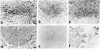
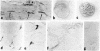
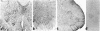
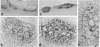
Abstract
Immunocytochemical evidence is presented for the existence of choline acetyltransferase (ChoAcTase), cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase (CSADCase), tyrosine hydroxylase (TyrOHase), and glutamic acid decarboxylase (GluDCase) in large motor neurons of the hypoglossal nucleus and the spinal cord and in nerve terminals of motor end plates in tongue and skeletal muscle of five mammalian species, including man. These enzymes, which are responsible for the synthesis of acetylcholine (AcCho), taurine, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA), respectively, were detected by immunocytochemical studies with monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies raised against the enzymes. Electron microscopy of the neuromuscular junctions showed that the immunoreactivity in each case was confined to the cytoplasmic matrix of presynaptic nerve terminals. Immunoreactivity obtained for each enzyme antibody varied with the species. It was highest in fresh, unfixed muscle and lowest in aldehyde-fixed specimens. Negative controls were obtained with preimmune sera and antisera preabsorbed with pure ChoAcTase, CSADCase, or GluDCase antigen. Double-labeling studies with ChoAcTase antibodies and acetylcholinesterase (AcChoEase) antibodies, AcChoEase enzyme activity, or alpha-bungarotoxin binding indicated that ChoAcTase, AcChoEase, and AcCho receptors were colocalized at the same end plates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown G. L., Dale H. H., Feldberg W. Reactions of the normal mammalian muscle to acetylcholine and to eserine. J Physiol. 1936 Sep 8;87(4):394–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Combined immunocytochemistry and autoradiography after in vivo injections of monoclonal antibody to substance P and 3H-serotonin: Coexistence of two putative transmitters in single raphe cells and fiber plexuses. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1979 Jul 26;156(3):241–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00299625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Engel A. G., Wu J. Y., Palay S. L. Coexistence in human and primate neuromuscular junctions of enzymes synthesizing acetylcholine, catecholamine, taurine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):7027–7030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.7027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Ito M., Tongroach P., Sakurai M., Palay S. Inhibitory effects of motilin, somatostatin, [Leu]enkephalin, [Met]enkephalin, and taurine on neurons of the lateral vestibular nucleus: interactions with gamma-aminobutyric acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3355–3359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Jonsson G., Palay S. L. Serotonin and substance P coexist i, neurons of the rat's central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1582–1586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Lin C. T., Palay S., Yamamoto M., Wu J. Y. Taurine in the mammalian cerebellum: demonstration by autoradiography with [3H]taurine and immunocytochemistry with antibodies against the taurine-synthesizing enzyme, cysteine-sulfinic acid decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2695–2699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Nilaver G., Palay S. L., Beinfeld M. C., Zimmerman E. A., Wu J. Y., O'Donohue T. L. Chemical heterogeneity in cerebellar Purkinje cells: existence and coexistence of glutamic acid decarboxylase-like and motilin-like immunoreactivities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7787–7791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Palay S. L., Wu J. Y. Sagittal cerebellar microbands of taurine neurons: immunocytochemical demonstration by using antibodies against the taurine-synthesizing enzyme cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4221–4225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Wu J. Y., Palay S. L. Immunocytochemical localization of gamma-aminobutyric acid transaminase at cellular and ultrastructural levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2067–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale H. H., Feldberg W., Vogt M. Release of acetylcholine at voluntary motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1936 May 4;86(4):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Lindstrom J. M., Lambert E. H., Lennon V. A. Ultrastructural localization of the acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis and in its experimental autoimmune model. Neurology. 1977 Apr;27(4):307–315. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.4.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Engel A. G., Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase of human erythrocytes and neuromuscular junctions: homologies revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1078–1082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh T. H., Shikimi T., Pickel V. M., Reis D. J. Brain tryptophan hydroxylase: purification of, production of antibodies to, and cellular and ultrastructural localization in serotonergic neurons of rat midbrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3575–3579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., McGeer P. L., Peng J. H., McGeer E. G. The central cholinergic system studied by choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Aug 1;200(2):151–201. doi: 10.1002/cne.902000202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. The number of transmitter molecules in a quantum: an estimate from iontophoretic application of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):465–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y. Purification and characterization of cysteic acid and cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase and L-glutamate decarboxylase from bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4270–4274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]