Abstract
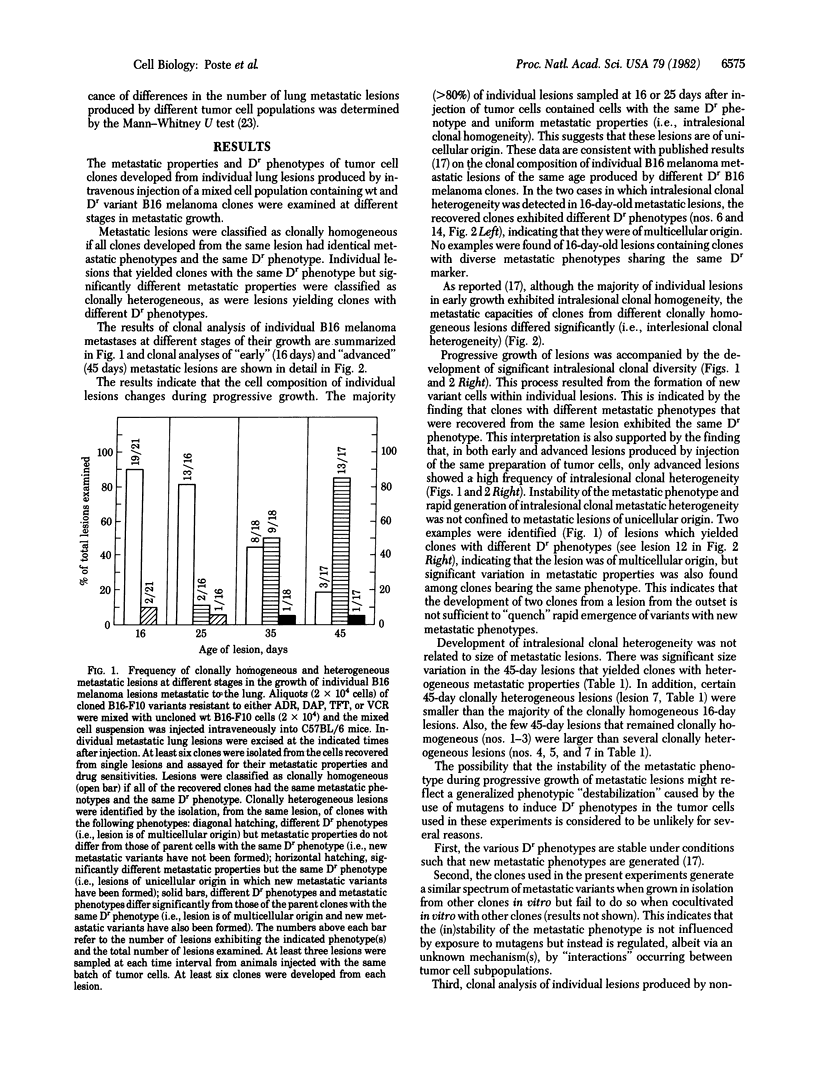
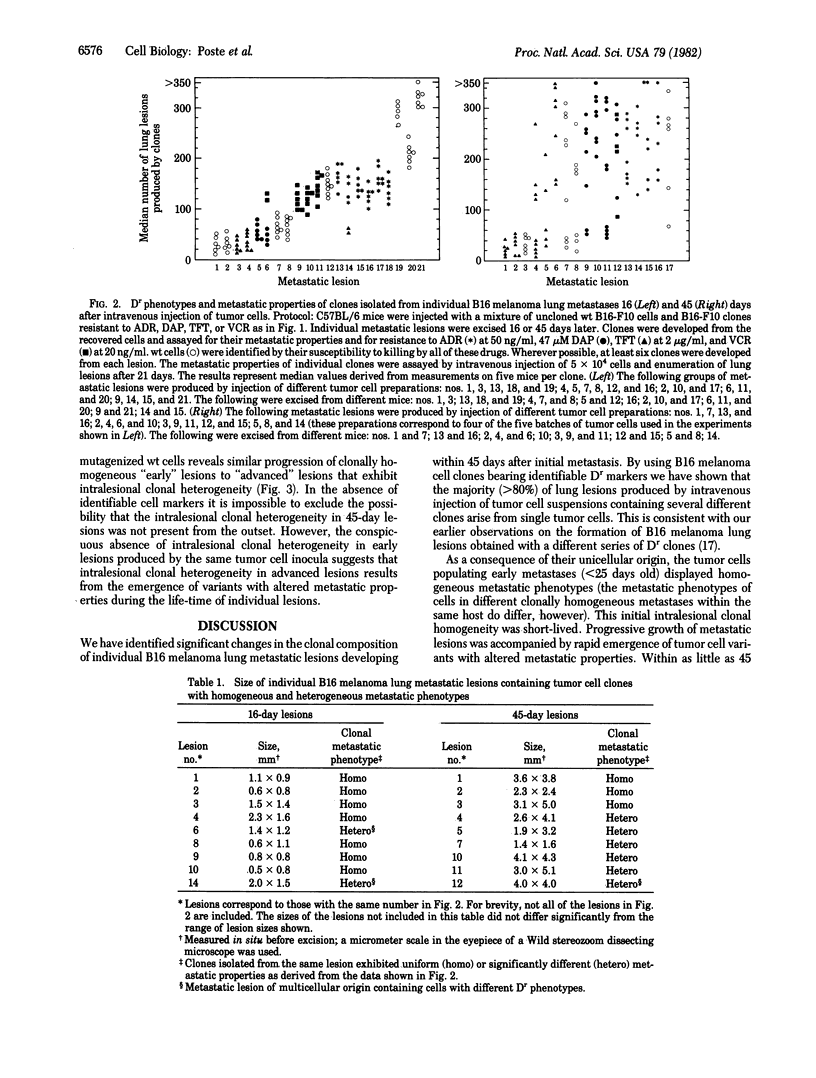
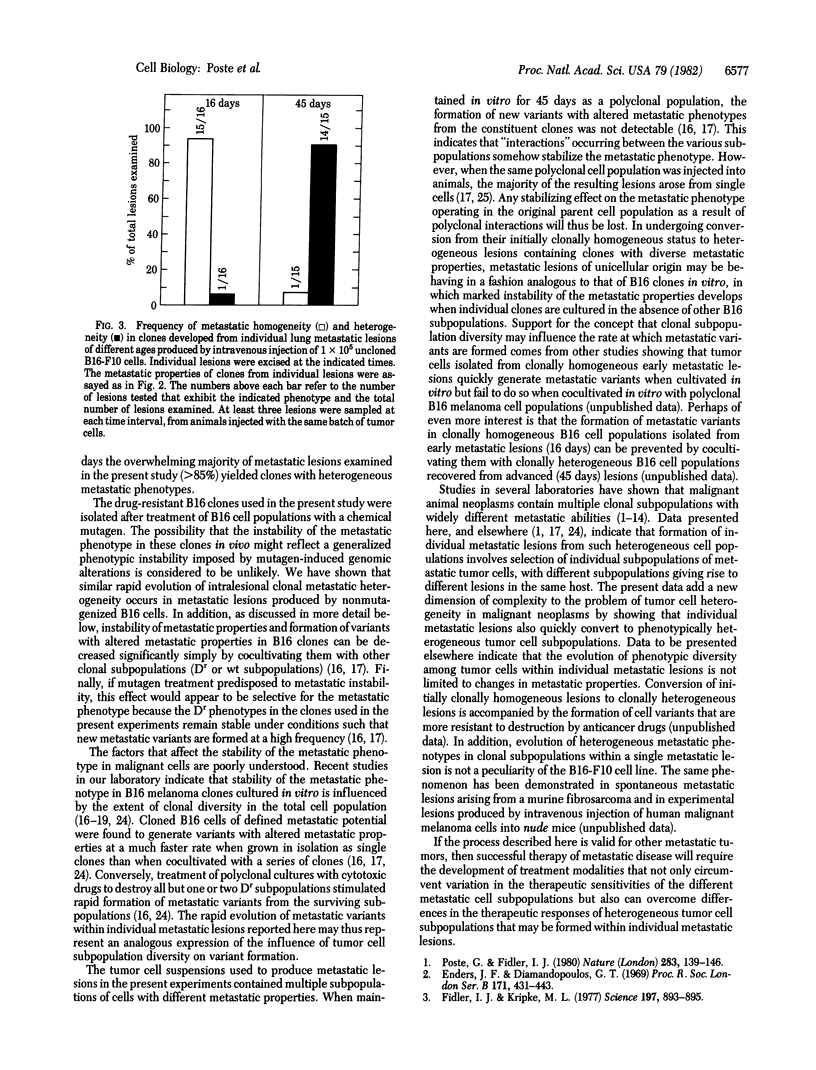
The metastatic properties of tumor cell clones isolated from individual lesions of B16 melanoma metastatic to lung have been examined at different stages in the evolution of metastasis. Clonal analysis of metastatic lesions produced by B16 melanoma populations containing clones with identifiable, stable drug-resistance markers revealed that the majority (greater than 80%) of experimental metastases produced by intravenous injection of tumor cells are of unicellular origin. During the early stages of their growth (less than 25 days after initial tumor cell arrest), the majority of metastatic lesions contain cells with indistinguishable metastatic phenotypes (intralesional clonal homogeneity) although different clonally homogeneous lesions from the same host contain tumor cells with different metastatic phenotypes (interlesional clonal heterogeneity). Progressive growth of metastatic lesions is accompanied by emergence, within originally clonally homogeneous lesions, of variant tumor cells with altered metastatic properties (intralesional clonal heterogeneity). By 40-45 days after initial arrest of injected tumor cells in the lung, 90% of the metastatic lesions are populated by cells with heterogeneous metastatic phenotypes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen T. R. In situ detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by fluorescent Hoechst 33258 stain. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Feb;104(2):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders J. F., Diamandopoulos G. T. A study of variation and progression in oncongenicity in an SV 40-transformed hamster heart cell line and its clones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Feb 25;171(1025):431–443. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Gruys E., Cifone M. A., Barnes Z., Bucana C. Demonstration of multiple phenotypic diversity in a murine melanoma of recent origin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Oct;67(4):947–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Kripke M. L. Metastasis results from preexisting variant cells within a malignant tumor. Science. 1977 Aug 26;197(4306):893–895. doi: 10.1126/science.887927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Selection of successive tumour lines for metastasis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 4;242(118):148–149. doi: 10.1038/newbio242148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart I. R. The selection and characterization of an invasive variant of the B16 melanoma. Am J Pathol. 1979 Dec;97(3):587–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L., Gruys E., Fidler I. J. Metastatic heterogeneity of cells from an ultraviolet light-induced murine fibrosarcoma of recent origin. Cancer Res. 1978 Sep;38(9):2962–2967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri A., Nicolson G. L. Phenotypic drift of metastatic and cell-surface properties of mammary adenocarcinoma cell clones during growth in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1981 Dec;28(6):731–738. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Brunson K. W., Fidler I. J. Specificity of arrest, survival, and growth of selected metastatic variant cell lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4105–4111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science. 1976 Oct 1;194(4260):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.959840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Doll J., Brown A. E., Tzeng J., Zeidman I. Comparison of the metastatic properties of B16 melanoma clones isolated from cultured cell lines, subcutaneous tumors, and individual lung metastases. Cancer Res. 1982 Jul;42(7):2770–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Doll J., Fidler I. J. Interactions among clonal subpopulations affect stability of the metastatic phenotype in polyclonal populations of B16 melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6226–6230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Doll J., Hart I. R., Fidler I. J. In vitro selection of murine B16 melanoma variants with enhanced tissue-invasive properties. Cancer Res. 1980 May;40(5):1636–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G. Experimental systems for analysis of the malignant phenotype. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1982;1(2):141–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00048224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Fidler I. J. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):139–146. doi: 10.1038/283139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Flood M. K. Cells transformed by temperature-sensitive mutants of avian sarcoma virus cause tumors in vivo at permissive and nonpermissive temperatures. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):789–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackpole C. W. Distinct lung-colonizing and lung-metastasizing cell populations in B16 mouse melanoma. Nature. 1981 Feb 26;289(5800):798–800. doi: 10.1038/289798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Withers H. R., Koehler M. W. Heterogeneity and variability of artificial lung colony-forming ability among clones from mouse fibrosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1978 Oct;38(10):3349–3351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge J. E., Starkey J. R., Davis W. C., Cohen A. L. Introduction of metastatic heterogeneity by short-term in vivo passage of a cloned transformed cell line. J Supramol Struct. 1979;12(2):227–243. doi: 10.1002/jss.400120208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Matter A., Vogel K., Burger M. M. Liver-colonizing melanoma cells selected from B-16 melanoma. Int J Cancer. 1979 Jun 15;23(6):854–857. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarin D., Price J. E. Metastatic colonization potential of primary tumour cells in mice. Br J Cancer. 1979 Jun;39(6):740–754. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Yu S. H., Liener I. E., Hebbel R. P., Eaton J. W., McKhann C. F. Characterization of high- and low-metastatic clones derived from a methylcholanthrene-induced murine fibrosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1982 Mar;42(3):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



