Abstract
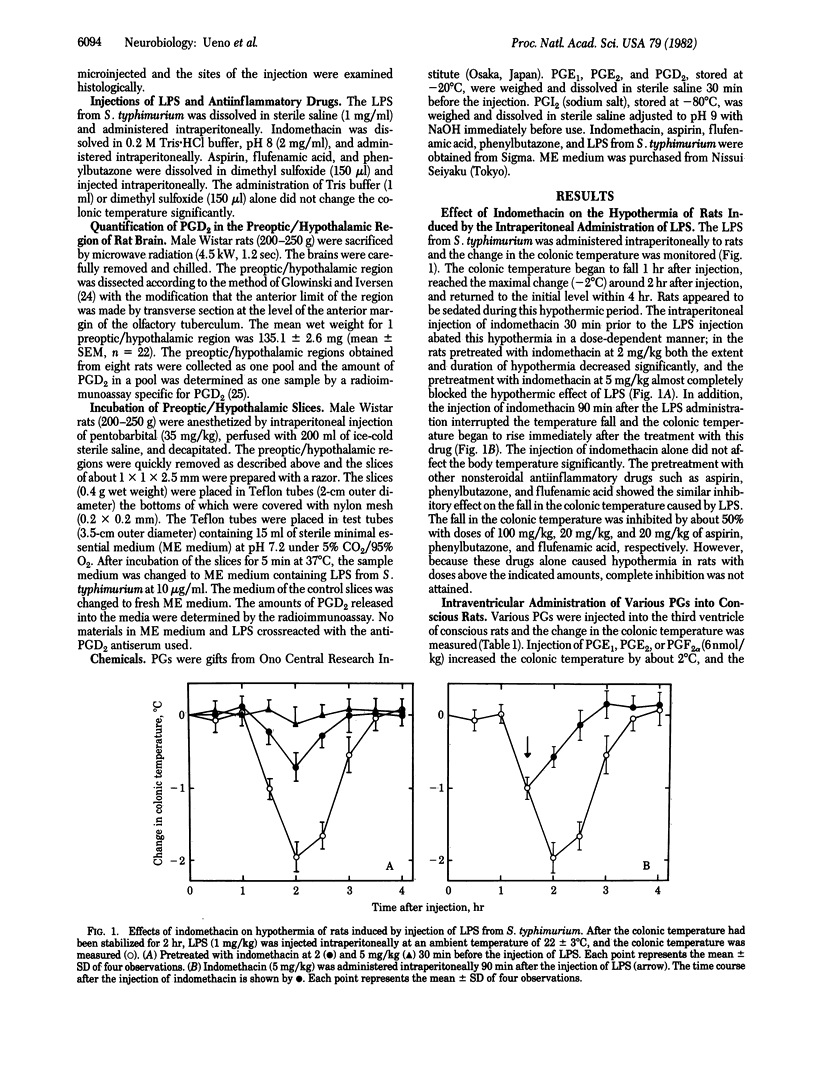
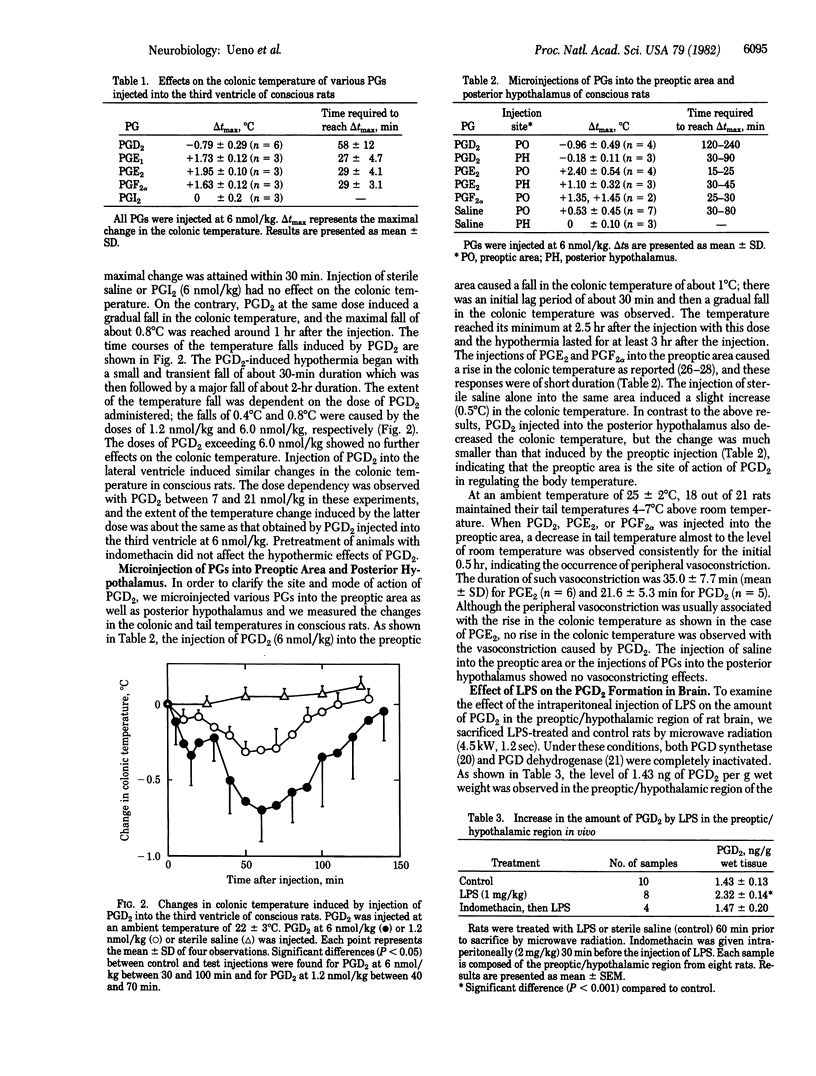
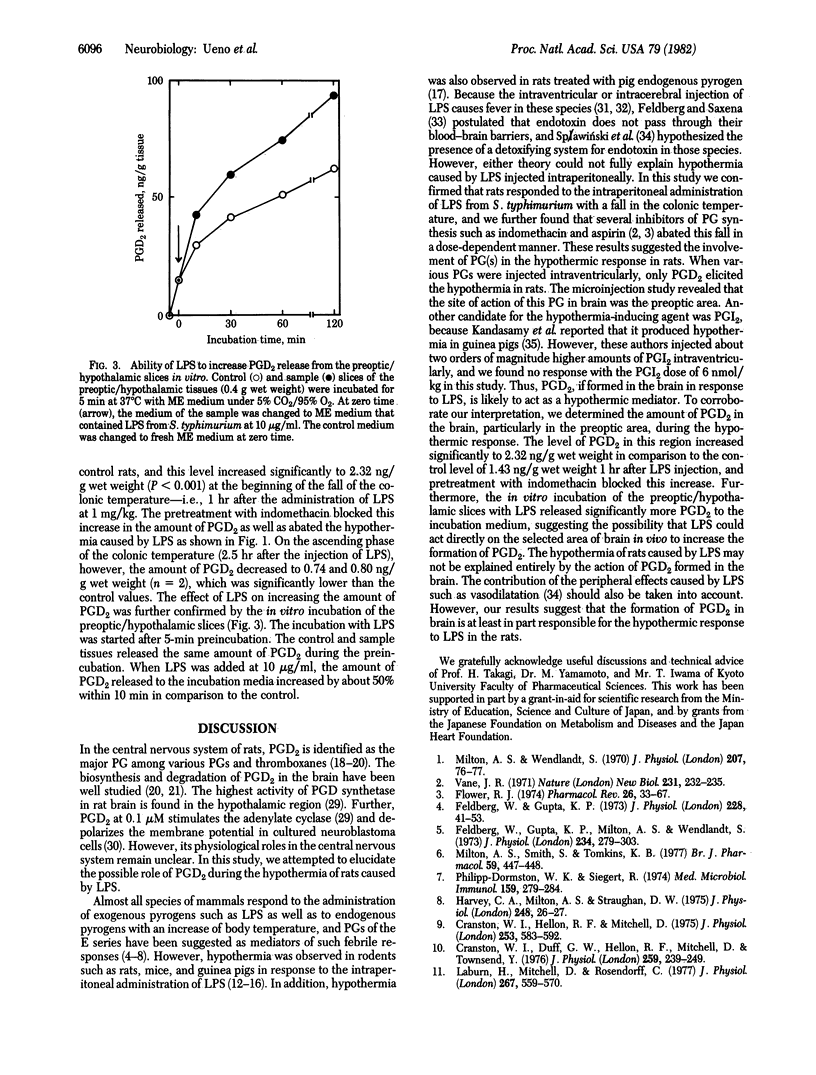
The intraperitoneal administration of lipopolysaccharide from Salmonella typhimurium (1 mg/kg) caused a fall in the rat colonic temperature of about 2 degrees C at an ambient temperature of 22 +/- 3 degrees C. The hypothermia induced by the lipopolysaccharide was abated in a dose-dependent manner by the administration of indomethacin. Other inhibitors of prostaglandin synthetase such as aspirin, flufenamic acid, and phenylbutazone had effects similar to those of indomethacin. When various prostaglandins were injected intracerebroventricularly, only prostaglandin D2 caused a dose-dependent fall in the colonic temperature at doses between 1.2 and 6 nmol/kg. Microinjection of prostaglandin D2 into the preoptic area caused hypothermia of about 1 degree C. However, injection of prostaglandin D2 into the posterior hypothalamus had little effect on the colonic temperature. The hypothermia caused by prostaglandin D2 was not abated by the administration of indomethacin. The amount of prostaglandin D2 increased significantly in the preoptic/hypothalamic region of rat brain 1 hr after the intraperitoneal administration of the lipopolysaccharide, whereas such increase was not observed in rats pretreated with indomethacin. The in vitro incubation of the preoptic/hypothalamic slices with the lipopolysaccharide also increased the amount of prostaglandin D2. These results suggest that the intraperitoneal administration of the lipopolysaccharide induces the release of prostaglandin D2 in the preoptic/hypothalamic area of rat brain and that the latter compound is involved in the hypothermic response of rats to the lipopolysaccharide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Halim M. S., Anggård E. Regional and species differences in endogenous prostaglandin biosynthesis by brain homogenates. Prostaglandins. 1979 Mar;17(3):411–418. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(79)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Halim M. S., Hamberg M., Sjöquist B., Anggård E. Identification of prostaglandin D2 as a major prostaglandin in homogenates of rat brain. Prostaglandins. 1977 Oct;14(4):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsook D., Laburn H., Mitchell D. The febrile responses in rabbits and rats to leucocyte pyrogens of different species. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:113–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston W. I., Duff G. W., Hellon R. F., Mitchell D., Townsend Y. Evidence that brain prostaglandin synthesis is not essential in fever. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(1):239–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston W. I., Hellon R. F., Mitchell D. A dissociation between fever and prostaglandin concentration in cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(2):583–592. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Gupta K. P., Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. Effect of pyrogen and antipyretics on prostaglandin acitvity in cisternal c.s.f. of unanaesthetized cats. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):279–303. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Gupta K. P. Pyrogen fever and prostaglandin-like activity in cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):41–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Saxena P. N. Prostaglandins, endotoxin and lipid A on body temperature in rats. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):601–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P., Di Luzio N. R. Endotoxin induced hypothermia and tolerance in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Dec;129(3):724–726. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer G. G., Rietschel E. T. Lipid A-induced tolerance and hyperreactivity to hypothermia in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):357–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.357-368.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandasamy S. B., Kirlin W. G., Kaul P. N. Prostacyclin-induced hypothermia: involvement of central histamine H2-receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Jun 1;28(22):2553–2560. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90598-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Shimizu T., Hayaishi O. Effects of prostaglandin D2 on membrane potential in neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells as determined with a cyanine dye. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 12;98(3):648–655. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laburn H., Mitchell D., Rosendorff C. Effects of prostaglandin antagonism on sodium arachidonate fever in rabbits. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):559–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuszek M., Ishikawa Y. Effects of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine and 6-hydroxydopamine on fever response in conscious rats. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm. 1981 Oct;33(3):305–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp-Dormston W. K., Siegert R. Prostaglandins of the E and F series in rabbit cerebrospinal fluid during fever induced by Newcastle disease virus, E. coli-endotoxin, or endogenous pyrogen. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun 19;159(4):279–284. doi: 10.1007/BF02123737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prashker D., Wardlaw A. C. Temperature responses of mice to Escherichia coli endotoxin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Feb;52(1):36–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prazma J., Orr J. L., Kidwell S. A. Device for nonstressful restraining of rats and guinea pigs. Physiol Behav. 1980 Jul;25(1):155–156. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(80)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Mizuno N., Amano T., Hayaishi O. Prostaglandin D2, a neuromodulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6231–6234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Yamamoto S., Hayaishi O. Purification and properties of prostaglandin D synthetase from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5222–5228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splawiński J. A., Górka Z., Zacny E., Kaluza J. Fever produced in the rat by intracerebral E. coli endotoxin. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Mar 11;368(1-2):117–123. doi: 10.1007/BF01063463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splawiński J. A., Zacny E., Górka Z. Fever in rats after intravenous E. coli endotoxin administration. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Mar 11;368(1-2):125–128. doi: 10.1007/BF01063464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spławiński J. A., Górka Z., Zacny E., Wojtaszek B. Hyperthermic effects of arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E2 and F2alpha in rats. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Apr 25;374(1):15–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00585692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T. Prosaglandin E1 fever induced in rabbits. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):163–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. C., Boorman L., Reid R. Assay of endotoxin by the hypothermic response of mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Apr;52(2):198–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Shimizu T., Iguchi S., Wakatsuka H., Hayashi M., Hayaishi O. An NADP-linked prostaglandin D dehydrogenase in swine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1779–1782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. W., Rudy T. A., Yaksh T. L., Viswanathan C. T. An extensive exploration of the rat brain for sites mediating prostaglandin-induced hyperthermia. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 21;120(2):251–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90904-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Miert A. S., Frens J. The reaction of different animal species to bacterial pyrogens. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1968;15(6):532–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0442.1968.tb00456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


