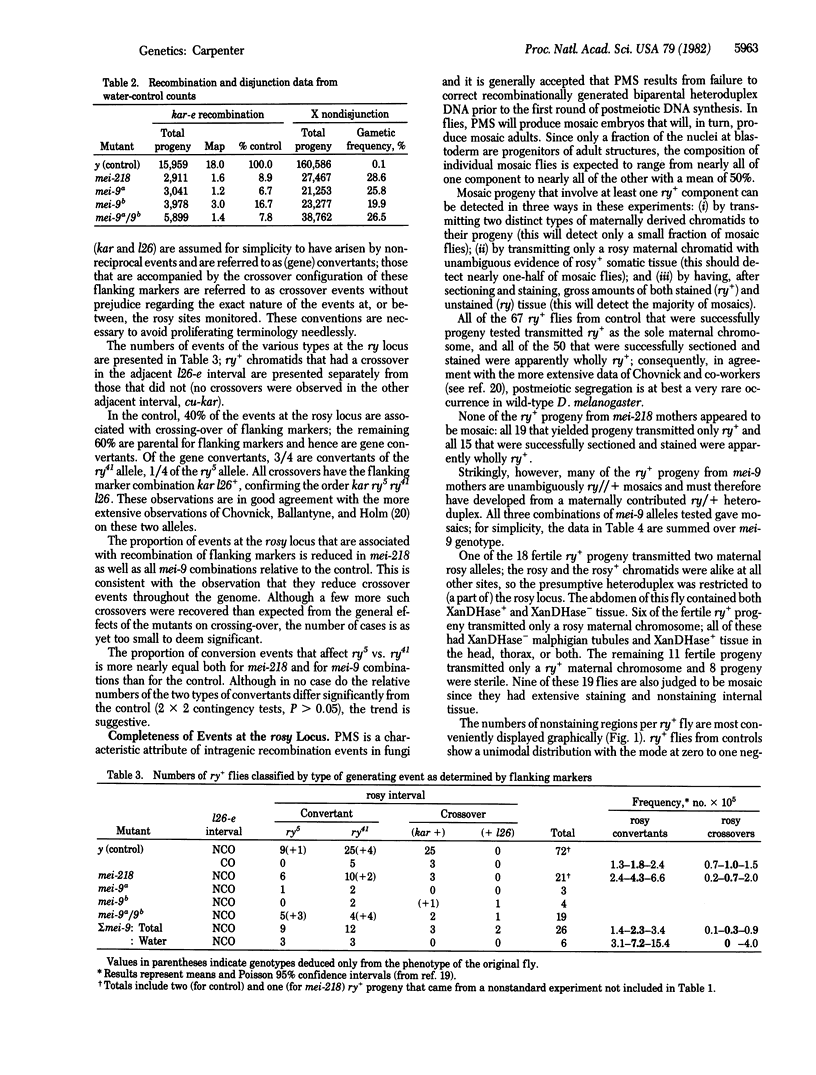
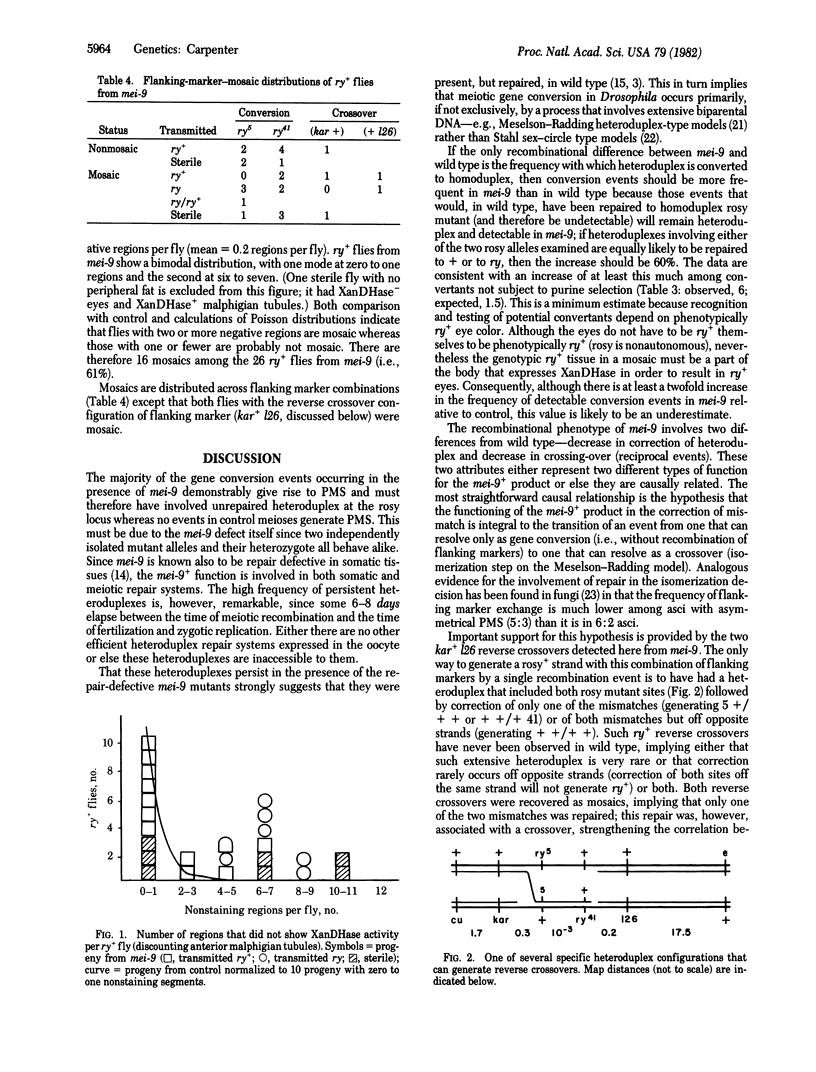

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker B. S., Boyd J. B., Carpenter A. T., Green M. M., Nguyen T. D., Ripoll P., Smith P. D. Genetic controls of meiotic recombination and somatic DNA metabolism in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4140–4144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Carpenter A. T., Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E., Sandler L. The genetic control of meiosis. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:53–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.000413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Carpenter A. T. Genetic analysis of sex chromosomal meiotic mutants in Drosophilia melanogaster. Genetics. 1972 Jun;71(2):255–286. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Carpenter A. T., Ripoll P. The Utilization during Mitotic Cell Division of Loci Controlling Meiotic Recombination and Disjunction in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1978 Nov;90(3):531–578. doi: 10.1093/genetics/90.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J. B., Golino M. D., Setlow R. B. The mei-9 alpha mutant of Drosophila melanogaster increases mutagen sensitivity and decreases excision repair. Genetics. 1976 Nov;84(3):527–544. doi: 10.1093/genetics/84.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter A. T. EM autoradiographic evidence that DNA synthesis occurs at recombination nodules during meiosis in Drosophila melanogaster females. Chromosoma. 1981;83(1):59–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00286016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter A. T. Electron microscopy of meiosis in Drosophila melanogaster females: II. The recombination nodule--a recombination-associated structure at pachytene? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3186–3189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter A. T. Recombination nodules and synaptonemal complex in recombination-defective females of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1979;75(3):259–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00293472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter A. T., Sandler L. On recombination-defective meiotic mutants in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1974 Mar;76(3):453–475. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter A. T. Synaptonemal complex and recombination nodules in wild-type Drosophila melanogaster females. Genetics. 1979 Jun;92(2):511–541. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chovnick A., Ballantyne G. H., Holm D. G. Studies on gene conversion and its relationship to linked exchange in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1971 Oct;69(2):179–209. doi: 10.1093/genetics/69.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chovnick A., Gelbart W., McCarron M. Organization of the Rosy locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel S., Mortimer R., Lusnak K., Tavares F. Meiotic gene conversion: a signal of the basic recombination event in yeast. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1325–1341. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti M. Genetic control of chromosome breakage and rejoining in Drosophila melanogaster: spontaneous chromosome aberrations in X-linked mutants defective in DNA metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1377–1381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti M., Pimpinelli S., Baker B. S. Relationships among chromatid interchanges, sister chromatid exchanges, and meiotic recombination in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamza H., Haedens V., Mekki-Berrada A., Rossignol J. L. Hybrid DNA formation during meiotic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7648–7651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker A. J., Chovnick A. Further observations on intragenic recombination in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1981 Dec;38(3):281–296. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W. One way to think about gene conversion. Genetics. 1969;61(1 Suppl):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


