Background: Saccharomyces cerevisiae responds to increased cytosolic iron through changes in the activity of the transcriptional activator Yap5.
Results: A genetic screen identified a mutation in SSQ1 that prevented Yap5-dependent transcription.
Conclusion: Reduced levels of proteins required for mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster synthesis prevented Yap5-dependent transcription.
Significance: The transcriptional response to low iron or high cytosolic iron is dependent on iron-sulfur clusters.
Keywords: Iron, Iron-Sulfur Protein, Mitochondria, Transcription, Yeast
Abstract
Yeast respond to increased cytosolic iron by activating the transcription factor Yap5 increasing transcription of CCC1, which encodes a vacuolar iron importer. Using a genetic screen to identify genes involved in Yap5 iron sensing, we discovered that a mutation in SSQ1, which encodes a mitochondrial chaperone involved in iron-sulfur cluster synthesis, prevented expression of Yap5 target genes. We demonstrated that mutation or reduced expression of other genes involved in mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster synthesis (YFH1, ISU1) prevented induction of the Yap5 response. We took advantage of the iron-dependent catalytic activity of Pseudaminobacter salicylatoxidans gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase expressed in yeast to measure changes in cytosolic iron. We determined that reductions in iron-sulfur cluster synthesis did not affect the activity of cytosolic gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase. We show that loss of activity of the cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly complex proteins or deletion of cytosolic glutaredoxins did not reduce expression of Yap5 target genes. These results suggest that the high iron transcriptional response, as well as the low iron transcriptional response, senses iron-sulfur clusters.
Introduction
Yeast respond to changes in the intracellular concentration of transition metal levels by altering transcription of genes that encode proteins required for metal acquisition, storage, or usage. Saccharomyces cerevisiae responds to iron deprivation by inducing the expression of about 20 genes collectively referred to as the iron regulon (for review, see Refs. 1 and 2). These genes encode cell surface and vacuolar elemental iron transporters, cell surface siderophore transporters, proteins involved in iron-independent metabolic pathways, and proteins that destabilize transcripts involved in iron storage and metabolism. The expression of these genes is regulated by the transcription factor Aft1 and to a lesser extent by the paralogous Aft2. Aft(s) reside in the cytosol and translocate into the nucleus in response to low iron where they occupy the promoters of iron regulon genes. Studies suggest that Aft1 responds to changes in mitochondrial iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster production and export, for which iron is an essential substrate (3). Defects in the assembly of cytosolic Fe-S cluster-containing proteins do not activate the iron regulon (4). The precise role of Fe-S clusters in regulating the iron regulon remains to be clarified, but it is thought that the cytosolic glutaredoxins Grx3 and Grx4, which can obtain Fe-S clusters independent of the cytosolic Fe-S machinery (5), may play a role in regulating Aft1 transcriptional activity (6, 7).
S. cerevisiae also respond to high iron conditions by activating the transcription factor Yap5. Yap5 is constitutively present in the nucleus, where it occupies the promoters of at least three genes (CCC1, TYW1, GRX4) (8–10). Most notably, CCC1, which encodes the vacuolar iron importer, plays a major role in regulating cytosolic iron concentration (8, 9). The activation domain of Yap5 contains 7 cysteines important for iron sensing as mutation of those cysteines reduces transcription. Iron is known to participate in redox reactions, which can affect cysteine sulfhydryls. We determined that Yap5 was not activated by oxygen radicals as H2O2 addition did not activate Yap5 transcription and high iron under anaerobic conditions activated Yap5 transcription (8).
We utilized a genetic screen to identify the mechanism of high iron induction of Yap5. We found that Yap5 activation is dependent on the mitochondrial production of Fe-S clusters as Yap5-dependent transcription does not occur in the absence of mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis. We showed that reductions in mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis do not decrease cytosolic iron levels. We also show that the cytosolic Fe-S assembly complex is not involved for Fe-S cluster dependent Yap5 activation.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Yeast Strains, Plasmids, and Culture Conditions
The wild type strains DY150 or DY1457 (W303 background) and deletion strains were used for most experiments. The Δccc1 and Δyfh1 strains were described previously (3, 11). The Δisu1 strain was generated in a DY150 background by PCR amplifying the deletion construct with the KanMX marker from the homozygous diploid deletion collection (Research Genetics, Stanford, CA). Deletion strains of Δgrx3Δgrx4 were derived from BY4742 (S288C background), and the GalDRE2 and GalNAR1 were gifts from Dr. Winge (University of Utah). The double deletion Δccc1Δyfh1 strain was generated by PCR amplification of the CCC1 deletion construct and recombination into the background strain. SSQ1 was deleted in DY1640 diploid cells by PCR amplification of the KanMX marker from the heterozygous diploid deletion collection (Research Genetics) and transformed with a plasmid containing MET3-SSQ1. Tetrads were dissected, and haploids with a SSQ1 deletion were isolated. The MET3-SSQ1 plasmid-expressing Δssq1 cells were crossed with Δccc1 cells to generate a Δssq1Δccc1 double deletion. All yeast strains used in this study are shown in Table 1. The complete minimal (CM)3 medium was composed of yeast nitrogen base without amino acids, dextrose, and the required amino acids. Dextrose was replaced by galactose as specified. Low iron media were made by adding 80 μm bathophenanthroline disulfonate (BPS) and the specified concentration of FeSO4 or ferrous ammonium sulfate. For anaerobic experiments, cells were grown in a BBLTM GasPakTM EZ anaerobic container system (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
TABLE 1.
Strains used in this study
| Yeast strain | Genotype | Source |
|---|---|---|
| DY150 | MATa ade2-1 his3-11 leu2-3.112 trp1-1 ura3-52 can1-100(oc) | Wild type |
| Δccc1 | MATa ade2-1 his3-11 leu2-3.112 trp1-1 ura3-52 can1-100(oc) Δccc1::HIS3 | Refs. 8 and 9 |
| Δccc1/FET3/FTR1 | MATa ade2-1 his3-11 leu2-3.112 trp1-1 ura3-52 can1-100(oc) Δccc1::HIS3 PGK1FET3/FTR1::ade2-1 FET3-lacZ::HO | Ref. 3 |
| Δisu1Δccc1 | MATa ade2-1 his3-11 leu2-3.112 trp1-1 ura3-52 can1-100(oc) Δisu1::KanMX Δccc1::HIS3 | This study |
| BY4742 | MATα his3Δ1, leu2Δ0, lys2Δ0, ura3Δ0 | Wild type |
| Δglr1 | MATα his3Δ1, leu2Δ0, lys2Δ0, ura3Δ0 Δglr1::KanMX | Ref. 8 |
| Δgrx3Δgrx4 | MATα his3Δ1, leu2Δ0, lys2Δ0, ura3Δ0 Δgrx3::LEU2 Δgrx4::KanMX | Ref. 6 |
| Δtrr1 | MATa ade2-1 his3-11 leu2-3.112 trp1-1 ura3-52 can1-100(oc) Δtrr1::HIS3 | Ref. 8 |
| Gal-DRE2 | MATa ura3-52 lys2-801(amber) ade2-101(ochre) trp1-Δ63 leu2-Δ1 GAL1-DRE2::HIS3 | Ref. 27 |
| Gal-NAR1 | MATa ura3-1 ade2-1 trp1-1 his3-11,15 leu2-3,112 GAL1-NAR1::HIS3 | Ref. 26 |
| Δyfh1 | MATa ade2-1 his3-11 leu2-3.112 trp1-1 ura3-52 can1-100(oc)Δyfh1::HIS3 MET3-YFH1 | Refs. 3 and 11 |
| Δssq1 | MATa ade2-1 his3-11 leu2-3.112 trp1-1 ura3-52 can1-100(oc)Δssq1::KanMX MET3-SSQ1 | This study |
| Δssq1Δccc1 | MATa ade2-1 his3-11 leu2-3.112 trp1-1 ura3-52 can1-100(oc)Δssq1::KanMX Δccc1::HIS3 MET3-SSQ1(URA3) | This study |
| Δyfh1Δccc1 | MATa ade2-1 his3-11 leu2-3.112 trp1-1 ura3-52 can1-100(oc)Δyfh1::HIS3 Δccc1::LEU2 MET3-YFH1(URA3) | This study |
Yeast Genetic Screen Designation
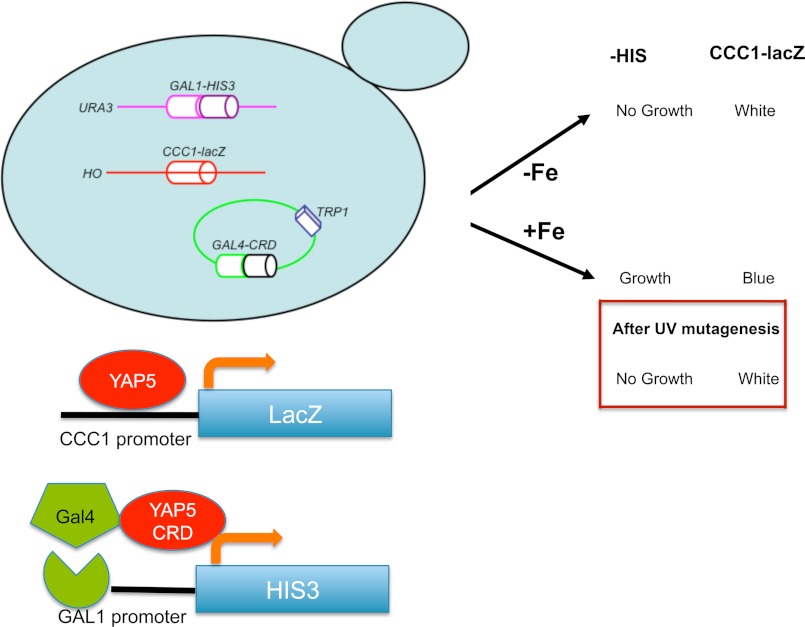
The parent strain is a Δccc1 strain in a DY1457 background with a KanMX marker. CCC1-lacZ was integrated into the genome at the HO locus, and a construct containing the GAL1 promoter (∼1000 up stream of GAL1 gene) fused to the HIS3 gene was integrated into the genome at the URA3 locus. A construct containing a GAL4-YAP5 chimera, which responds to iron (8), with a TRP1 marker was transformed into the parent strain. Cells were plated on 200 μm iron-containing plates and exposed to UV for 12 s. Candidates were selected by a β-galactosidase color assay and −HIS plate spot assay.
β-Galactosidase Assay
β-Galactosidase activity was measured by a kinetic assay (7). Protein determinations were performed using the bicinchoninic acid assay (Pierce), and enzyme activity is expressed as nmol/min/mg of protein. Blue color colony assays were performed by transferring fresh yeast colonies to a nitrocellulose membrane, cells were permeabilized by freeze/thaw in liquid nitrogen, and color was developed by adding X-gal overnight at 30 °C (12).
Total RNA Extraction and RT-PCR Assay
Total RNA was isolated from cells grown to mid-log phase using an Agilent RNA kit (Agilent). First-strand cDNA synthesis was performed using a SuperScript III kit from Invitrogen. Real-time PCR was performed using primers for the detection of CCC1 transcription (5′-tcggtggcggttatctactt-3′ and 5′-accacccacaacaaccattt-3′), primers for the detection of FET3 (5′-tca cag ttt cga tcc gga caa cca-3′ and 5′-tcc ac gaga aca aga ccc aaa cct-3′), and primers for the detection of TYW1 (5′-aac aaa tgg tgg cga aag ac-3′ and 5′-tgg atg aac atg cca aag aa-3′). Expression levels were normalized to the internal control CMD1, as described previously (8).
Western Blot Analysis
For Western blot assays, cell extracts were prepared by homogenization with glass beads in 25 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 50 mm NaCl lysate buffer with 1× protease inhibitor tablets (Roche) and 0.5 mm phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (Sigma-Aldrich). Mouse anti-FLAG antibody and mouse anti-PGK antibody were purchased from Invitrogen. Rabbit anti-Yap5 (1:500) was generated in our laboratory using purified Yap5 as an antigen. Mouse anti-carboxypeptidase Y (1:3000) was obtained from Mitosciences Inc. (Eugene, OR). Mouse anti-HIS-G (1:5000) was obtained from Invitrogen. Peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:5000) or goat anti-mouse IgG (1:5000) (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories) was used as secondary antibody. Western blots were developed using Western Lightning reagent (PerkinElmer Life Sciences).
Gentisate 1,2-Dioxygenase Assay
Gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (GDO) plasmid was a generous gift from Dr. Stolz from Stuttgart University, Germany. The gene was cloned into yeast vector pRS426 using SpeI and BamHI restriction sites, and its expression was under the control of ADH1 promoter. A FLAG tag was added to the carboxyl terminus of GDO. Plasmids were transformed into yeast cells, grown on suitable selective medium to exponential growth phase, and harvested by centrifugation. Transformed cells were washed with deionized water and lysed by glass bead agitation in a lysis buffer (25 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 50 mm NaCl, 0.5 mm phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (Sigma-Aldrich)). The cell lysates were then subjected to GDO activity assay as described previously (12). The assay mixture contained 20 mm Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) and 0.1 mm 2,3-dihydroxy-benzoic acid (gentisic acid) as substrate (Sigma-Aldrich). Absorbance was monitored at 340 nm, and enzyme activity was calculated using an extinction coefficient of 10.2 cm−1mm−1. The activity was expressed as nmol of substrate converted per minute per mg of protein.
RESULTS
A Genetic Screen for High Iron Sensing Identifies a Role for Fe-S Clusters
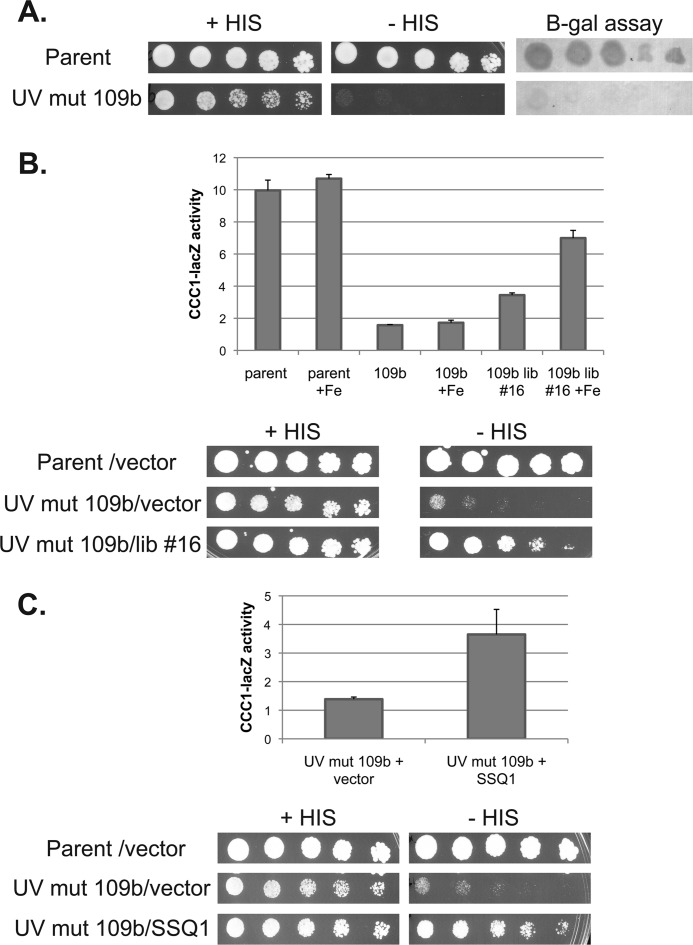
We designed a genetic screen to identify genes involved in iron-dependent Yap5 transcription. We engineered a Δccc1 strain that contained two independent Yap5 reporters. The strain was deleted for HIS3 and contained an integrated HIS3 gene under the control of a GAL1 promoter (Fig. 1). This strain also contained a plasmid-based chimeric transcription factor composed of the GAL4 DNA binding domain and the cysteine-rich activation domain of YAP5. The fusion protein encoded by this plasmid responds to iron and will induce GAL1 promoter-regulated genes (8). Thus, this strain will be a HIS auxotroph in the absence of iron-induced Gal4-Yap5 activity. The second reporter was an integrated CCC1-lacZ construct containing the CCC1 promoter fused to the lacZ gene. Incubation of the strain in low iron results in cells auxotrophic for histidine, which do not express β-galactosidase. The addition of iron resulted in HIS prototrophy and expression of β-galactosidase. The use of two different reporter constructs, which respond to two different transcription factors, ensures that any identified mutation must be in a common iron-sensing system rather than in an individual transcription factor/reporter system. The engineered cells were UV-mutagenized and exposed to high iron, and LacZ-negative cells (“white” cells) were selected for LacZ activity and then examined for HIS auxotrophy. Candidates that showed decreased CCC1-lacZ activity and HIS auxotrophy were selected for further study. One candidate, UV mutant 109b, showed these phenotypes (Fig. 2A). The phenotypes were recessive as determined by diploid analysis (data not shown).
FIGURE 1.
Diagram of selection screen to identify genes involved in the high iron transcriptional response. A Δccc1 yeast strain was generated that contained the promoter region of CCC1 region fused to a lacZ reporter integrated at the HO locus. The strain also contained a deletion in the HIS3 gene and a copy of HIS3 under the control of the GAL1 promoter integrated at the URA3 locus. The strain was transformed with a TRP1 plasmid containing the GAL4 DNA binding domain fused to a YAP5 cysteine-rich activation domain (CRD). In the presence of iron, the cells are HIS3 prototrophs and express β-galactosidase.
FIGURE 2.
Identification of a mutant SSQ1 that affects Yap5 induction of CCC1. A, serial dilutions of the parental strain and UV mutant (UV mut) 109b cells were spotted on plates in the presence or absence of histidine. Cells were grown for 3 days, and then a β-galactosidase assay was performed. B, parental, UV mutant 109b, and UV mutant 109b, transformed with library plasmid 16 (lib #16), were grown overnight in low iron medium, 500 μm iron was added for 2.5 h, and a quantitative β-galactosidase assay performed. Cell protein was determined, and the data are expressed as specific activity. The data are the average of at least three experiments and are presented as the mean ± S.D. Bottom panel: cells from above were spotted in a serial dilution in the presence or absence or histidine and grown for 3 days. C, a β-galactosidase assay and a plate spot assay were performed for mutant cells transformed with a control vector or a subcloned SSQ1 plasmid. Cell protein was determined, and the β-galactosidase assay data are expressed as specific activity. The data are the average of at least three experiments and are presented as the mean ± S.D.
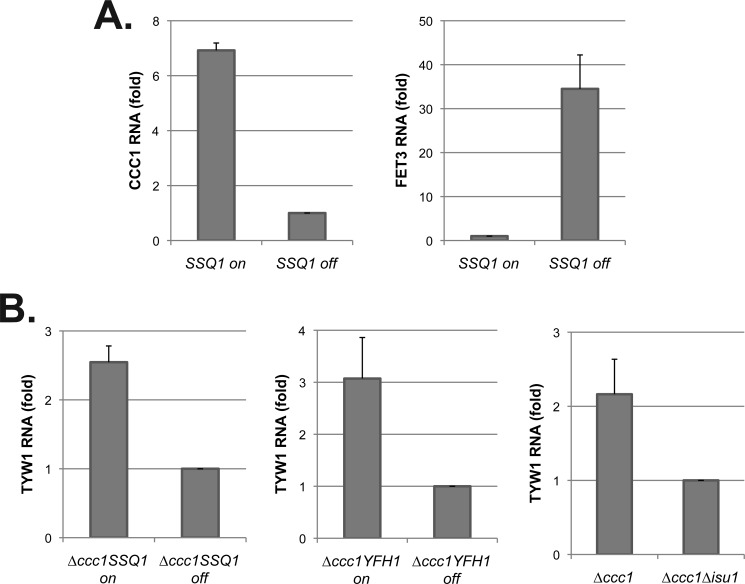
UV mutant 109b was transformed with a LEU2 genomic library and selected for cells that could express β-galactosidase and grow on −HIS medium (Fig. 2B). Library plasmid 16 conferred iron-dependent growth on −HIS plates and restored iron-dependent β-galactosidase activity. The library clone 16 plasmid was recovered and sequenced, and subcloning identified SSQ1 as the gene responsible for complementation. We sequenced the chromosomal copy of SSQ1 in UV mutant 109b and identified a missense mutation, which resulted in an amino acid substitution L217S. Deletion of SSQ1 in our parental strain W303 resulted in lethality, suggesting that the missense mutation was hypomorphic. The finding that the mutation was a hypomorph might explain why complementation was partial, although it is possible that there was a second mutation in the strain. The observation that a conditional shut-off of SSQ1 phenocopies the inhibition of Yap5-mediated transcription, however, ensures that SSQ1 is the gene responsible for the phenotype.
SSQ1 is a nuclear gene that encodes a mitochondrial protein chaperone that plays an important role in the mitochondrial synthesis of Fe-S clusters (13, 14). Decreased levels of Ssq1 compromise Fe-S cluster synthesis, leading to decreased activities of Fe-S cluster-containing enzymes, an inability to grow on respiratory substrates, and induction of the iron regulon. All three of these phenotypes are seen in mutant 109b (data not shown). The inability to induce CCC1-lacZ in mutant 109b and the inability to grow on −HIS medium were complemented by transformation with an SSQ1-containing plasmid (Fig. 2C). As shown below, reduced levels of other proteins required for mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis prevent iron-induced expression of Yap5 target genes.
There are a number of explanations for why cells defective in Fe-S cluster synthesis fail to induce Yap5 target genes. Notably, defects in Fe-S cluster synthesis lead to increased mitochondrial iron, and mitochondrial iron sequestration may result in low cytosolic iron, preventing the high iron transcriptional response. Previously, we suggested that cytosolic iron is not low in cells with defects in mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis (3), a result confirmed by others (15). To measure cytosolic iron, we utilized a mutant enzyme involved in ergosterol synthesis. Erg25 is a methyl sterol oxidase required for the demethylation of 4,4,-dimethylzymosterol to zymosterol. Erg25 is a putative iron-containing enzyme, and the mutant Erg25-2 showed decreased activity when cytosolic iron levels were decreased (16). Loss of Fe-S cluster synthesis did not affect the activity of the Erg25-2, suggesting that cytosolic iron was not decreased. The measurement of Erg25 activity, however, was indirect and was based on the accumulation of sterol intermediates in intact cells. Further, the methyl sterol oxidase enzymatic reaction requires mitochondrial-produced heme, which in turn is dependent on mitochondrial iron. It is possible that decreased Erg25 activity reflected decreased mitochondrial function rather than decreased cytosolic iron. Based on these concerns, we looked for an independent measure of cytosolic iron to assay the effect of decreased Fe-S cluster synthesis on induction of the low and high iron response.
Use of GDO to Measure Cytosolic Iron
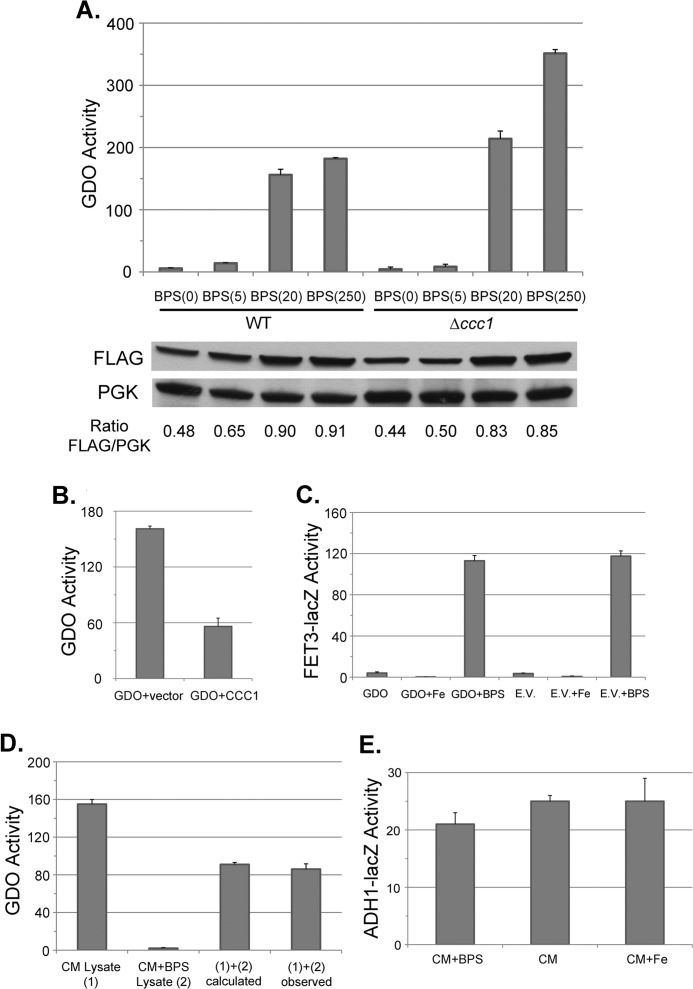
Pseudaminobacter salicylatoxidans GDO catalyzes the ring fission reaction that degrades gentisate (17). This pathway does not exist in yeast, and yeast do not express GDO. The crystal structure for GDO has been solved, and it shows that Fe(II) is the sole cofactor (18). The iron binding site is solvent-accessible, and GDO has a relatively low affinity for iron as it binds iron with only three ligands (3 His residues). In contrast, Escherichia coli iron-superoxide dismutase binds iron with four ligands (3 His residues and 1 Asp residue) (19). GDO-bound iron can be removed by ferrous chelators, and the inactivated enzyme can be incompletely reactivated by the addition of reduced iron but not other metals (20). Based on these observations, we generated a yeast plasmid expressing GDO under the control of the ADH1 promoter. GDO expressed in yeast showed activity using gentisate as a substrate. Similar levels of activity were seen for both untagged and carboxyl-terminal FLAG-tagged versions of GDO (data not shown). There was low GDO activity in medium made into low iron medium through the addition of the impermeable iron chelator BPS (Fig. 3A). Deletion of CCC1, which prevents import of iron to vacuoles, resulted in increased GDO activity in iron-replete medium. The addition of iron to BPS medium resulted in increased GDO activity. Cells overexpressing the vacuolar iron transporter Ccc1 showed decreased GDO activity (Fig. 3B). Expression of GDO did not lead to induction of FET3-lacZ, suggesting that GDO did not consume enough iron to affect iron homeostasis (Fig. 3C). Measurement of GDO activity in combined extracts from iron-replete cells and iron-depleted cells showed that GDO activity was the average of the two (Fig. 3D). These results indicate that cell breakage did not affect GDO activity and that iron was stable within GDO for at least 5 h unless an iron chelator was added, permitting accurate measurements of activity. Further, GDO protein was found in the cytosolic fraction, demonstrating that GDO activity reflected cytosolic iron and not organellar iron (data not shown).
FIGURE 3.
The activity of expressed GDO in yeast can be used as a measure of cytosolic iron. A, wild type or Δccc1 cells were transformed with a plasmid expressing GDO with a carboxyl-FLAG epitope, under the control of the ADH1 promoter. Cells were grown in CM medium supplemented with 80 μm BPS and various concentrations of FeSO4 (i.e. BPS(5) indicates 80 μm BPS with 5 μm FeSO4) added back. Cells were grown overnight to mid-log phase and homogenized as described under ”Experimental Procedures,“ and GDO activity and cell protein were determined. GDO activity is expressed as nanomoles of substrate converted per minute per mg of protein. The amount of GDO-FLAG was detected by Western blot with phosphoglucose kinase (PGK) as a loading control. The ratio of GDO-FLAG to PGK was determined by densitometry. B, wild type cells were transformed with either a control plasmid or a plasmid containing CCC1 under the control of its endogenous promoter and a plasmid containing GDO under the control of the ADH1 promoter. Cells were grown overnight in selective medium and homogenized, and GDO activity and cell protein were determined. The data are expressed as specific activity, and the results are the mean of three separate experiments (± S.D.). C, wild type cells containing a FET3-lacZ reporter construct integrated at the HO locus were transformed with a GDO expression plasmid or an empty vector (E.V.). Cells were grown in CM medium with or without 40 μm BPS (+BPS) with 100 μm FeSO4 added (+Fe); cell lysates were prepared, and β-galactosidase activity and cell protein were determined. The data are presented as specific activity, and the results are the mean of three separate experiments (± S.D.). D, cells expressing GDO were grown overnight in CM medium without BPS added (CM Lysate (1)) or CM medium with 80 μm BPS added (CM+BPS Lysate (2)). Cells were harvested, and the lysates from these two conditions were assayed separately or were mixed together at a 1:1 volume ratio prior to determining GDO activity. The calculated value ((1)+(2) calculated) indicates the theoretical GDO activity assuming no activity change occurring upon mixing. The data are presented as specific activity, and the results are the mean of three separate experiments (± S.D.). E, WT cells (DY150) were transformed with a plasmid containing a ADH1-lacZ construct and grown in low iron medium (CM supplemented with 80 μm BPS, CM+BPS), regular medium (CM), or high iron (CM supplemented with 100 μm FeSO4, CM+Fe). Cells were harvested and lysed, and β-galactosidase activity and cell protein were determined. The data are presented as specific activity, and the results are the mean of three separate experiments (± S.D.).
We note that the level of GDO-FLAG was reduced in iron-depleted medium, although the effect of iron on specific activity was more sensitive than the effect of iron on protein level (Fig. 3A). The decrease in GDO level in low iron conditions was not due to a decrease in expression. GDO is expressed using an ADH1 promoter, and analysis of ADH1-lacZ expression constructs indicated that modulation of cellular iron levels did not affect β-galactosidase activity (Fig. 3E). Together, these results suggest that GDO has reduced stability in the absence of iron.
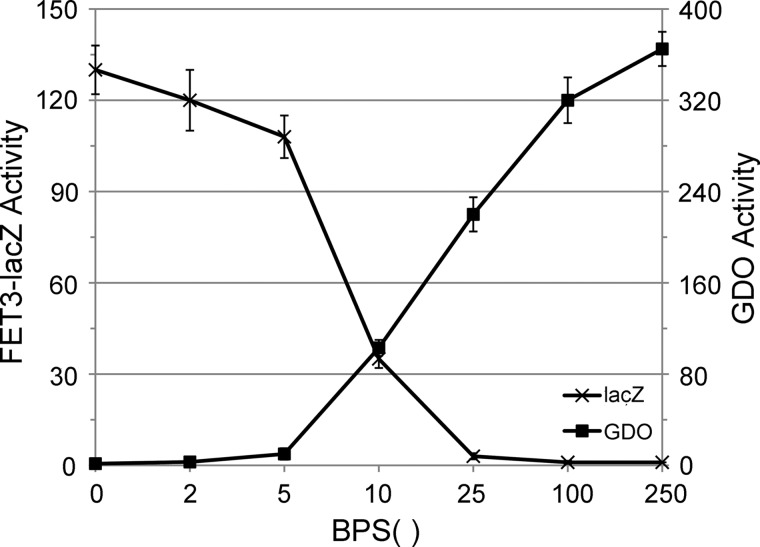
We examined GDO activity and induction of FET3-lacZ as a function of medium iron. To eliminate the variable of induction of high affinity iron transporters we used Δccc1 cells that constitutively expressed FET3/FTR1 under the control of the PGK1 promoter (21). There was an inverse relationship between external iron and FET3-lacZ activity and a direct relationship between external iron and GDO activity (Fig. 4). At 80 μm BPS with 10 μm FeSO4, the reduction in GDO was 80%, whereas induction of FET3-lacZ was 32% of maximum, leading to a large dynamic range in GDO activity. Although not giving absolute concentrations of cytosolic iron, these data demonstrate that GDO can be used to assess cytosolic iron levels.
FIGURE 4.
Cytosolic GDO activity responds to changes in medium iron. A strain was constructed in which Δccc1 cells contained a FET3-lacZ reporter integrated at the HO locus and a FET3/FTR1 construct under the control of the PGKI promoter integrated at the ADE2 locus. Cells were transformed with a GDO plasmid. The cells were incubated overnight in CM with 80 μm BPS and varying amounts of FeSO4. Cells were homogenized, and β-galactosidase, GDO activity, and cell protein were determined. The data are expressed as specific activity of GDO or β-galactosidase. The data are the average of at least three experiments and are presented as the mean ± S.D.
Failure to Induce the Yap5 Transcriptional Response due to Decreased Fe-S Clusters Does Not Result from Vacuolar or Mitochondrial Iron Sequestration
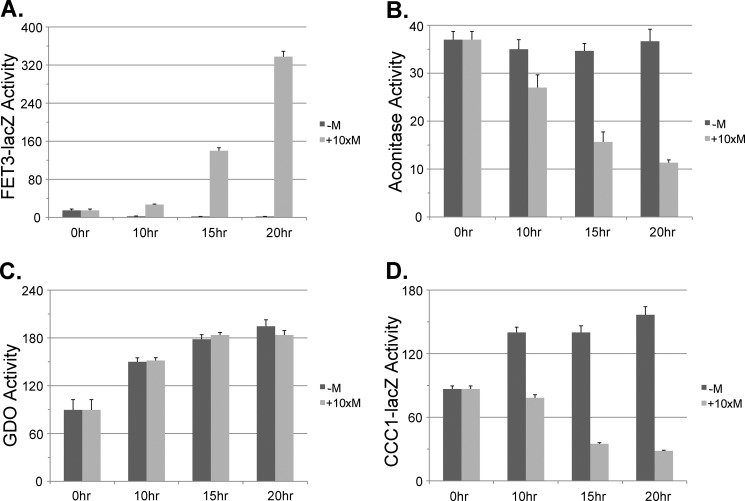
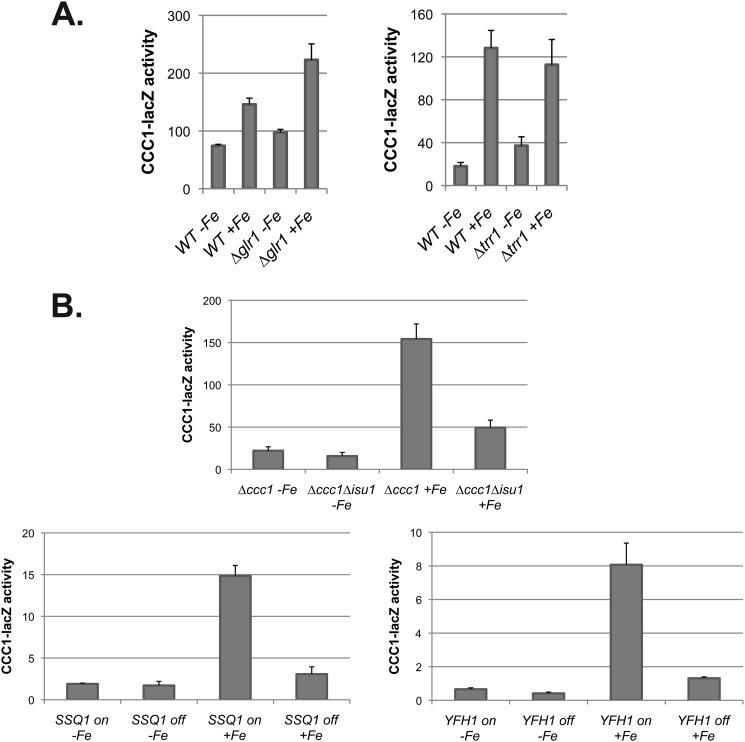
We utilized the GDO assay to examine the effect of decreased Fe-S cluster synthesis on cytosolic iron levels. We generated a SSQ1 deletion strain that was kept alive by a plasmid that contained a MET3-regulated SSQ1. The strain was also deleted for CCC1 to eliminate vacuolar iron sequestration. The strain was transformed with either a FET3-lacZ reporter or a CCC1-lacZ reporter. The addition of methionine resulted in a time-dependent increase in FET3-lacZ expression (Fig. 5A) and a decrease in the activity of the Fe-S cluster-containing protein aconitase (Fig. 5B). We note that the iron regulon was induced even in the absence of CCC1, indicating that loss of Fe-S clusters did not result from vacuolar iron sequestration. We then examined the effect of loss of SSQ1 on induction of the high iron regulon. The addition of iron to cells grown in the absence of methionine resulted in an increase in cytosolic iron as measured by GDO activity (Fig. 5C) and an increase in CCC1-lacZ expression (Fig. 5D). In the absence of SSQ1 expression, GDO activity showed a response to increased medium iron, but there was no increase in CCC1-lacZ activity in response to added iron; rather there was a decrease in CCC1-lacZ. This result indicates that loss of SSQ1 does not result in decreased cytosolic iron but does result in decreased CCC1-lacZ expression.
FIGURE 5.
Reduction in SSQ1 affects the induction of both the low and the high iron response without affecting cytosolic iron levels. Cells (Δssq1Δccc1) were transformed with plasmids containing a MET3-regulated SSQ1. The cells were also transformed with a GDO-expressing plasmid, a FET3-lacZ reporter construct, or a CCC1-lacZ reporter construct. Cells were grown overnight in CM without methionine to mid-log phase. Cells were harvested and placed in growth medium containing 100 μm FeSO4 with or without 10× methionine for the specified times. Cells were homogenized, and β-galactosidase activity, GDO activity, aconitase activity, and cell protein were determined. A, FET3-lacZ. B, aconitase. C, GDO. D, CCC1-lacZ. The data are presented as specific activity, and the error bars reflect the S.D. of three independent experiments.
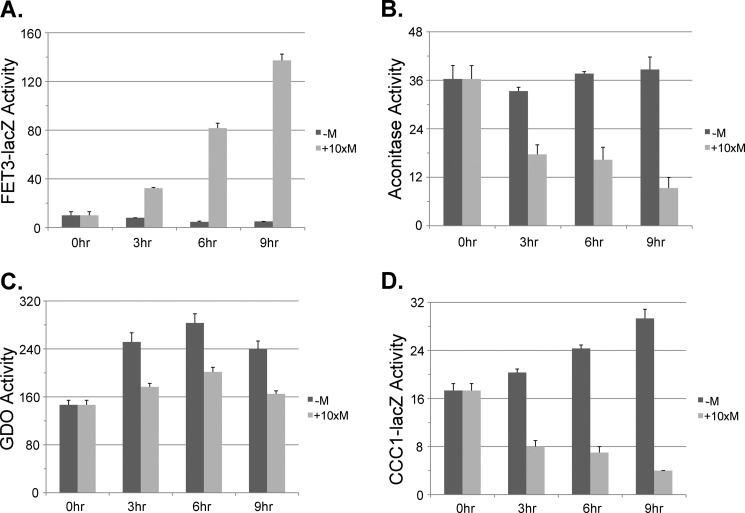
Yfh1 is thought to act as an iron chaperone in the synthesis of Fe-S clusters. In the absence of Yfh1, there is a severe reduction in mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis (22). We used Δyfh1 cells that contained a MET3-regulated YFH1 (23). This strain was also deleted for CCC1 to rule out effects due to vacuolar iron sequestration. The strain was transformed with either a FET3-lacZ reporter or a CCC1-lacZ reporter. In the absence of methionine, which permits expression of Yfh1, there was a low level of FET3-lacZ (Fig. 6A). The addition of methionine, which prevents expression of Yfh1, resulted in a time-dependent induction of FET3-lacZ and a time-dependent decrease in aconitase activity (Fig. 6B). We note that decreased expression of Yfh1 resulted in a more rapid loss of aconitase activity than did decreased expression of Ssq1, which might reflect either a shorter half-life for Yfh1 than for Ssq1 or that the function of Ssq1 requires less protein. GDO activity increased over time in the absence of Yfh1 expression (Fig. 6C). In the presence of methionine, GDO activity showed less of an increase, but stayed above the base line. The absence of methionine resulted in a time-dependent increase in CCC1-lacZ activity (Fig. 6D). In contrast, in the presence of methionine, there was a decrease in CCC1-lacZ activity, suggesting that Fe-S cluster synthesis is required for the iron-dependent induction of CCC1.
FIGURE 6.
Reduction in YFH1 affects the induction of the low and high iron response without affecting cytosolic iron levels. Cells (Δyfh1Δccc1) were transformed with a plasmid containing a MET3-regulated YFH1. The cells were also transformed with a GDO plasmid and either a FET3-lacZ reporter construct or a CCC1-lacZ reporter construct. Cells were grown overnight in CM without methionine to mid-log phase. Cells were harvested and placed in growth media containing 100 μm FeSO4 with or without 10× methionine for the specified times. Cells were homogenized, and FET3-lacZ (A), aconitase (B), GDO (C), and CCC1-lacZ (D) activities and cell protein were determined. The data are presented as specific activity, and the error bars reflect the S.D. of three independent experiments.
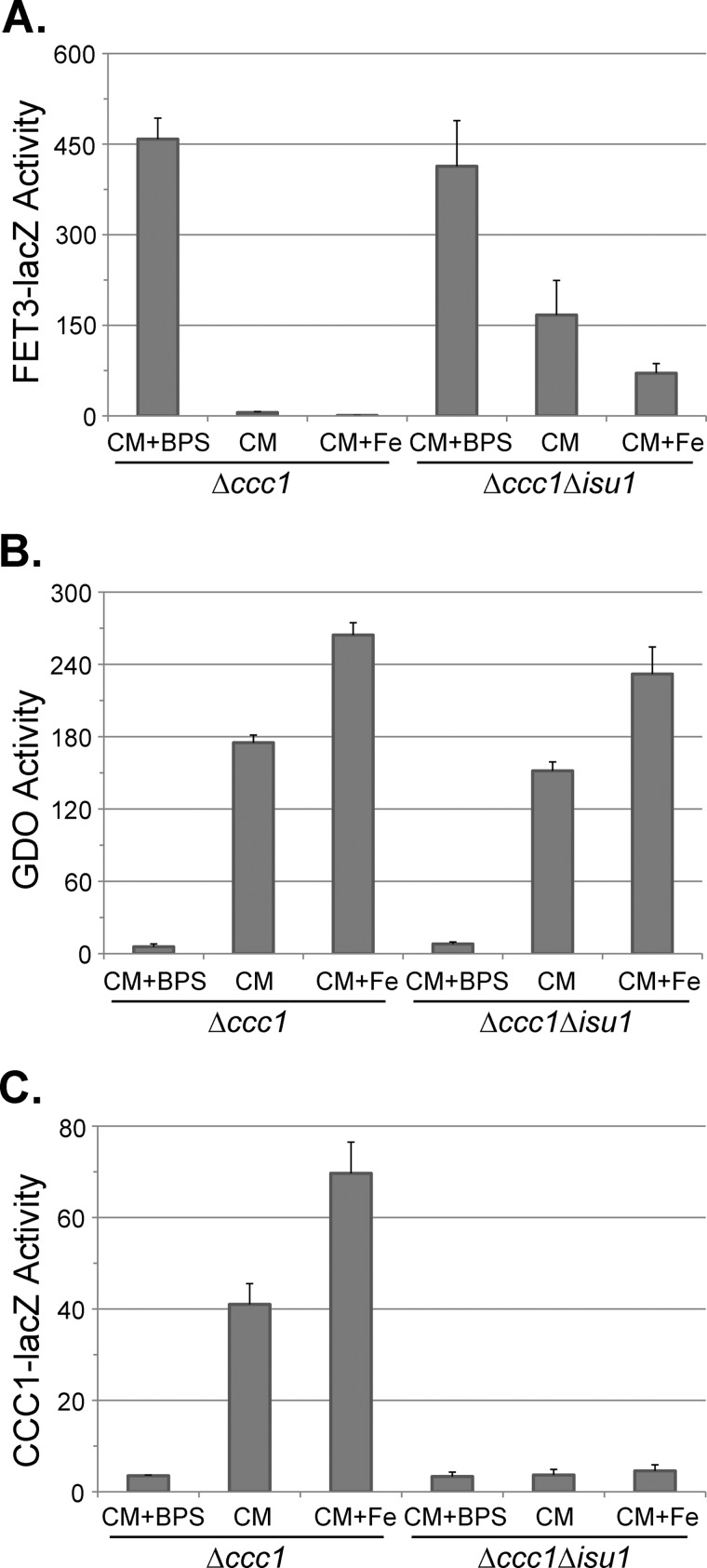
Isu1 is one of two Fe-S scaffold proteins, and deletion of ISU1 results in increased mitochondrial iron and induction of the iron regulon (24). Cells with a deletion of ISU1 and CCC1 show increased FET3-lacZ activity when compared with Δccc1 cells in normal iron or iron-supplemented conditions (Fig. 7A). GDO activity in response to either iron depletion or iron addition was similar in Δccc1 and Δccc1Δisu1 cells (Fig. 7B). Loss of ISU1 prevented the iron-dependent induction of CCC1-lacZ (Fig. 7C). Thus, the decrease in CCC1-lacZ in Δisu1Δccc1 cells cannot be ascribed to decreased cytosolic iron.
FIGURE 7.
Loss of ISU1 prevents iron-dependent induction of CCC1-lacZ. Δccc1 or Δccc1Δisu1 cells were transformed with a GDO plasmid and either FET3-lacZ or CCC1-lacZ reporter constructs. Cells were grown overnight in CM medium (CM) or CM medium with 80 μm BPS plus (CM+Fe) or minus 100 μm FeSO4 (CM+BPS). Cells were homogenized, and FET3-lacZ (A), GDO (B), and CCC1-lacZ (C) activities and cell protein were determined. The data are presented as specific activity, and the error bars reflect the S.D. of three independent experiments.
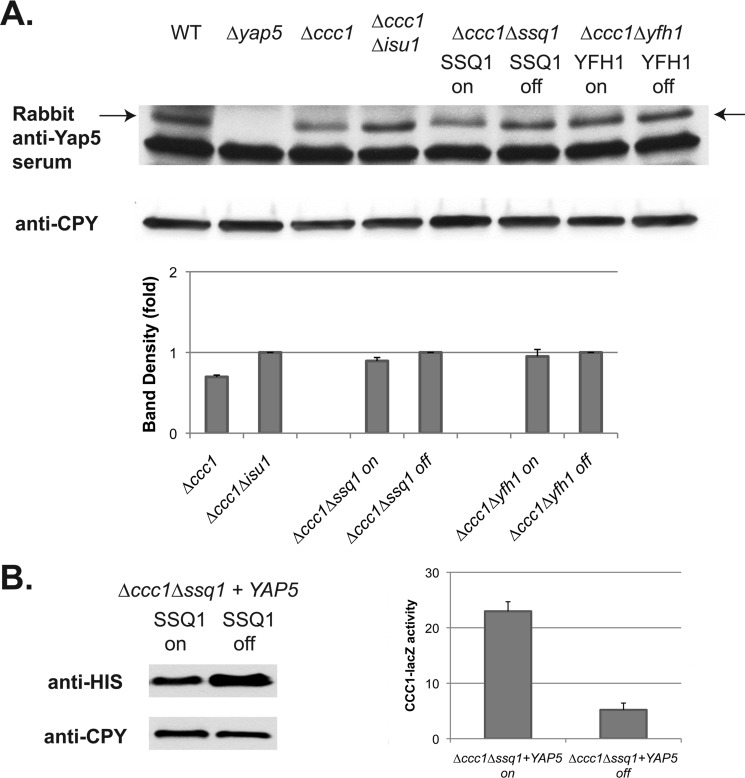
Previously, we showed that Yap5 levels were not affected by changes in cytosolic iron (8). It is possible, however, that the levels of Yap5 may be altered under decreased Fe-S synthesis and that decrease could be responsible for changes in Yap5-dependent transcription. We examined the levels of endogenous Yap5 using a polyclonal rabbit anti-Yap5 antibody. We did not observe any significant changes in the levels of Yap5 in wild type cells relative to Δisu1 cells (Fig. 8A). Similarly, the level of Yap5 showed no difference in either the presence or the absence of SSQ1 or YFH1. To confirm these results, we overexpressed HIS-tagged Yap5 (8) in Δccc1 cells containing the MET3-regulated SSQ1 as described above. The level of HIS-Yap5 was not decreased by the absence of SSQ1. There was, however, a decrease in CCC1-lacZ activity when compared with SSQ1-expressing cells (Fig. 8B). We conclude that changes in Yap5 protein levels are not responsible for the Yap5-dependent transcription changes seen when Fe-S cluster synthesis is blocked.
FIGURE 8.
Loss of Fe-S cluster synthesis does not lead to decreased Yap5 levels. A, cells (wild type, Δyap5, Δccc1, Δccc1Δisu1, Δssq1Δccc1 (pMET3SSQ1), and Δyfh1Δccc1(pMET3YFH1)) were grown in CM medium in the presence (off) or absence (on) of methionine overnight. Cells were harvested, treated with 10% trichloroacetic acid, and broken with glass beads, and cell extracts were analyzed by Western blot using a polyclonal rabbit anti-Yap5 and a mouse anti-carboxypeptidase Y (CPY) antibody. The arrow denotes the Yap5-specific band. A representative blot is shown. Western blots were quantified using carboxypeptidase Y as a loading control from three separate experiments. B, cells (Δssq1Δccc1 (pMET3SSQ1)) containing a CCC1-lacZ reporter construct were transformed with a high copy plasmid containing HIS-tagged Yap5 under the control of its endogenous promoter. Cells were grown as in A, and HIS-Yap5 levels were determined by Western blot using mouse anti-HIS antibody. CCC1-lacZ activity in these cells was determined. The data are presented as specific activity, and the error bars reflect the S.D. of three independent experiments.
We confirmed that the effect of decreased mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis on the high iron transcriptional response was not an artifact of the CCC1-lacZ reporter construct. Loss of SSQ1 prevented iron induction of CCC1 transcripts, whereas increased transcripts were seen in iron-incubated cells expressing SSQ1 (Fig. 9A). Under the same conditions, FET3 mRNA was increased in the absence of SSQ1. We then assayed the levels of TYW1, another Yap5 target gene (9). In Δccc1 cells, TYW1 mRNA levels were decreased in the absence of SSQ1, YFH1, or ISU1 when compared with Δccc1 cells with unimpaired Fe-S cluster synthesis (Fig. 9B). These results demonstrate that decreased mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis affects the high iron transcriptional response.
FIGURE 9.
Mutations in Fe-S cluster synthesis genes lead to decreased transcripts for Yap5 targets. Total RNA was isolated from cells grown in an iron-replete medium. A, Δssq1 cells containing a MET3-regulated SSQ1-expressing plasmid were grown in a medium without methionine (on) or with 10× methionine (off) overnight. CCC1 mRNA and FET3 mRNA were measured by real-time PCR. B, Δccc1Δssq1 cells containing a MET3-regulated SSQ1-expressing plasmid or Δccc1Δyfh1 cells with a MET3-regulated YFH1-expressing plasmid were grown in a medium without methionine (on) or with 10× methionine (off) overnight. Δccc1 and Δccc1Δisu1 were grown in an iron-replete medium overnight. Real-time PCR was performed for TYW1 transcription (a Yap5-regulated gene). -Fold changes of each gene transcriptional level were quantified based on CMD1 as an internal control. The error bars reflect the S.D. of two independent experiments.
Iron Induction of Yap5-regulated Genes Is Independent of the CIA Complex or Grx3 and Grx4
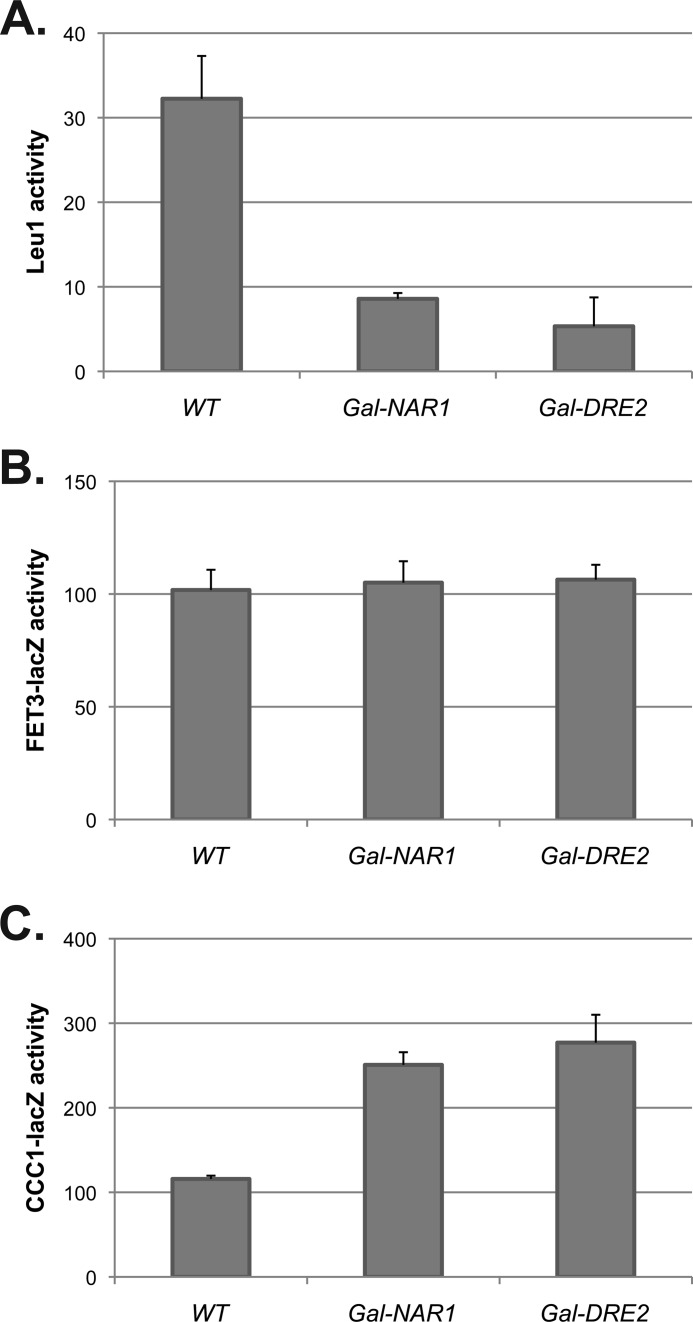
A complex of cytosolic proteins, termed the CIA complex, is required to insert Fe-S clusters on cytosolic or nuclear apoproteins (25). Rutherford et al. (4) showed that the CIA complex is not involved in the low iron-signaling pathway as reduced expression of CIA proteins did not result in induction of the iron regulon. To test whether the CIA complex is required for the high iron-signaling pathway, we utilized strains containing regulated expression of NAR1 (Δnar1 pGALNAR1) or DRE2 (Δdre2pGALDRE2), which encode components of the CIA complex (26, 27). Reduced levels of either protein resulted in a decrease in the activity of the cytosolic Fe-S-containing protein Leu1, indicating decreased Fe-S cluster assembly of cytosolic proteins (Fig. 10A). Loss of either protein did not result in induction of the low iron transcriptional response, confirming previous results (4) (Fig. 10B). Loss of either protein did not prevent the iron-induced Yap5 response, and in fact, there was an increase in CCC1-lacZ activity (Fig. 10C). These results indicate that although the Yap5 response requires mitochondrial Fe-S clusters, it does not require assembly of Fe-S clusters on cytosolic or nuclear proteins, although there may be CIA-independent routes for Fe-S cluster assembly. These data suggest that if Fe-S clusters are not incorporated into cytosolic proteins, they may accumulate in the cytosol, resulting in an increased Yap5 response.
FIGURE 10.
Decreased activity of the cytosolic Fe-S machinery does not prevent induction of CCC1. Cells containing a galactose-regulated NAR1 or a galactose-regulated DRE2, transformed with either a CCC1-lacZ plasmid or a FET3-lacZ plasmid, were grown in galactose medium overnight. Cells were washed and reinoculated into glucose medium for another 16 h to turn off NAR1 or DRE2 expression. Cells were homogenized, and Leu1 activity (A), FET3-lacZ activity (B), and CCC1-lacZ activity (C) and cell protein were assayed. The data are presented as specific activity normalized to cell protein, and the error bars reflect the S.D. of three independent experiments.
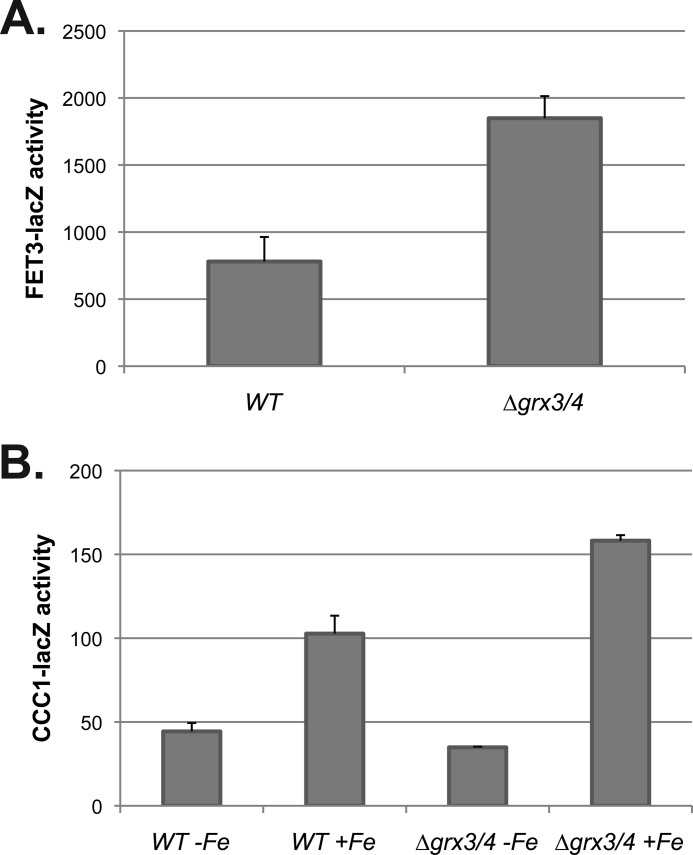
The low iron transcriptional response is increased upon deletion of the cytosolic glutaredoxins GRX3 and GRX4 in the BY4743 background strain (6, 7). Deletion of both genes resulted in increased expression of FET3-lacZ (Fig. 11A). CCC1-lacZ was only increased in Δgrx3Δgrx4 cells when iron was added (Fig. 11B). There was no increase in CCC1-lacZ in the absence of added iron. We conclude that deletion of GRX3 and GRX4 does not directly affect Yap5-dependent transcription. We then examined whether overexpression of Grx3 or Grx4 would affect CCC1-lacZ expression. Overexpression of either Grx3 or Grx4 had no effect on CCC1-lacZ activity in CM medium (data not shown).
FIGURE 11.
Loss of GRX3/GRX4 affects the low iron transcriptional response but does not directly affect the high iron transcriptional response. A and B, wild type and Δgrx3/grx4 cells were transformed with either a FET3-lacZ reporter construct (A) or a CCC1-lacZ reporter construct (B). The cells were grown overnight in CM, in CM made iron-limited by the addition of 80 μm BPS, or in high iron (500 μm). Cells were homogenized, and β-galactosidase activity and cell protein determined. The data are presented as specific activity normalized to cell protein, and the error bars reflect the S.D. of three independent experiments.
The Effect of Decreased Fe-S Cluster Synthesis on Induction of the Yap5 Response Is Not due to Increased Oxidants
It is recognized that loss of mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis leads to increased oxidant damage (15, 28). Previously, we reported that deletion of glutaredoxin 1 (GLR1) or thioredoxin reductase 1 (TRR1), which encode antioxidant enzymes, did not lead to induction of CCC1-lacZ, suggesting that Yap5-dependent transcription was not due to increased oxidants (8). We used these strains to determine whether increased oxidants would prevent iron-induced expression of the CCC1-lacZ reporter construct. In both deletion strains, iron induced β-galactosidase expression to the same extent as in iron-treated wild type cells (Fig. 12A). Second, we had also shown that iron could induce Yap5-dependent transcription under anaerobic conditions (8). In anaerobic conditions, iron had a marginal effect on the expression of CCC1-lacZ in cells with a deletion in ISU1 (Fig. 12B). Similarly, when the levels of Ssq1 or Yfh1 were reduced, iron was unable to induce CCC1-lacZ under anaerobic conditions. These results support the view that the lack of induction of Yap5-dependent transcription resulted from the loss of Fe-S clusters and not from an oxidant-induced suppression of Yap5 activation.
FIGURE 12.
Increased oxidants do not suppress Yap5-induced expression of CCC1. A, wild type, Δglr1, and Δtrr1 cells were transformed with a CCC1-lacZ plasmid. Cells were incubated in low iron medium, and then 500 μm iron was added. After a further 2-h incubation, cells were harvested, and β-galactosidase and cell protein were determined. B, cells (Δccc1, Δccc1Δisu1, Δccc1Δssq1 transformed with MET3-SSQ1, and Δccc1Δyfh1 transformed with MET3-YFH1) were transformed with CCC1-lacZ. Expression of MET3-SSQ1 and MET3-YFH1 was controlled by the presence (off) (10×) or absence (on) of methionine. Cells were grown in low iron medium anaerobically overnight, and 500 μm iron was added for an additional 2.5 h under anaerobic conditions. Cells were harvested, and β-galactosidase activity and cell protein were determined. The data are presented as specific activity normalized to cell protein, and the error bars reflect the S.D. of three independent experiments.
DISCUSSION
Cells respond to increased levels of cytosolic iron by decreasing iron uptake and increasing iron storage. Most eukaryotes store cytosolic iron in ferritin, a protein whose synthesis is translationally regulated by increased iron. Plants and fungi store cytosolic iron in vacuoles, which requires expression of the vacuolar iron importer CCC1 (yeast) or VTA1 (plants). CCC1 mRNA is destabilized under low iron conditions by binding of Cth1 and Cth2 (29). Transcription of CTH1 and CTH2 is controlled by the low iron transcription factor Aft1. Iron induces the Yap5-mediated transcription of CCC1 and a limited number of other genes. Yap5 constitutively occupies the CCC1 promoter and is activated by high iron (8). The mechanism by which Yap5 “senses” iron is unknown. The results of this study suggest that Yap5 transcription is reduced by the loss of Fe-S cluster synthesis even under conditions in which cytosolic iron is increased. This result implies that the high iron transcriptional response, like the low iron transcriptional response, is coordinated by the availability of Fe-S clusters.
Critical to this conclusion was the finding that defects in Fe-S cluster synthesis affected iron-dependent signaling independent of changes in cytosolic iron. Previously, we utilized the iron-dependent activity of a mutant methyl sterol oxidase to establish that point (3). We confirm and expand that conclusion by taking advantage of the iron-dependent activity of GDO. Use of GDO has several strategic and technical advantages when compared with use of the mutant Erg25-2. The activity of GDO is not essential, and expression of GDO does not affect cellular iron metabolism. The enzyme is easy and inexpensive to assay. Iron binds to GDO with relatively low affinity, and enzyme activity shows a large dynamic range in response to iron deprivation and excess. GDO has a strict requirement for Fe(II), which is thought to be the predominant form of available iron in cytosol. Using GDO to monitor cytosolic iron, we confirmed our initial observation that reduction in enzymes involved in mitochondrial Fe-S synthesis induced the iron regulon with little decrease in cytosolic iron. This conclusion was supported by others using iron-sensitive fluorescent dyes (15).
Our genetic screen showed that a mutation in SSQ1, a gene required for mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis, prevented the high iron transcriptional response. We then determined that reduced expression of other genes involved in mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis also prevented iron induction of the Yap5 response even under anaerobic conditions. This finding has two implications. First, it suggests that the lack of Yap5 induction is not due to production of oxidative radicals resulting from defective mitochondrial activities. Second, it provides evidence that the lack of Yap5-dependent transcription was not due to mitochondrial iron sequestration. Under aerobic conditions, defects in mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis result in mitochondrial iron accumulation in which iron accumulates as a detergent-insoluble particulate, referred to as a nanoparticle. Under anaerobic conditions, cells with reduced levels of Yfh1 or Atm1 do not accumulate iron in mitochondria (15, 30). The lack of mitochondrial iron accumulation again rules out mitochondrial iron sequestration as causal to the lack of Yap5-dependent transcription.
Rutherford et al. (4) showed that the iron regulon responded to decreased mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis but did not respond to loss of members of the cytosolic machinery that are required to assemble Fe-S clusters on most apoproteins. Reductions in the cytosolic glutaredoxins Grx3 and Grx4 result in induction of the iron regulon, whereas overexpression of either Grx3 or Grx4 leads to termination of the low iron transcriptional response and binding of Grx3 or Grx4 to Aft1 (6, 7). Interestingly, although the CIA complex is required for formation of most Fe-S holoproteins, it is not required for acquisition of iron by Grx3 or Grx4 (5). These data support a role for Grx3/4 in mediating the Fe-S cluster signal from mitochondria to Aft1. We confirmed that reduction in CIA members does not lead to transcription of the low iron regulon and find that it also does not prevent transcription of the high iron regulon. We also confirmed that reduction in Grx3 and Grx4 results in induction of the low iron regulon and that it also induces the high iron regulon. Our data suggested that induction of the high iron regulon by reduced levels of Grx3 and Grx4 is a secondary consequence of increased expression of cell surface iron transporters, which permits increased cellular iron. There was no induction of the high iron regulon in Δgrx3Δgr4 cells placed on low iron medium.
Currently, we do not know how Fe-S clusters affect the high iron transcriptional response. Yap5 contains clusters of cysteines, which are critical for iron-induced transcription (8). It might well be that these cysteines can bind Fe-S clusters directly without the requirement for accessory proteins. That possibility is currently being tested. A finding that both the low iron and the high iron transcriptional response are sensitive to the same metabolite, Fe-S clusters, has precedence. Post-transcriptional regulation of mammalian iron acquisition by regulation of transferrin receptors as well as regulation of cytosolic iron levels through regulation of iron storage (ferritin) and iron export (ferroportin) respond to the binding of iron regulatory proteins (IRPs) to iron-responsive elements in the untranslated regions of mRNAs (31). Loss of RNA binding activity of IRP1 results from conversion of IRP1 into a Fe-S cluster-containing aconitase. Thus, both iron acquisition and iron storage respond to Fe-S cluster synthesis.
The cell surface high affinity iron transport system of Schizosaccharomyces pombe is highly homologous to that of S. cerevisiae, composed of a ferroxidase and a transmembrane iron permease (32). The regulation of this transport system, as well as other genes involved in adaptation to a low iron response, is quite different in the two yeasts. In S. cerevisiae, the low iron-sensing transcription factor Aft1 is an activator, and iron induces Aft1 binding to promoters (33). In S. pombe, the transcriptional regulator for genes involved in iron acquisition, Fep1, is a repressor, and iron induces the loss of Fep1 from promoters (34). Iron sensing by Fep1 is dependent on its interaction with the S. pombe monothiol glutaredoxin Grx4 (35–37). Deletion of Grx4 results in constitutive repression of the iron regulon. Iron does not promote binding of Grx4 to Fep1, but it does affect Fep1 conformation. Under iron-replete conditions, proteins involved in iron utilization and storage are transcribed; under iron-limited conditions, they are repressed by Php4. Php4 is regulated transcriptionally by Fep1, but it also regulates post-transcriptionally by binding to Grx4 (38). Deletion of Grx4 results in constitutive activation of Php4. Additionally, Php4 transits between nucleus and cytosol, and loss of Grx4 prevents Php4 exit from the nucleus. Although we do not know the mechanistic details of how Fe-S clusters regulate iron-dependent transcription in S. cerevisiae, our finding that Fe-S clusters affect both low and high iron sensing shows a conservation of signal transduction in evolutionarily disparate species of yeast and vertebrates.
Acknowledgments
We express our appreciation to members of the Kaplan laboratory for reading the manuscript.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant DK30534 from the NIDDK (to J. K.).
- CM
- complete minimal
- BPS
- bathophenanthroline disulfonate
- GDO
- gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase
- PGK
- phosphoglucose kinase
- CIA
- cytosolic iron-sulfur protein assembly
- IRP
- iron regulatory protein.
REFERENCES
- 1. Kaplan J., McVey Ward D., Crisp R. J., Philpott C. C. (2006) Iron-dependent metabolic remodeling in S. cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1763, 646–651 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ehrensberger K. M., Bird A. J. (2011) Hammering out details: regulating metal levels in eukaryotes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 36, 524–531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Chen O. S., Crisp R. J., Valachovic M., Bard M., Winge D. R., Kaplan J. (2004) Transcription of the yeast iron regulon does not respond directly to iron but rather to iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 29513–29518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Rutherford J. C., Ojeda L., Balk J., Mühlenhoff U., Lill R., Winge D. R. (2005) Activation of the iron regulon by the yeast Aft1/Aft2 transcription factors depends on mitochondrial but not cytosolic iron-sulfur protein biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 10135–10140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Mühlenhoff U., Molik S., Godoy J. R., Uzarska M. A., Richter N., Seubert A., Zhang Y., Stubbe J., Pierrel F., Herrero E., Lillig C. H., Lill R. (2010) Cytosolic monothiol glutaredoxins function in intracellular iron sensing and trafficking via their bound iron-sulfur cluster. Cell Metab. 12, 373–385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ojeda L., Keller G., Muhlenhoff U., Rutherford J. C., Lill R., Winge D. R. (2006) Role of glutaredoxin-3 and glutaredoxin-4 in the iron regulation of the Aft1 transcriptional activator in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 17661–17669 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Pujol-Carrion N., Belli G., Herrero E., Nogues A., de la Torre-Ruiz M. A. (2006) Glutaredoxins Grx3 and Grx4 regulate nuclear localization of Aft1 and the oxidative stress response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Sci. 119, 4554–4564 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Li L., Bagley D., Ward D. M., Kaplan J. (2008) Yap5 is an iron-responsive transcriptional activator that regulates vacuolar iron storage in yeast. Mol. Cell Biol. 28, 1326–1337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Li L., Jia X., Ward D. M., Kaplan J. (2011) Yap5 protein-regulated transcription of the TYW1 gene protects yeast from high iron toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 38488–38497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Pimentel C., Vicente C., Menezes R. A., Caetano S., Carreto L., Rodrigues-Pousada C. (2012) The role of the Yap5 transcription factor in remodeling gene expression in response to iron bioavailability. PLoS One 7, e37434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Chen O. S., Hemenway S., Kaplan J. (2002) Inhibition of Fe-S cluster biosynthesis decreases mitochondrial iron export: evidence that Yfh1p affects Fe-S cluster synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 12321–12326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hintner J. P., Lechner C., Riegert U., Kuhm A. E., Storm T., Reemtsma T., Stolz A. (2001) Direct ring fission of salicylate by a salicylate 1,2-dioxygenase activity from Pseudaminobacter salicylatoxidans. J. Bacteriol. 183, 6936–6942 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Lutz T., Westermann B., Neupert W., Herrmann J. M. (2001) The mitochondrial proteins Ssq1 and Jac1 are required for the assembly of iron sulfur clusters in mitochondria. J. Mol. Biol. 307, 815–825 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Dutkiewicz R., Schilke B., Knieszner H., Walter W., Craig E. A., Marszalek J. (2003) Ssq1, a mitochondrial Hsp70 involved in iron-sulfur (Fe-S) center biogenesis: similarities to and differences from its bacterial counterpart. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 29719–29727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Irazusta V., Obis E., Moreno-Cermeño A., Cabiscol E., Ros J., Tamarit J. (2010) Yeast frataxin mutants display decreased superoxide dismutase activity crucial to promote protein oxidative damage. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 48, 411–420 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Li L., Kaplan J. (1996) Characterization of yeast methyl sterol oxidase (ERG25) and identification of a human homologue. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 16927–16933 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Hintner J. P., Reemtsma T., Stolz A. (2004) Biochemical and molecular characterization of a ring fission dioxygenase with the ability to oxidize (substituted) salicylate(s) from Pseudaminobacter salicylatoxidans. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 37250–37260 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Matera I., Ferraroni M., Bürger S., Scozzafava A., Stolz A., Briganti F. (2008) Salicylate 1,2-dioxygenase from Pseudaminobacter salicylatoxidans: crystal structure of a peculiar ring-cleaving dioxygenase. J. Mol. Biol. 380, 856–868 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Lah M. S., Dixon M. M., Pattridge K. A., Stallings W. C., Fee J. A., Ludwig M. L. (1995) Structure-function in Escherichia coli iron superoxide dismutase: comparisons with the manganese enzyme from Thermus thermophilus. Biochemistry 34, 1646–1660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Harpel M. R., Lipscomb J. D. (1990) Gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas: purification, characterization, and comparison of the enzymes from Pseudomonas testosteroni and Pseudomonas acidovorans. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 6301–6311 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Stearman R., Dancis A., Klausner R. D. (1998) YIpDCE1: an integrating plasmid for dual constitutive expression in yeast. Gene 212, 197–202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Mühlenhoff U., Richhardt N., Ristow M., Kispal G., Lill R. (2002) The yeast frataxin homologue Yfh1p plays a specific role in the maturation of cellular Fe-S proteins. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 2025–2036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Radisky D. C., Babcock M. C., Kaplan J. (1999) The yeast frataxin homologue mediates mitochondrial iron efflux. Evidence for a mitochondrial iron cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 4497–4499 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Schilke B., Voisine C., Beinert H., Craig E. (1999) Evidence for a conserved system for iron metabolism in the mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 10206–10211 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Lill R., Mühlenhoff U. (2008) Maturation of iron-sulfur proteins in eukaryotes: mechanisms, connected processes, and diseases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 669–700 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Balk J., Pierik A. J., Netz D. J., Mühlenhoff U., Lill R. (2004) The hydrogenase-like Nar1p is essential for maturation of cytosolic and nuclear iron-sulfur proteins. EMBO J. 23, 2105–2115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Zhang Y., Lyver E. R., Nakamaru-Ogiso E., Yoon H., Amutha B., Lee D. W., Bi E., Ohnishi T., Daldal F., Pain D., Dancis A. (2008) Dre2, a conserved eukaryotic Fe-S cluster protein, functions in cytosolic Fe-S protein biogenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 28, 5569–5582 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Bellí G., Molina M. M., García-Martínez J., Pérez-Ortín J. E., Herrero E. (2004) Saccharomyces cerevisiae glutaredoxin 5-deficient cells subjected to continuous oxidizing conditions are affected in the expression of specific sets of genes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 12386–12395 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Puig S., Askeland E., Thiele D. J. (2005) Coordinated remodeling of cellular metabolism during iron deficiency through targeted mRNA degradation. Cell 120, 99–110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Miao R., Kim H., Koppolu U. M., Ellis E. A., Scott R. A., Lindahl P. A. (2009) Biophysical characterization of the iron in mitochondria from Atm1p-depleted Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 48, 9556–9568 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Rouault T. A. (2006) The role of iron regulatory proteins in mammalian iron homeostasis and disease. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2, 406–414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Askwith C., Kaplan J. (1997) An oxidase-permease-based iron transport system in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and its expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 401–405 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Stearman R., Dancis A., Klausner R. D. (1996) Iron-regulated DNA binding by the AFT1 protein controls the iron regulon in yeast. EMBO J. 15, 3377–3384 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Pelletier B., Trott A., Morano K. A., Labbé S. (2005) Functional characterization of the iron regulatory transcription factor Fep1 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 25146–25161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Kim K. D., Kim H. J., Lee K. C., Roe J. H. (2011) Multidomain CGFS-type glutaredoxin Grx4 regulates iron homeostasis via direct interaction with a repressor Fep1 in fission yeast. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 408, 609–614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Jbel M., Mercier A., Labbé S. (2011) Grx4 monothiol glutaredoxin is required for iron limitation-dependent inhibition of Fep1. Eukaryot. Cell 10, 629–645 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Mercier A., Pelletier B., Labbé S. (2006) A transcription factor cascade involving Fep1 and the CCAAT-binding factor Php4 regulates gene expression in response to iron deficiency in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Eukaryot. Cell 5, 1866–1881 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Vachon P., Mercier A., Jbel M., Labbé S. (2012) The monothiol glutaredoxin Grx4 exerts an iron-dependent inhibitory effect on Php4 function. Eukaryot. Cell 11, 806–819 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]