Abstract
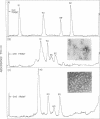
The amino-terminal amino acid sequences of the four major peptides (Mr 41,000, 50,000, 55,000, and 62,000) present in purified preparations of Electrophorus electricus nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AcChoR) have been determined for 24 cycles by automated sequence analysis procedures yielding four unique polypeptide sequences. The sequences showed a high degree of similarity, having identical residues in a number of positions ranging between 37% and 50% for specific pairs of subunits. Comparison of the sequences obtained with those of the subunits of similar molecular weight from Torpedo californica AcChoR revealed an even higher degree of homology (from 46% to 71%) for these two highly diverged species. Simultaneous sequence analysis of the amino termini present in native, purified Electrophorus AcChoR showed that these four related sequences were the only ones present and that they occur in a ratio of 2:1:1:1, with the smallest subunit ("alpha 1") being present in two copies. Genealogical analysis suggests that the subunits of both Torpedo and Electrophorus AcChoRs derive from a common ancestral gene, the divergence having occurred early in the evolution of the receptor. This shared ancestry and the very early divergence of the four subunits, as well as the highly conserved structure of the AcChoR complex along animal evolution, suggest that each of the subunits evolved to perform discrete crucial roles in the physiological function of the AcChoR.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Changeux J. P., Heidmann T., Popot J. L., Sobel A. Reconstitution of a functional acetylcholine regulator under defined conditions. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 1;105(1):181–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80913-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T. R., Raftery M. A. Is experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis induced only by acetylcholine receptors? J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1130–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Raftery M. A. Immunological comparison of acetylcholine receptors and their subunits from species of electric ray. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Dunn S. M., Raftery M. A. Functional stability of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Effects of protease treatment. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 2;21(5):893–899. doi: 10.1021/bi00534a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Fumagalli G., Scotti A., Brigonzi A., Sher E., Morgutti M., Clementi F. Myasthenia gravis: an example of receptor disease. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1980;21:473–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B. Myasthenia gravis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 19;298(3):136–142. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801192980305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M., Racker E. Reconstitution of carbamylcholine-dependent sodium ion flux and desensitization of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6660–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Ros J. M., Paraschos A., Martinez-Carrion M. Reconstitution of functional membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from isolated Torpedo californica receptor protein and electroplax lipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1796–1800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess G. P., Pasquale E. B., Walker J. W., McNamee M. G. Comparison of acetylcholine receptor-controlled cation flux in membrane vesicles from Torpedo californica and Electrophorus electricus: chemical kinetic measurements in the millisecond region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):963–967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. New protein sequenator with increased sensitivity. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):523–525. doi: 10.1126/science.7352258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Anholt R., Einarson B., Engel A., Osame M., Montal M. Purification of acetylcholine receptors, reconstitution into lipid vesicles, and study of agonist-induced cation channel regulation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8340–8350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Cooper J., Tzartos S. Acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo and Electrophorus have similar subunit structures. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1454–1458. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Walter B., Einarson B. Immunochemical similarities between subunits of acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo, Electrophorus, and mammalian muscle. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4470–4480. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Bernhard S. A. Structure and symmetry of oligomeric enzymes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1973;4:257–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.02.060173.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Hartig P. R., Raftery M. A. Correlation of polypeptide composition with functional events in acetylcholine receptor-enriched membranes from Torpedo californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6265–6269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Raftery M. A. Direct spectroscopic studies of cation translocation by Torpedo acetylcholine receptor on a time scale of physiological relevance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Anholt R., Lindstrom J., Montal M. Reconstitution of purified acetylcholine receptors with functional ion channels in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):3057–3061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Quast U. Functional acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo marmorata in planar membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):3052–3056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. A simple assay for the study of solubilized acetylcholine receptors. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Raftery M. A. Topographic studies of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor subunits as a transmembrane complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Lindstrom J. M. Monoclonal antibodies used to probe acetylcholine receptor structure: localization of the main immunogenic region and detection of similarities between subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Moore H. P., Raftery M. A. Quantitation of cation transport by reconstituted membrane vesicles containing purified acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):775–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Raftery M. A. Carbamylcholine-induced rapid cation efflux from reconstituted membrane vesicles containing purified acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):26–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Raftery M. A. Reconstitution of acetylcholine receptor function using purified receptor protein. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):694–701. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]