Abstract
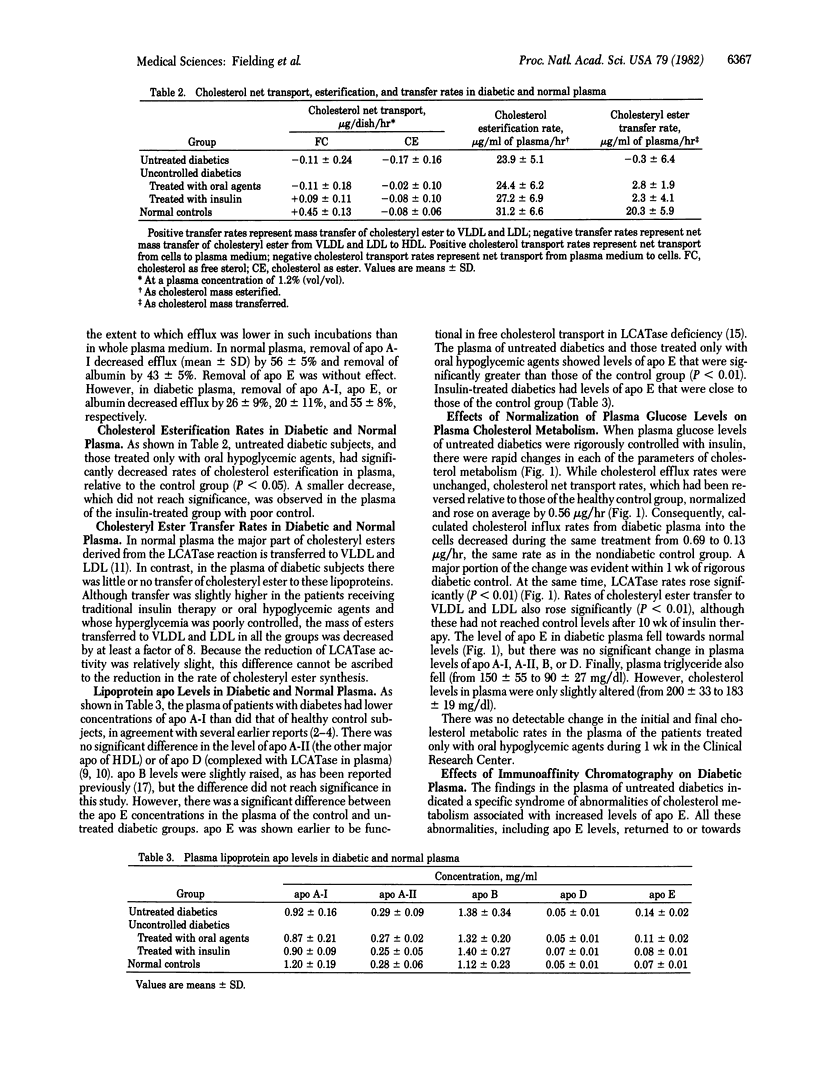
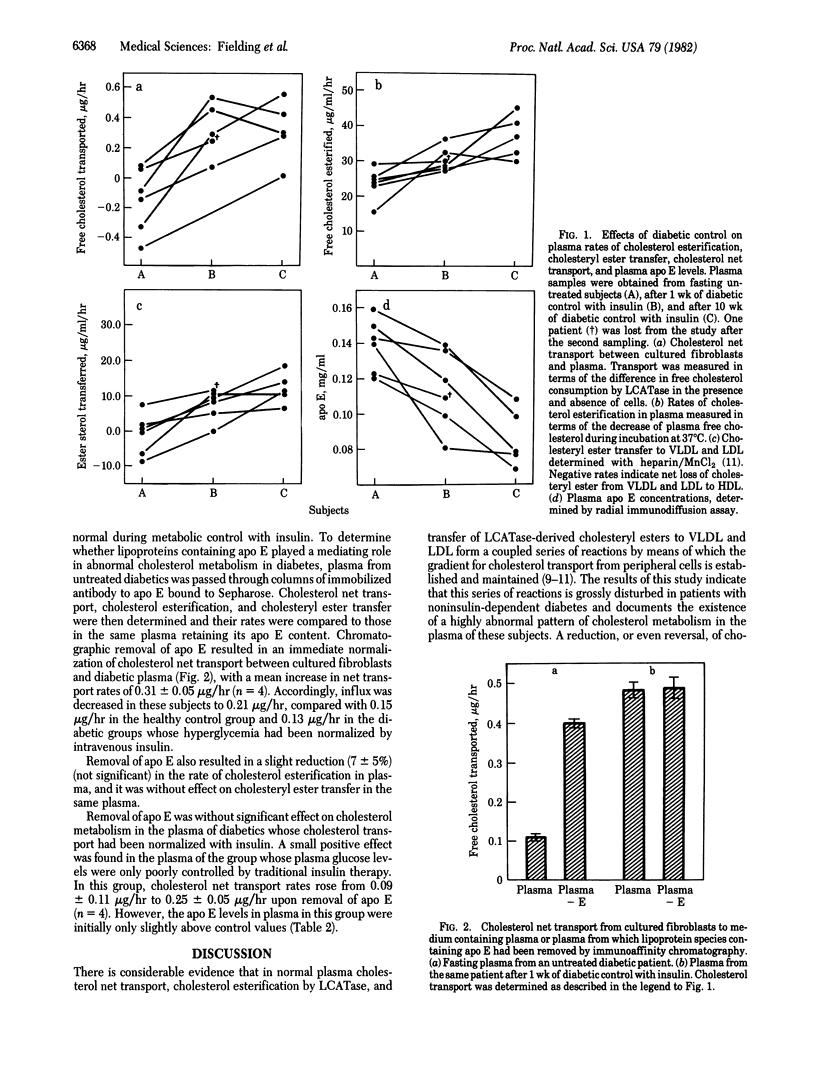
Plasma cholesterol metabolism in patients with poorly controlled noninsulin-dependent diabetes was characterized by inhibition of cholesterol net transport between cultured cells (fibroblasts) and plasma, inhibition of cholesterol esterification, and inhibition of cholesteryl ester transfer to low and very low density lipoproteins, relative to a normal control group. Plasma from these patients also contained a 2-fold higher level of apolipoprotein E (apo E). Effective control of hyperglycemia with insulin normalized both the parameters of plasma cholesterol metabolism and plasma levels of apo E. Removal of apo E by immunoaffinity chromatography normalized cell-to-plasma cholesterol transport but was without effect on the rate of cholesterol esterification or of cholesteryl ester transfer. These findings suggest that an inhibition in the chain of reactions by which cellular cholesterol is transferred in esterified form to low and very low density lipoproteins is associated with the appearance of an apo E-dependent "shunt" pathway, returning cholesterol from plasma back to the cells and so nullifying the normal cell-to-plasma transport pathway.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum C. B., Aron L., Sciacca R. Radioimmunoassay studies of human apolipoprotein E. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1240–1250. doi: 10.1172/JCI109975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn F. L., Pietri A., Raskin P. Plasma lipid and lipoprotein levels with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in type I diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Oct;95(4):426–431. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-4-426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Cholesterol transport between cells and body fluids. Role of plasma lipoproteins and the plasma cholesterol esterification system. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Mar;66(2):363–373. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Evidence for a lipoprotein carrier in human plasma catalyzing sterol efflux from cultured fibroblasts and its relationship to lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3911–3914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Regulation of human plasma lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activity by lipoprotein acceptor cholesteryl ester content. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2102–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding P. E., Fielding C. J. A cholesteryl ester transfer complex in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3327–3330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganda O. P. Pathogenesis of macrovascular disease in the human diabetic. Diabetes. 1980 Nov;29(11):931–942. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.11.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The LDL receptor defect in familial hypercholesterolemia. Implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Mar;66(2):335–362. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield M., Kolterman O., Olefsky J., Reaven G. M. Mechanism of hypertriglyceridaemia in diabetic patients with fasting hyperglycaemia. Diabetologia. 1980 Jun;18(6):441–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00261698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. New aspects of pathogenesis and diagnosis. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Mar;66(2):441–454. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kotite L., Vigne J. L., Kane J. P., Tun P., Phillips N., Chen G. C. Radioimmunoassay of human arginine-rich apolipoprotein, apoprotein E. Concentration in blood plasma and lipoproteins as affected by apoprotein E-3 deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1351–1362. doi: 10.1172/JCI109988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heider J. G., Boyett R. L. The picomole determination of free and total cholesterol in cells in culture. J Lipid Res. 1978 May;19(4):514–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V., Savage P. J., Bennion L. J., Bennett P. H. Lipoprotein composition in diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis. 1978 Jun;30(2):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(78)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Virella M. F., Stone P. G., Colwell J. A. Serum high density lipoprotein in diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1977 Aug;13(4):285–291. doi: 10.1007/BF01223267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcel Y. L., Vézina C., Emond D., Verdery R. B., Milne R. W. High density lipoprotein subfractions isolated by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography and their role in cholesteryl ester transfer to very low density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1981 Nov;22(8):1198–1205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikkilä E. A., Kekki M. Plasma triglyceride transport kinetics in diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1973 Jan;22(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Birge C., Miller J. P., Kessler G., Santiago J. Apolipoprotein B levels and altered lipoprotein composition in diabetes. Diabetes. 1974 Oct;23(10):827–834. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.10.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T., Norum K. R. Determination of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransfer in human blood plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamborlane W. V., Sherwin R. S., Genel M., Felig P. Restoration of normal lipid and aminoacid metabolism in diabetic patients treated with a portable insulin-infusion pump. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1258–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



