Abstract
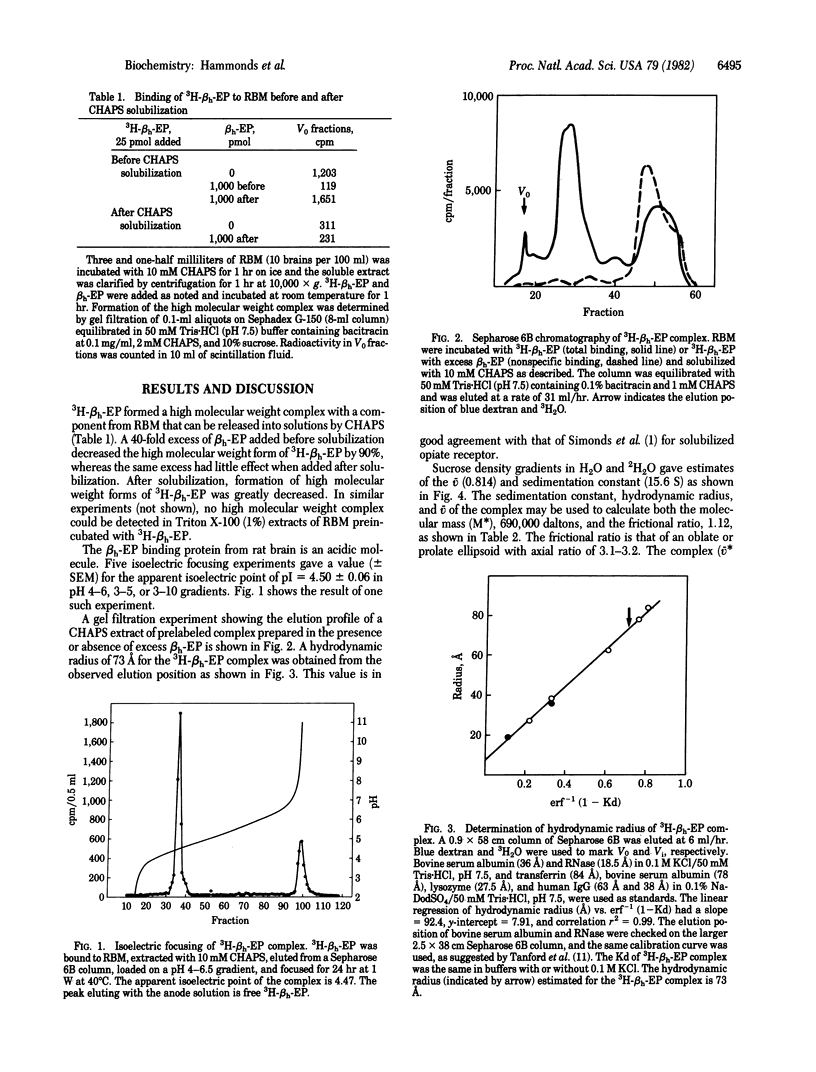
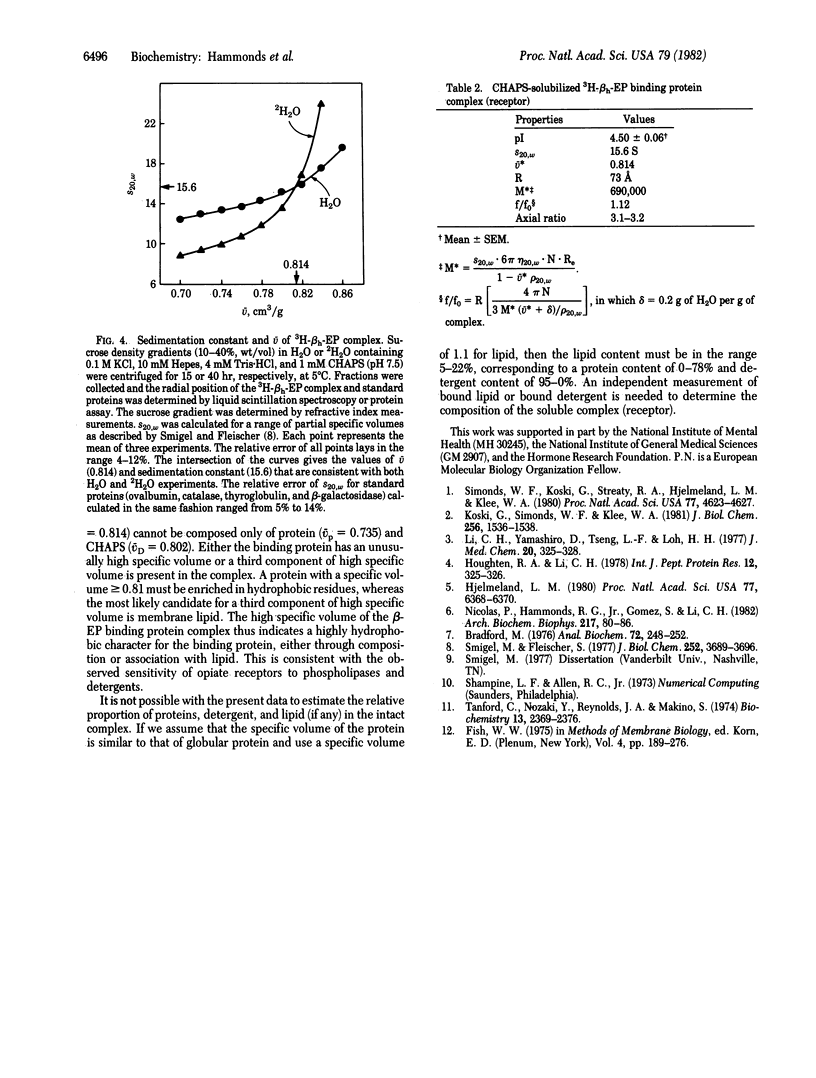
Rat brain membranes (RBM) bind beta-endorphin with high affinity and specificity. We report herein the identification of a high molecular weight beta-endorphin complex (receptor) in extracts of RBM preincubated with tritiated beta-endorphin, by using the zwitterionic detergent 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate (CHAPS). Upon isoelectric focusing, this complex gives a single peak with an isoelectric point (+/- SEM) of 4.50 +/- 0.06. Sucrose density gradient experiments in H2O and 2H2O yield effective partial specific volume (v = 0.814 cm3/g and sedimentation constant s20,w = 15.6 S. Gel filtration yields an estimate of the hydrodynamic radius of 73 A. The corresponding frictional ratio of 1.12 is consistent with an elliptical spheroid with an axial ratio of 3.1-3.2. The molecular mass of the complex is estimated to be 690,000 daltons. The v of the complex is greater than that of CHAPS or most globular proteins.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmeland L. M. A nondenaturing zwitterionic detergent for membrane biochemistry: design and synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6368–6370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Li C. H. Preparation and properties of tritiated human beta-endorphin with high specific radioactivity. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Nov;12(5):325–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski G., Simonds W. F., Klee W. A. Guanine nucleotides inhibit binding of agonists and antagonists to soluble opiate receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1536–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Tseng L. F., Loh H. H. Synthesis and analgesic activity of human beta-endorphin. J Med Chem. 1977 Mar;20(3):325–328. doi: 10.1021/jm00213a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas P., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Gomez S., Li C. H. Beta-endorphin: thermodynamics of the binding reaction with rat brain membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Aug;217(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Koski G., Streaty R. A., Hjelmeland L. M., Klee W. A. Solubilization of active opiate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4623–4627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smigel M., Fleischer S. Characterization of triton X-100-solubilized prostaglandin E binding protein of rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3689–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Nozaki Y., Reynolds J. A., Makino S. Molecular characterization of proteins in detergent solutions. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2369–2376. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



