Abstract
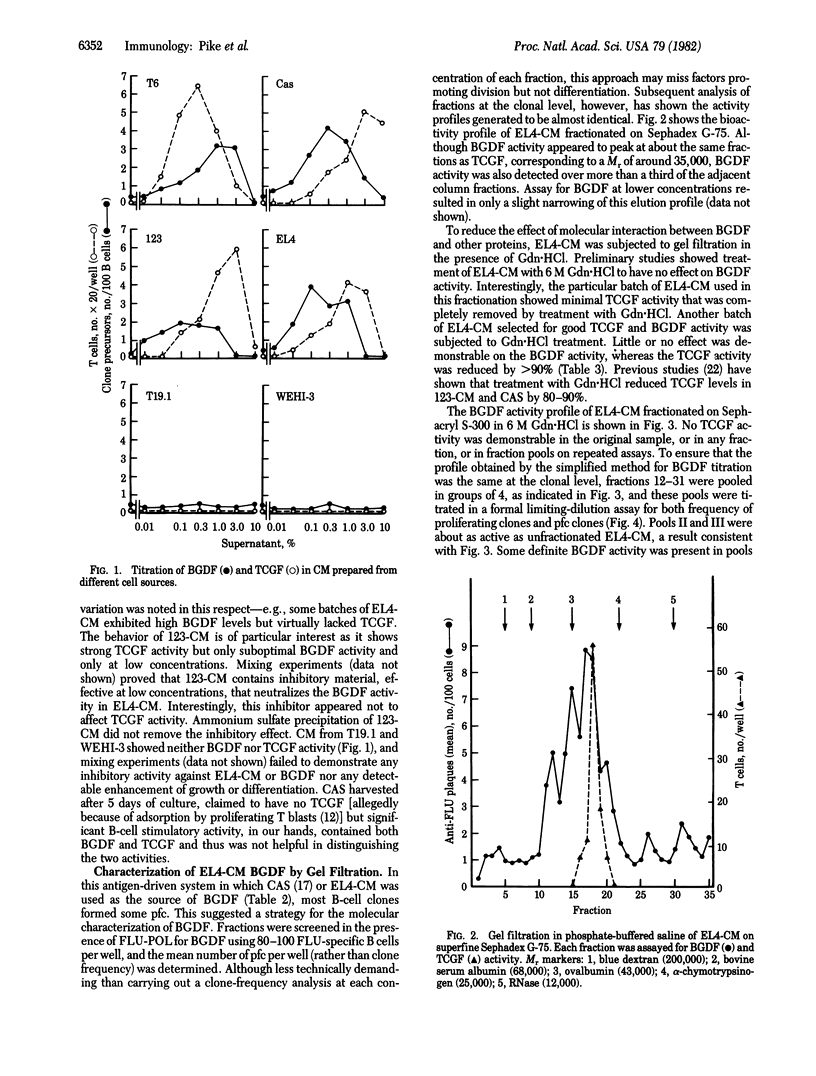
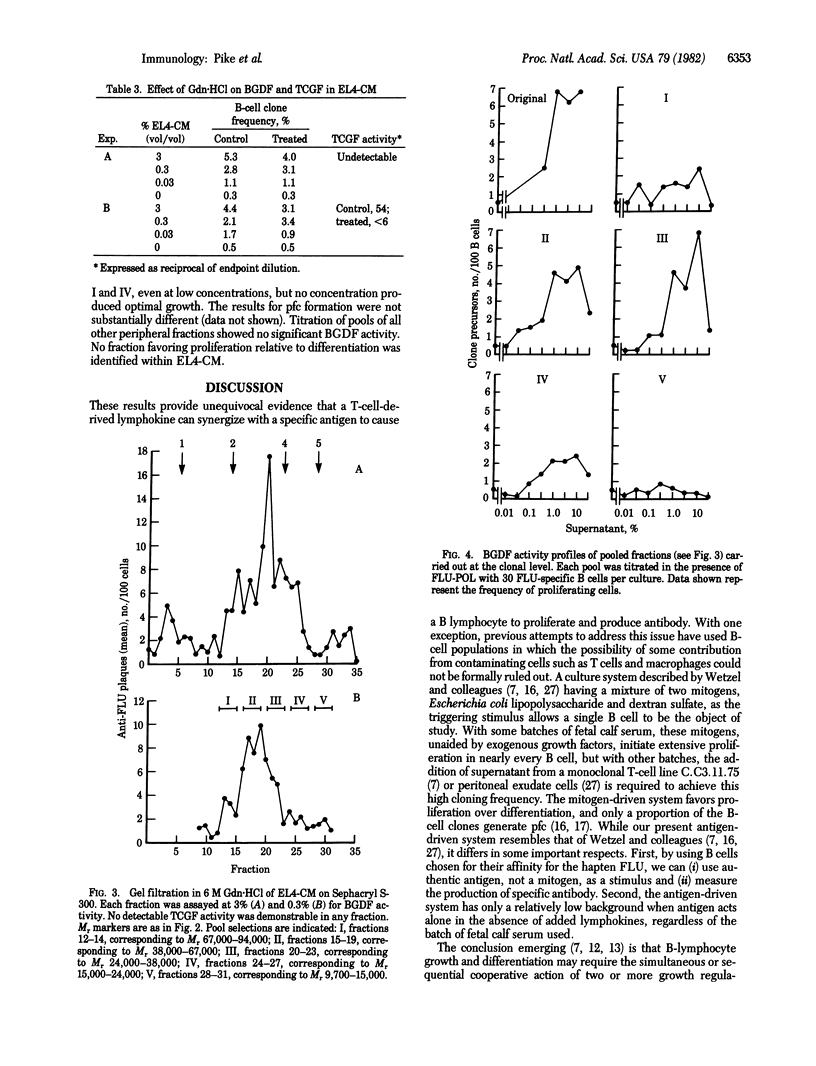
Hapten-specific B lymphocytes reactive to fluorescein were prepared from mouse spleen, placed singly in 10-microliters culture wells, and stimulated with fluorescein-polymerized flagellin in the presence of conditioned media (CM) from various concanavalin A-stimulated cloned T-cell tumors or hybridomas. Antigen plus appropriate CM triggered 5-9% of the B cells into both clonal proliferation and differentiation into antibody-forming cells. Antigen alone stimulated 0.5-0.8% of B cells and CM alone stimulated less than 0.1%. This bioactivity was termed B-cell growth and differentiation factor(s) (BGDF). Four CM rich in T-cell growth factor (TCGF)--namely, CM from spleen and the lines EL4, T6, and 123--contained BGDF. The lines T19.1 and WEHI-3 lacked BGDF and TCGF. Four lines of evidence suggested that BGDF and TCGF were distinct molecules. First, the BGDF/TCGF ratios in the various CM varied. Second, on gel filtration, TCGF eluted as a sharp peak corresponding to a Mr of about 35,000, whereas BGDF eluted over a range corresponding to a Mr of 25,000-60,000. Third, the activity of TCGF in EL4-CM was markedly reduced by treatment with guanidine HCl while BGDF activity was not. Fourth, BGDF showed more heterogeneity than TCGF on hydrophobic chromatography. All CM or fractions active in promoting B-cell division also promoted differentiation to antibody-forming cells. These results provide unequivocal evidence that antigen and a T-cell product can synergize to directly activate a single B lymphocyte.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark-Lewis I., Schrader J. W. Biochemical characterization of regulatory factors derived from T cell hybridomas and spleen cells. I. Separation of T cell growth factor and T cell replacing factor from granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):168–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Benjamin W. R., Hilfiker M. L., Howard M., Farrar W. L., Fuller-Farrar J. The biochemistry, biology, and role of interleukin 2 in the induction of cytotoxic T cell and antibody-forming B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:129–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. II. The cellular source of potentiating mediator(s). J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):143–155. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann M. K. Macrophages and T cells control distinct phases of B cell differentiation in the humoral immune response in vitro. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2076–2081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Farrar J., Hilfiker M., Johnson B., Takatsu K., Hamaoka T., Paul W. E. Identification of a T cell-derived b cell growth factor distinct from interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):914–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland J. I., Kincade P. W., Moore M. A. Regulation of B-lymphocyte clonal proliferation by stimulatory and inhibitory macrophage-derived factors. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1420–1435. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Iscove N. N., Coutinho A. Two distinct factors are required for induction of T-cell growth. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):664–666. doi: 10.1038/283664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Graham S. D., Jr, Kushnir E., Leibson H. J., Roehm N., Kappler J. W. Nonspecific factors in B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:33–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Wilson J. W., Shortman K., Miller J. F., Stocker J. The nature of the cells generating B-lymphocyte colonies in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1976 May;88(1):107–116. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Pike B. L., Battye F. L. Mechanisms of clonal abortion tolerogenesis. II. Clonal behaviour of immature B cells following exposure to anti-mu chain antibody. Immunology. 1979 May;37(1):203–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Pike B. L., Battye F. L. Sequential use of hapten-gelatin fractionation and fluorescence-activated cell sorting in the enrichment of hapten-specific B llymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Mar;8(3):151–157. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Pike B. L. Improved procedure for the fraction and in vitro stimulation of hapten-specific B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Pike B. L. Single cell studies on the antibody-forming potential of fractionated, hapten-specific B lymphocytes. Immunology. 1976 Feb;30(2):189–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike B. L., Jennings G., Shortman K. A simple semi-automated plaque method for the detection of antibody-forming cell clones in microcultures. J Immunol Methods. 1982;52(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puré E., Isakson P. C., Takatsu K., Hamaoka T., Swain S. L., Dutton R. W., Dennert G., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Induction of B cell differentiation by T cell factors. I. Stimulation of IgM secretion by products of a T cell hybridoma and a T cell line. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1953–1958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpl A., Wecker E. A third signal in B cell activation given by TRF. Transplant Rev. 1975;23:176–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Arnold B., Clark-Lewis I. A con A-stimulated T-cell hybridoma releases factors affecting haematopoietic colony-forming cells and B-cell antibody responses. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):197–199. doi: 10.1038/283197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Clark-Lewis I. T cell hybridoma-derived regulatory factors. I. Production of T cell growth factor following stimulation by concanavalin A. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1101–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W. Mechanism of activation of the bone marrow-derived lymphocyte. 3. A distinction between a macrophage-produced triggering signal and the amplifying effect on triggered B lymphocytes of allogeneic interactions. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1466–1480. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Wetzel G. D., Soubiran P., Dutton R. W. T cell replacing factors in the B cell response to antigen. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:111–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Pike B. L., Nossal G. J. Antibody production by single, hapten-specific B lymphocytes: an antigen-driven cloning system free of filler or accessory cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7702–7706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Gillis S., Marbrook J., Mochizuki D., Smith K. A. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. I. Purification of a class of murine lymphokines. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):849–861. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel G. D., Kettman J. R. Activation of murine B cells. II. Dextran sulfate removes the requirement for cellular interaction during lipopolysaccharide-induced mitogenesis. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jun;61(1):176–189. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel G. D., Kettman J. R. Activation of murine B lymphocytes. III. Stimulation of B lymphocyte clonal growth with lipopolysaccharide and dextran sulfate. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):723–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. D., Gaul S. L. Enhancement of the humoral response of T cell-depleted murine spleens by a factor derived from human monocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):925–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



