Abstract
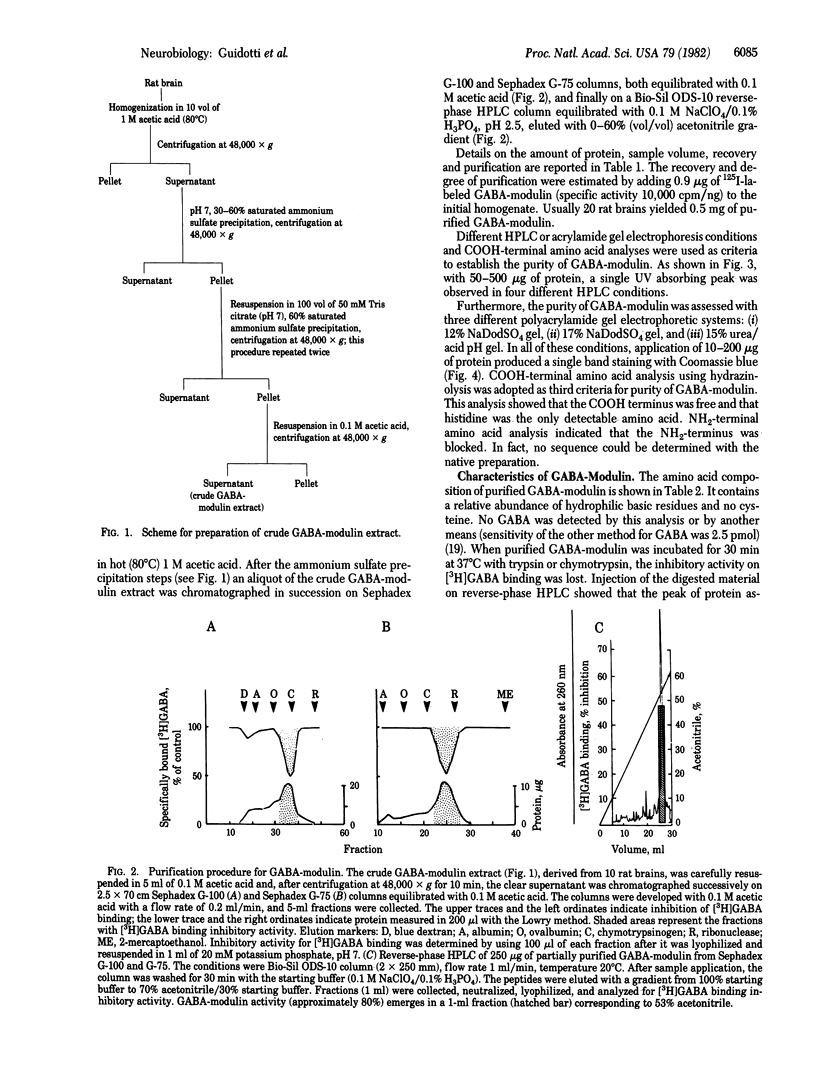
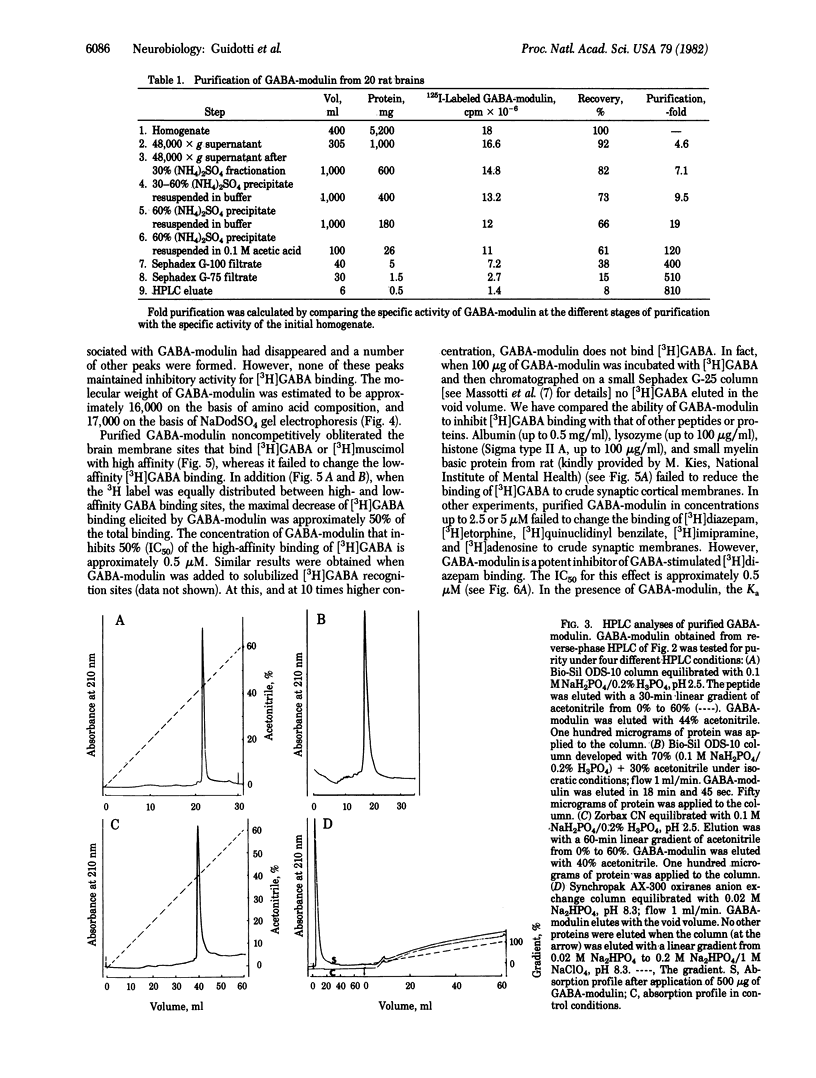
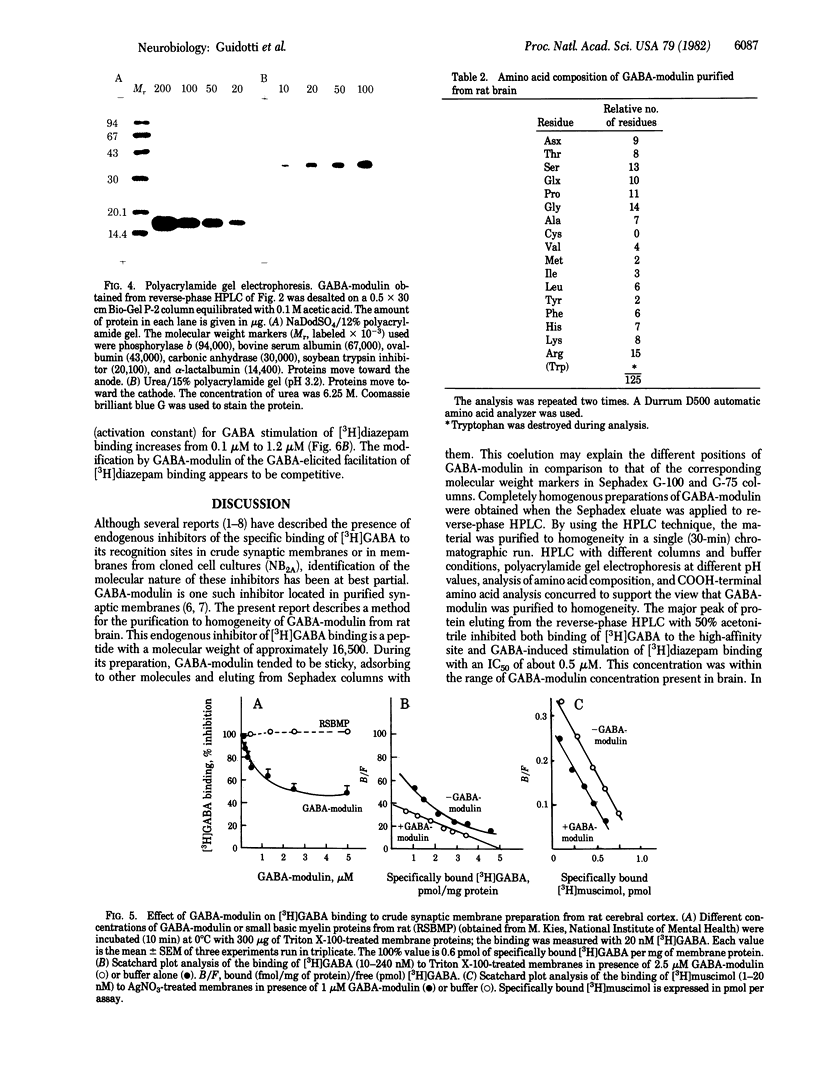
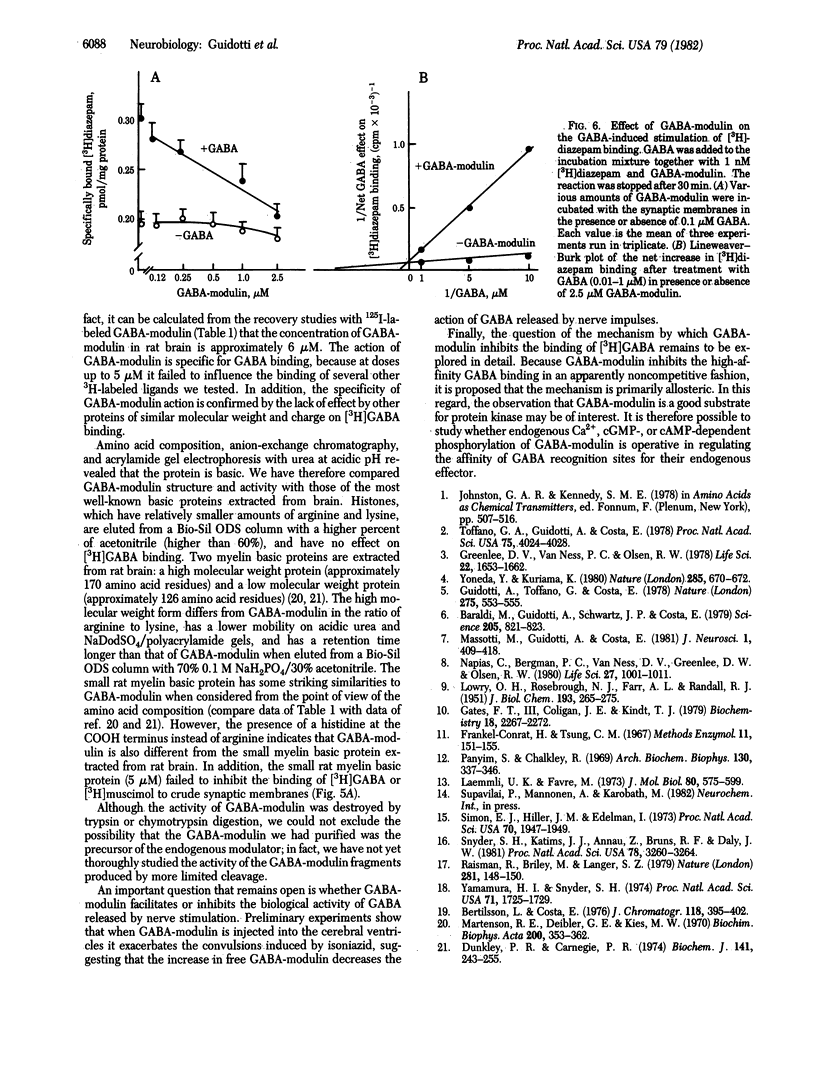
gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA)-modulin is a brain neuropeptide that appears to modulate specific high-affinity (20 nM) GABA recognition sites in brain. When added to crude synaptic membranes this peptide inhibits binding of [3H]GABA to the high-affinity site and prevents facilitation of [3H]diazepam binding elicited by GABA. GABA-modulin has been purified to homogeneity by ammonium sulfate precipitation, gel chromatography, and reverse-phase HPLC. Homogeneity was confirmed by a variety of means, including chromatography under four different HPLC conditions, two different polyacrylamide gel electrophoreses, and end group analysis. Purified GABA-modulin contains approximately 126 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 16,500. The GABA-modulin molecule contains an abundance of hydrophilic basic residues, and neither cysteine nor GABA is present. End group analyses of GABA-modulin showed that histidine is the free COOH terminus and the NH2 terminus is blocked. GABA-modulin specifically blocked both [3H]GABA binding to synaptic membranes (IC50, 0.5 microM) and GABA-stimulated [3H]diazepam binding; the binding of [3H]GABA to low-affinity sites was not affected.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraldi M., Guidotti A., Schwartz J. P., Costa E. GABA receptors in clonal cell lines: a model for study of benzodiazepine action at molecular level. Science. 1979 Aug 24;205(4408):821–823. doi: 10.1126/science.462192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertilsson L., Costa E. Mass fragmentographic quantitation of glutamic acid and gamma-aminobutyric acid in cerebellar nuclei and sympathetic ganglia of rats. J Chromatogr. 1976 Apr 7;118(3):395–402. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)82177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley P. R., Carnegie P. R. Amino acid sequence of the smaller basic protein from rat brain myelin. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):243–255. doi: 10.1042/bj1410243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates F. T., 3rd, Coligan J. E., Kindt T. J. Complete amino acid sequence of rabbit beta 2-microglobulin. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2267–2272. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee D. V., Van Ness P. C., Olsen R. W. Endogenous inhibitor of GABA binding in mammalian brain. Life Sci. 1978 May 8;22(18):1653–1662. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Toffano G., Costa E. An endogenous protein modulates the affinity of GABA and benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):553–555. doi: 10.1038/275553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E., Kies M. W. Myelin basic proteins of the rat central nervous system. Purification, encephalitogenic properties, and amino acid compositions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massotti M., Guidotti A., Costa E. Characterization of benzodiazepine and gamma-aminobutyric recognition sites and their endogenous modulators. J Neurosci. 1981 Apr;1(4):409–418. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-04-00409.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napias C., Bergman M. O., Van Ness P. C., Greenlee D. V., Olsen R. W. GABA binding in mammalian brain: inhibition by endogenous GABA. Life Sci. 1980 Sep 15;27(11):1001–1011. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisman R., Briley M., Langer S. Z. Specific tricyclic antidepressant binding sites in rat brain. Nature. 1979 Sep 13;281(5727):148–150. doi: 10.1038/281148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M., Edelman I. Stereospecific binding of the potent narcotic analgesic (3H) Etorphine to rat-brain homogenate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1947–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Katims J. J., Annau Z., Bruns R. F., Daly J. W. Adenosine receptors and behavioral actions of methylxanthines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toffano G., Guidotti A., Costa E. Purification of an endogenous protein inhibitor of the high affinity binding of gamma-aminobutyric acid to synaptic membranes of rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4024–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. Muscarinic cholinergic binding in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda Y., Kuriyama K. Presence of a low molecular weight endogenous inhibitor on 3H-muscimol binding in synaptic membranes. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):670–673. doi: 10.1038/285670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]