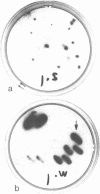
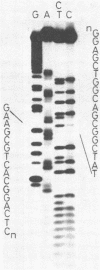
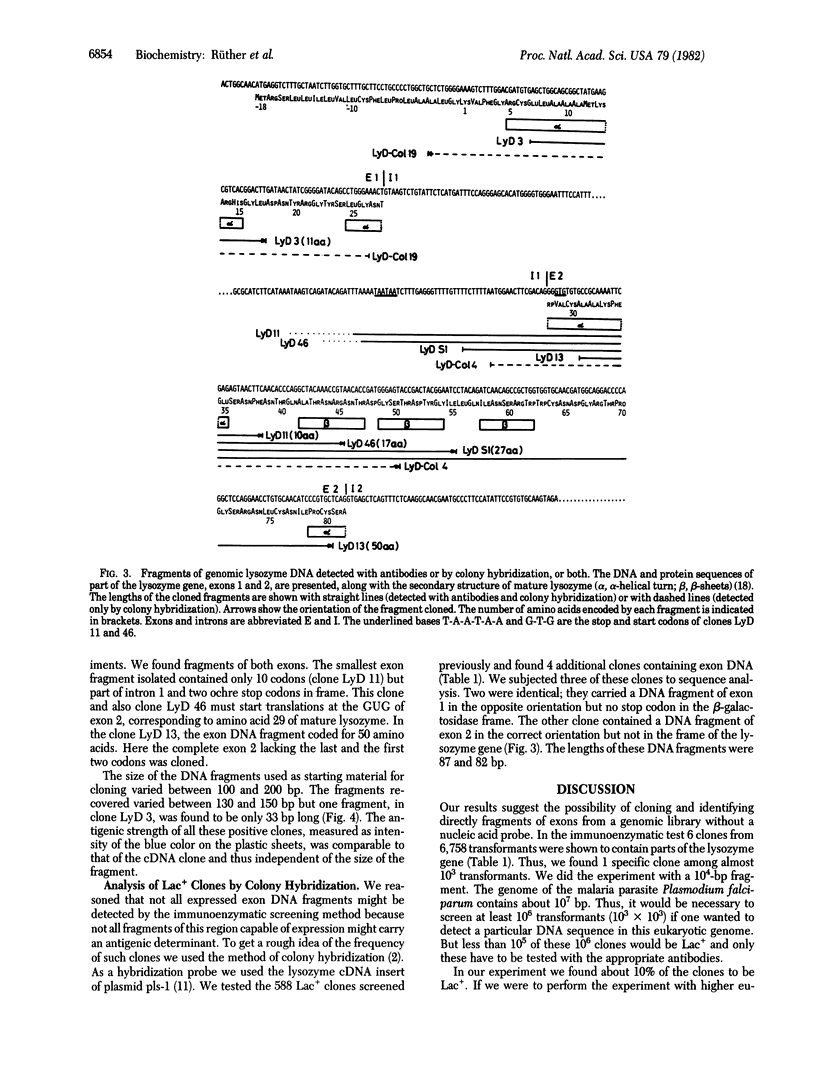
Abstract
A 10-kilobase DNA fragment containing exons 1 and 2 of the chicken lysozyme gene has been randomly cleaved with DNase I. After tailing and cloning into the plasmid pUK230, Lac+ colonies were selected. Colonies harboring expressed fragments of the exons could be detected by an immunoenzymatic assay using antibodies against lysozyme. The smallest fragment coded for 10 amino acids and the largest coded for almost all residues of exon 2. These results suggest that any gene of any genome cloned in this way can be detected if antibodies against the gene product are available.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atassi M. Z., Lee C. L. The precise and entire antigenic structure of native lysozyme. Biochem J. 1978 May 1;171(2):429–434. doi: 10.1042/bj1710429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome S., Gilbert W. Immunological screening method to detect specific translation products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2746–2749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner B., Hynes N. E., Sippel A. E., Jeep S., Chi-Nguyen-Huu M., Schütz G. Immunoadsorption of specific chicken oviduct polysomes. Isolation of ovalbumin, ovomucoid, and lysozyme messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6666–6674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Sippel A. E., Grez M., Schütz G. Exons encode functional and structural units of chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenen M., Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Immunoenzymatic detection of expressed gene fragments cloned in the lac Z gene of E. coli. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):509–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmaier W., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Lurz R., Stratmann M., Blin N., Wurtz T., Hauser H. J., Sippel A. E., Schütz G. Arrangement of coding and intervening sequences of chicken lysozyme gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B., Hans Hopschneider P. Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B., Kania J. Lac repressor can be fused to beta-galactosidase. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):561–563. doi: 10.1038/249561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Wu R. Terminal transferase-catalyzed addition of nucleotides to the 3' termini of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):43–62. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U. Construction and properties of a new cloning vehicle, allowing direct screening for recombinant plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(2):475–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00270503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Koenen M., Otto K., Müller-Hill B. pUR222, a vector for cloning and rapid chemical sequencing of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4087–4098. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A. E., Land H., Lindenmaier W., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Wurtz T., Timmis K. N., Giesecke K., Schütz G. Cloning of chicken lysozyme structural gene sequences synthesized in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3275–3294. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Wallace R. B., Hirose T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6613–6617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Hirayama A., Fujio H., Amano T. A local antigenic determinant distribution in a continuous antigenic region at residues 38-54 of hen egg white lysozyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 1;214(2):750–762. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90082-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]