Abstract
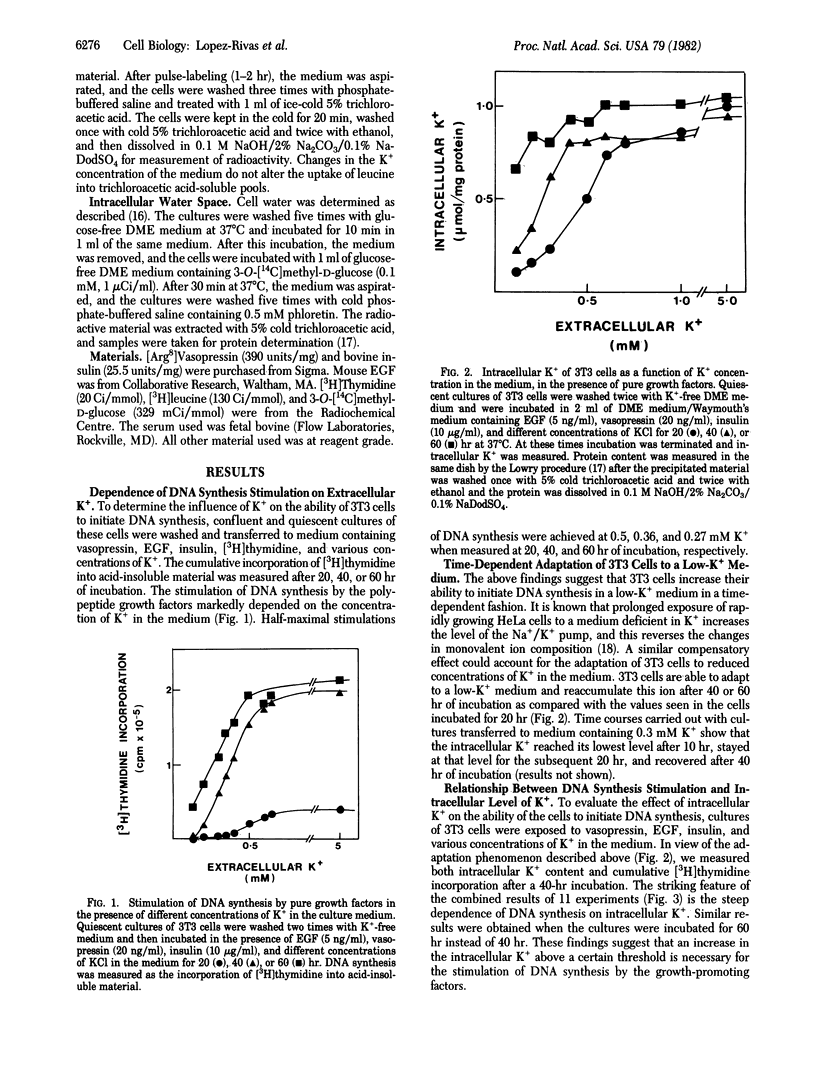
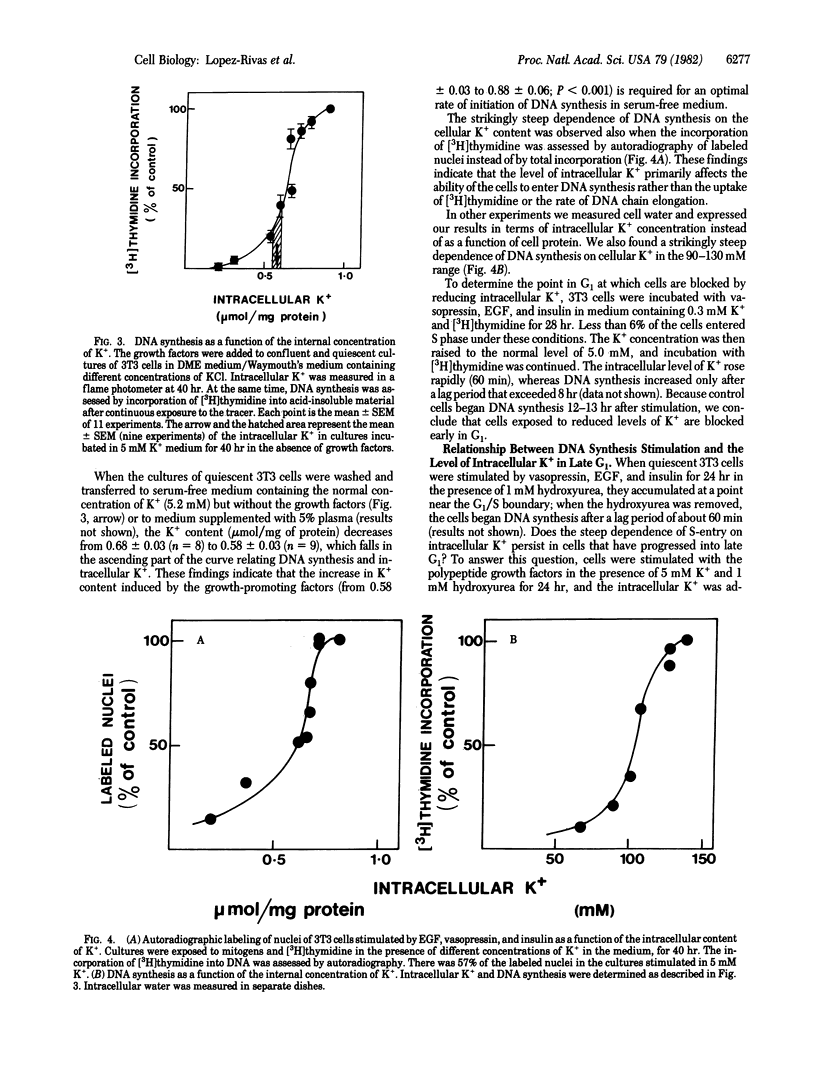
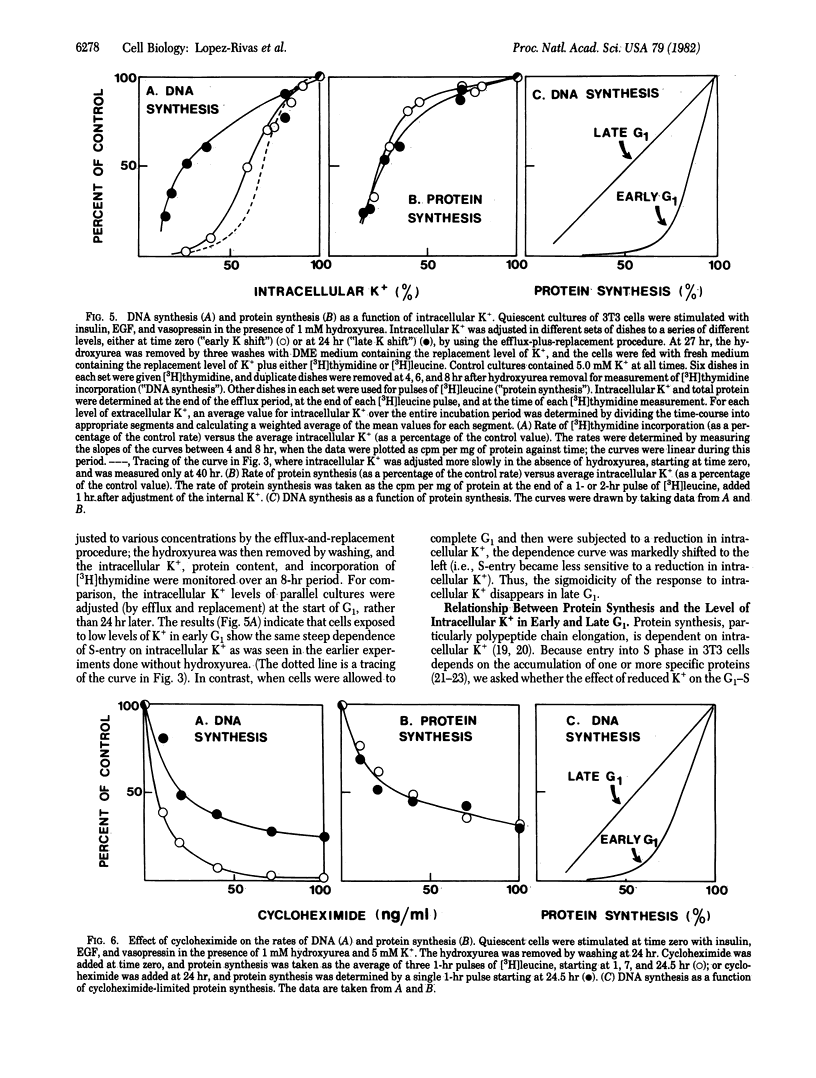
The stimulation of DNA synthesis in cultures of Swiss 3T3 cells by vasopressin, epidermal growth factor, and insulin added in serum-free medium is strikingly dependent on the intracellular K+ content or concentration. The relationship between these parameters is sigmoid; DNA synthesis commences only when the intracellular K+ increases above a certain threshold level (0.56 mumol/mg of protein; 90 mM). Addition of K+ to K+- depleted cultures reverses the block on DNA synthesis after a lag period of at least 8 hr. The sigmoid dependence of DNA synthesis on intracellular K+ is generated in early G1 phase rather than at the G1/S boundary. The effects of K+ on the G1-S transition are, at least in part, exerted through its control of protein synthesis. In serum-free medium, the K+ content is close to the threshold required for allowing a mitogenic response. The findings suggest that a small change in the intracellular K+ level can influence the ability of these cells to initiate DNA synthesis in serum-free medium.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R., Rozengurt E. An 18,000 molecular weight polypeptide induces early events and stimulates DNA synthesis in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4555–4559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendler T., Godefroy-Colburn T., Yu S., Thach R. E. The role of mRNA competition in regulating translation. III. Comparison of in vitro and in vivo results. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11755–11761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. F. Continuous protein synthesis is required to maintain the probability of entry into S phase. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn F., Lubin M. Inhibition of elongation steps of protein synthesis at reduced potassium concentrations in reticulocytes and reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7798–7803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Phorbol ester stimulation of Na influx and Na-K pump activity in Swiss 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):433–441. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz C. N., Nathan D. G., Scher C. D. Intracellular univalent cations and the regulation of the BALB/c-3T3 cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):51–56. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Topp W. C., Ozanne B. Simian virus 40 induces the production of a polypeptide transforming factor(s). Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):484–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90455-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F., Pariza M. W., Becker J. E., Potter V. R. A method using 3-O-methyl-D-glucose and phloretin for the determination of intracellular water space of cells in monolayer culture. Anal Biochem. 1975 Oct;68(2):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90649-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter M. L., Lubin M. Control of protein synthesis in human fibroblasts by intracellular potassium. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 15;105(2):223–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin M. Control of growth by intracellular potassium and sodium concentrations is relaxed in transformed 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 16;97(3):1060–1067. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza S. A., Wigglesworth N. M., Pohjanpelto P., Rozengurt E. Na entry and Na-K pump activity in murine, hamster, and human cells--effect of monensin, serum, platelet extract, and viral transformation. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Apr;103(1):17–27. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza S. A., Wigglesworth N. M., Rozengurt E. Vasopressin rapidly stimulates Na entry and Na-K pump activity in quiescent cultures of mouse 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Oct;105(1):153–162. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierzejewski K., Rozengurt E. Vitamin B12 enhances the stimulation of DNA synthesis by serum in resting cultures of 3T6 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1977 May;106(2):394–397. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Rozengurt E. Cyclic AMP stimulation of Na-K pump activity in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Aug;112(2):273–280. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack L. R., Tate E. H., Cook J. S. Turnover and regulation of Na-K-ATPase in HeLa cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Nov;241(5):C173–C183. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.5.C173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossow P. W., Riddle V. G., Pardee A. B. Synthesis of labile, serum-dependent protein in early G1 controls animal cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4446–4450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Gelehrter T. D., Legg A., Pettican P. Melittin stimulates Na entry, Na-K pump activity and DNA synthesis in quiescent cultures of mouse cells. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):781–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Serum rapidly stimulates ouabain-sensitive 86-RB+ influx in quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4492–4495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Legg A., Pettican P. Vasopressin stimulation of mouse 3T3 cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Legg A., Strang G., Courtenay-Luck N. Cyclic AMP: a mitogenic signal for Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4392–4396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in quiescent cultured cells: exogenous agents, internal signals, and early events. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1980;17:59–88. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152817-1.50007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman M. H., Dewey W. C., Highfield D. P. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in synchronized Chinese hamster cells treated in G1 with cycloheximide. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jul;67(1):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90630-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Rozengurt E. Serum stimulates the Na+,K+ pump in quiescent fibroblasts by increasing Na+ entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5560–5564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper J. T., Zorgniotti F., Mills B. Potassium transport and content during G1 and S phase following serum stimulation of 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):429–440. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick E. T., Lane L. K., Schwartz A. Biochemical mechanism of the sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:397–411. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



