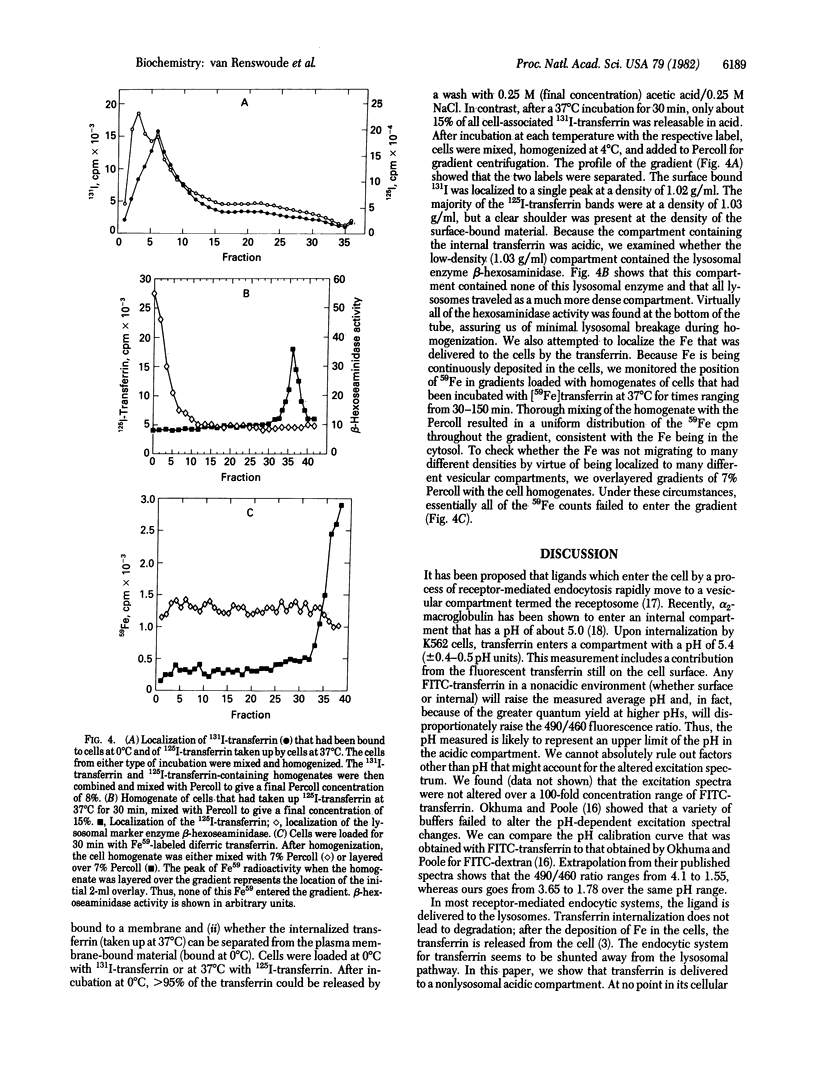
Abstract
At physiological temperature, the Fe-carrier transferrin is taken up by K562 human erythroleukemia cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis. Both ligand (now minus Fe) and receptor recycle back to the cell surface where the receptor is rapidly reutilized. After endocytosis, transferrin becomes transiently lodged within an acidic compartment inside the cell, as judged by the changed spectral characteristics and quantum yield of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled transferrin that is cell-associated at 37 degrees C. Upon binding to transferrin, anti-fluorescein antibody strongly quenches the emission of the fluorescein-labeled residues on the protein and is used to assess whether the transferrin is at the cell surface (incubation at 0 degrees C) or mainly internalized into the cell (incubation at 37 degrees C). Using Percoll gradient fractionation of postnuclear supernatants, we show that the acidic compartment is not the lysosomal compartment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Listowsky I. Iron transport and storage proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:357–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Morell A. G. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):99–128. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges K., Harford J., Ashwell G., Klausner R. D. Fate of receptor and ligand during endocytosis of asialoglycoproteins by isolated hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):350–354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: insights from the lipoprotein receptor system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3330–3337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Noriega A., Grubb J. H., Talkad V., Sly W. S. Chloroquine inhibits lysosomal enzyme pinocytosis and enhances lysosomal enzyme secretion by impairing receptor recycling. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):839–852. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Mintz B. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin in developmentally totipotent mouse teratocarcinoma stem cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3245–3252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin D. E., Voss E. W., Jr Fluorescein. Hapten and antibody active-site probe. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):208–213. doi: 10.1021/bi00778a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. H., Huebers H., Finch C. A. Differences between the binding sites for iron binding and release in human and rat transferrin. Blood. 1978 Dec;52(6):1219–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Octave J. N., Schneider Y. J., Crichton R. R., Trouet A. Transferrin protein and iron uptake by isolated rat erythroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 11;137(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80328-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Octave J. N., Schneider Y. J., Crichton R. R., Trouet A. Transferrin uptake by cultured rat embryo fibroblasts. The influence of temperature and incubation time, subcellular distribution and short-term kinetic studies. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):611–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Octave J. N., Schneider Y. J., Hoffmann P., Trouet A., Crichton R. R. Transferrin protein and iron uptake by cultured rat fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Willingham M. C. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of hormones in cultured cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:239–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Schlesinger P. H., Sigardson E., Rodman J. S., Lee Y. C. Receptor-mediated pinocytosis of mannose glycoconjugates by macrophages: characterization and evidence for receptor recycling. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer C. J., Ashwell G. Studies on a mammalian hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. Evidence for receptor recycling in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3008–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan A. L., Grasso J. A., Weintraub L. R. Micropinocytosis of transferrin by developing red cells: an electron-microscopic study utilizing ferritin-conjugated transferrin and ferritin-conjugated antibodies to transferrin. Blood. 1976 Jan;47(1):133–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tycko B., Maxfield F. R. Rapid acidification of endocytic vesicles containing alpha 2-macroglobulin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Van den Berghe H. Uptake and degradation of alpha2-macroglobulin-protease complexes in human cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I. The receptosome: an intermediate organelle of receptor mediated endocytosis in cultured fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





