Abstract
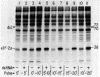
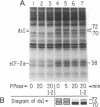
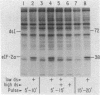
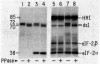
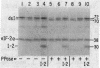
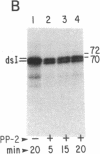
Protein synthesis initiation in reticulocyte lysates is inhibited by low concentrations (1-20 ng/ml) of double-stranded RNA (ds RNA) due to the activation of a ds RNA-dependent cAMP-independent protein kinase (ds I) that phosphorylates the α subunit of the eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2. In lysates, ds I is present in the latent inactive form and is associated with the ribosome complement. Latent ds I is solubilized by extraction with high-salt buffers and can be purified in its latent form. Activation of purified latent ds I requires ds RNA and ATP and is accompanied by the ds RNA-dependent autophosphorylation of a polypeptide doublet of 70,000 and 72,000 daltons (“70k/72k”), which represent different phosphorylated states of the same polypeptide. These are phosphorylated in the sequence 70k→72k; increased phosphorylation of 72k is associated with increased ds I activation. Lysates (or Sepharose 6B ribosomes) treated with ds RNA display a similar ds I phosphoprotein profile, and this is accompanied by the phosphorylation of endogenous eIF-2α (38,000 daltons). Delayed 32P pulses in ds RNA-inhibited lysates indicate that the phosphates on ds I and eIF-2α turn over. Under defined conditions, activated ds I in lysates is selectively dephosphorylated by endogenous protein phosphatase(s), and this is accompanied by the dephosphorylation of eIF-2α. Similarly, purified activated ds I is rapidly dephosphorylated by unfractionated lysate protein phosphatase(s) and by type 2 protein phosphatase but not by type 1 protein phosphatase. The dephosphorylation of ds I occurs in the sequence 72k→70k and is correlated with ds I inactivation. The heat-stable protein phosphatase inhibitor-2, which selectively blocks type 1 protein phosphatase, does not significantly affect the dephosphorylation of ds I by type 2 protein phosphatase or by unfractionated lysate phosphatases. The data support the conclusion that a ds I phosphatase activity with type 2 characteristics is involved in the regulation of ds I activity.
Keywords: inhibition of protein chain initiation, phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2α, translational control
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniw J. F., Nimmo H. G., Yeaman S. J., Cohen P. Comparison of the substrate specificities of protein phosphatases involved in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):423–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1620423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. T., Condon G. D., Cohen P. Evidence for the involvement of protein phosphatase-1 in the regulation of metabolic processes other than glycogen metabolism. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 1;92(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80723-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Das A., Ghosh-Dastidar P., Ralston R. O., Yaghmai B., Roy R., Gupta N. K. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes. Purification and characterization of a double-stranded RNA-dependent protein synthesis inhibitor from reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6491–6495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst V., Levin D. H., Leroux A., London I. M. Site-specific phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2 by the heme-regulated and double-stranded RNA-activated eIF-2 alpha kinases from rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst V., Levin D. H., London I. M. Evidence that glucose 6-phosphate regulates protein synthesis initiation in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7163–7172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst V., Levin D. H., London I. M. In situ phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 in reticulocyte lysates inhibited by heme deficiency, double-stranded RNA, oxidized glutathione, or the heme-regulated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2118–2122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. The regulation of glycogen metabolism. Purification and properties of protein phosphatase inhibitor-2 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):195–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosfeld H., Ochoa S. Purification and properties of the double-stranded RNA-activated eukaryotic initiation factor 3 kinase from rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6526–6530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Mendelewski J. Additional evidence that the hemin-controlled translational repressor from rabbit reticulocytes is a protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90340-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. L., Glinsmann W. H. Separation and characterization of two phosphorylase phosphatase inhibitors from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):419–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T., Ehrenfeld E. Cytoplasm from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells inhibits cell-free haemoglobin synthesis. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):91–94. doi: 10.1038/newbio230091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T., Vanderhoff G., London I. M. Control of globin synthesis: the role of heme. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Robertson H. D. The characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded ribonucleic acid in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. The use of hexose phosphates to support protein synthesis and generate [gamma-32P]ATP in reticulocyte lysates. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 15;93(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G., Cimadevilla J. M., Hardesty B. Specificity of the protein kinase activity associated with the hemin-controlled repressor of rabbit reticulocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroux A., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha in intact reticulocytes and reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Petryshyn R., London I. M. Characterization of double-stranded-RNA-activated kinase that phosphorylates alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2 alpha) in reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):832–836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Petryshyn R., London I. M. Characterization of purified double-stranded RNA-activated eIF-2 alpha kinase from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7638–7641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis: activation by double-stranded RNA of a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1121–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., Ranu R. S., Ernst V., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates: phosphorylation of methionyl-tRNAf binding factor by protein kinase activity of translational inhibitor isolated from hemedeficient lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3112–3116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo G. A., Cohen P. The regulation of glycogen metabolism. Purification and characterisation of protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):341–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Levin D. H., London I. M. Purification and characterization of a latent precursor of a double-stranded RNA dependent protein kinase from reticulocyte lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1190–1198. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90545-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: purification and initial characterization of the cyclic 3':5'-AMP independent protein kinase of the heme-regulated translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4349–4353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: purification and initial characterization of the double stranded RNA activated protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 17;97(1):252–262. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Hemmings B. A., Cohen P., Goris J., Merlevede W. The MgATP-dependent protein phosphatase and protein phosphatase 1 have identical substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):197–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Ranu R. S., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: purification and characterization of heme-reversible translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3654–3658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]