Abstract
We have investigated the chromosomal organization of genes that are expressed specifically in the asexual spores (conidia) of the Ascomycete fungus Aspergillus nidulans, using two experimental approaches. In the first, 30 different recombinant clones, containing long nuclear DNA inserts and at least one spore-specific gene, were selected randomly. The total number of spore-specific genes present in each clone was then determined by RNA blot analysis. In the second approach, several chromosomal recombinant DNA libraries, having average insert lengths ranging from 1 to 15 kilobases, were constructed. The fraction of clones in each library having one or more spore-specific poly(A)+RNA-coding regions was then determined by colony or plaque filter hybridization with radiolabeled, spore-specific, complementary DNA. The results from these experiments were compared to statistical predictions based on the assumption that the spore-specific genes are randomly distributed in the Aspergillus genome. In both cases, the experimental values deviated significantly from the predicted values, demonstrating that the spore-specific genes are nonrandomly arranged in the genome. Rather, they appear frequently to occur in tightly linked clusters.
Full text
PDF

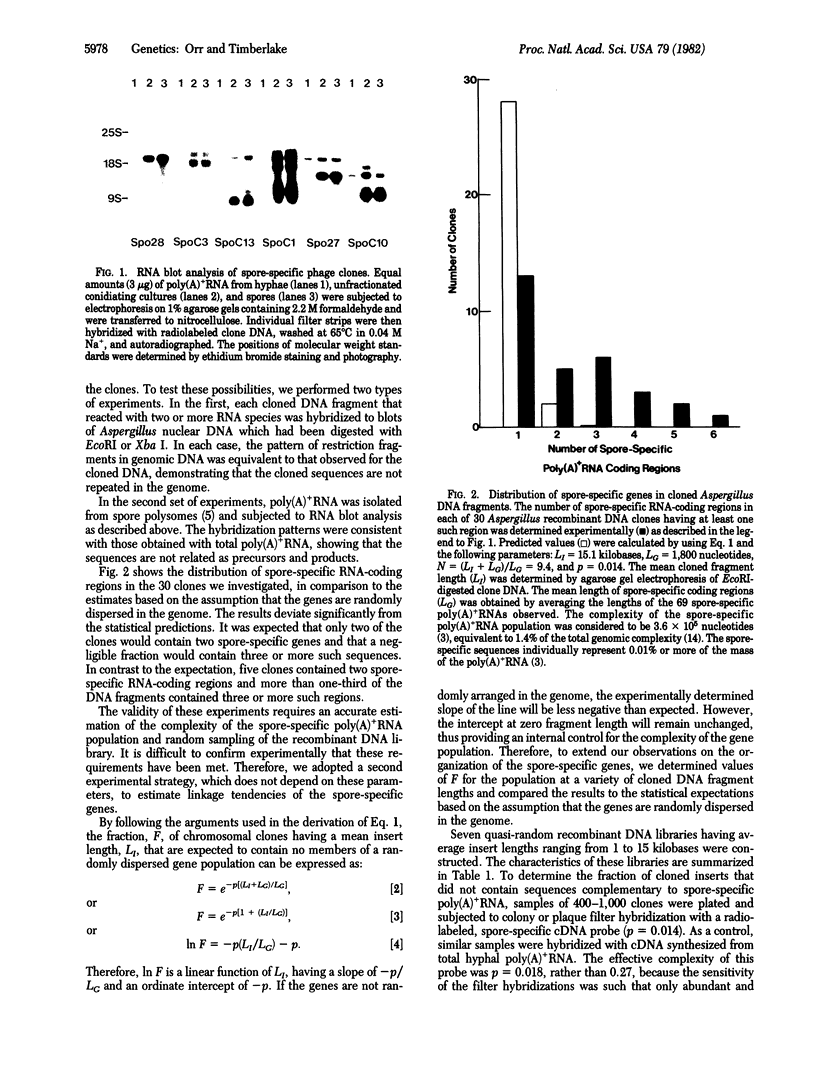
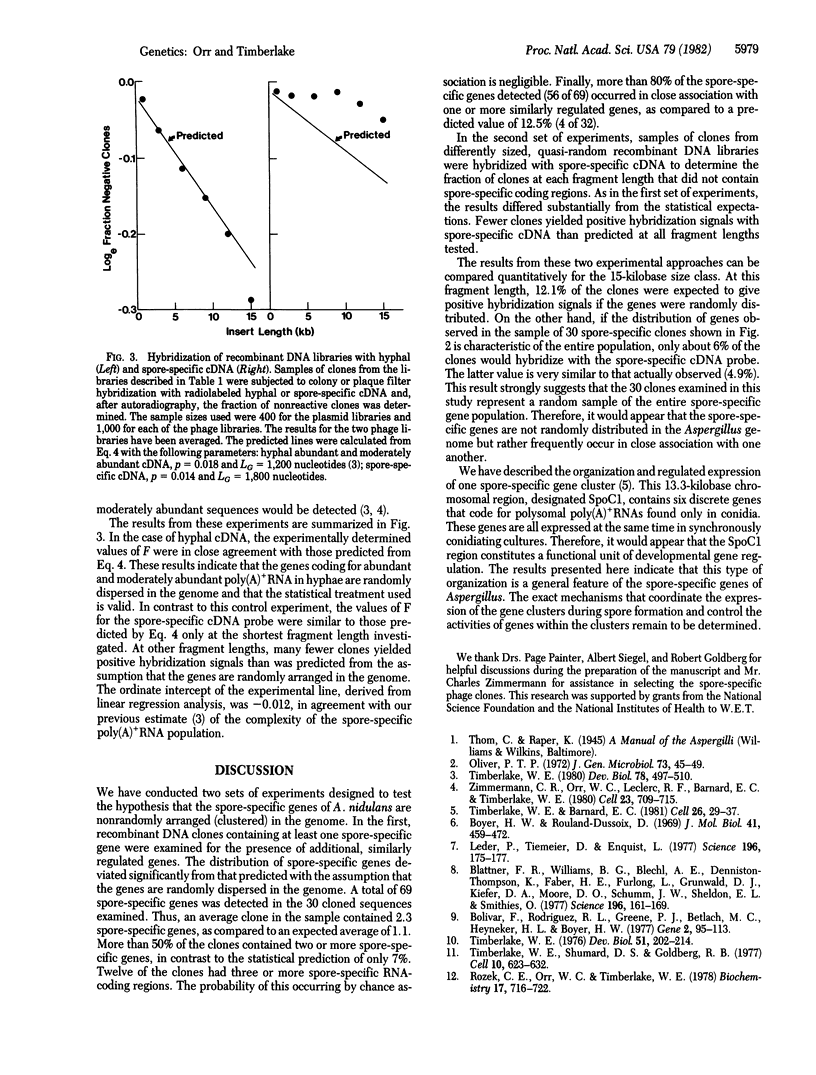

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gealt M. A., Sheir-Neiss G., Morris N. R. The isolation of nuclei from the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):204–210. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. H., Grossman L. I. Electrophoresis of DNA in agarose gels. Optimizing separations of conformational isomers of double- and single-stranded DNAs. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4217–4225. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. W., Florini J. R. Effect of sucrose gradient composition on resolution of RNA species. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver P. T. Conidiophore and spore development in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(1):45–54. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Orr W. C., Timberlake W. E. Diversity and abundance of polyadenylated RNA from Achlya ambisexualis. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):716–722. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Alterations in RNA and protein synthesis associated with steroid hormone-induced sexual morphogenesis in the water mold Achlya. Dev Biol. 1976 Jul 15;51(2):202–214. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E., Barnard E. C. Organization of a gene cluster expressed specifically in the asexual spores of A. nidulans. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Developmental gene regulation in Aspergillus nidulans. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Low repetitive DNA content in Aspergillus nidulans. Science. 1978 Dec 1;202(4371):973–975. doi: 10.1126/science.362530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E., Shumard D. S., Goldberg R. B. Relationship between nuclear and polysomal RNA populations of Achlya: a simple eucaryotic system. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):623–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann C. R., Orr W. C., Leclerc R. F., Barnard E. C., Timberlake W. E. Molecular cloning and selection of genes regulated in Aspergillus development. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90434-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




