Abstract
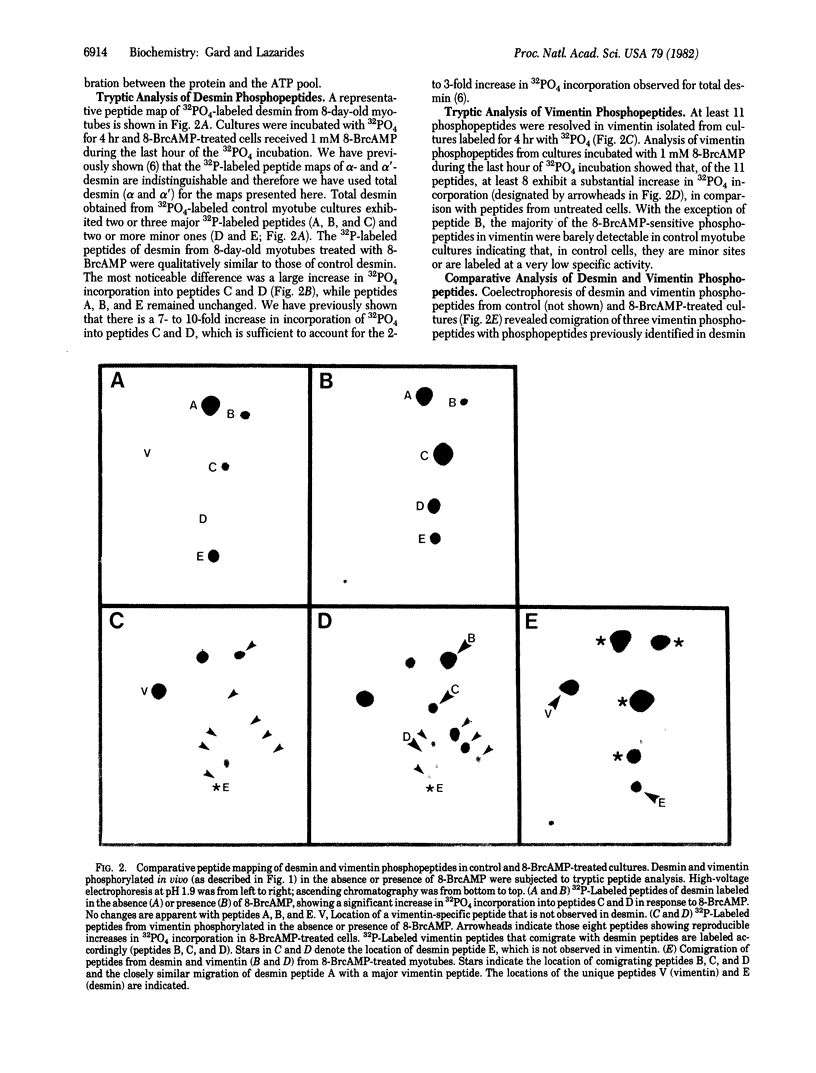
The intermediate filament proteins desmin and vimentin are two of the major 32P phosphate acceptors in chicken myotubes differentiating in tissue culture. Analysis of the desmin and vimentin phosphopeptides by two-dimensional tryptic peptide mapping shows that both proteins are phosphorylated at multiple sites, giving rise to 5 phosphopeptides in desmin and as many as 11 in vimentin. Addition of the cAMP analogue 8-bromoadenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (8-BrcAMP) to the culture medium of mature (8-day-old) myotubes results in a 2- to 3-fold increase in PO4 incorporation into desmin and vimentin. Two-dimensional tryptic analysis of desmin and vimentin from 8-BrcAMP-treated myotubes shows increased 32PO4 incorporation into a subset of the phosphopeptides observed in control cells. Comparison of phosphopeptides from the two proteins shows the presence of at least three comigrating peptides. All three comigrating peptides exhibit cAMP-dependent increases in 32PO4 incorporation in vimentin, while only two of the three exhibit 8-BrcAMP-dependent responses in desmin. While these peptides are the only two that are sensitive to 8-BrcAMP in desmin, vimentin contains additional peptides that exhibit increased 32PO4 incorporation in response to 8-BrcAMP. This result suggests the existence of both common and distinct phosphorylation sites between desmin and vimentin that may be differentially regulated by cAMP. Thus, desmin and vimentin, even though structurally related, may be capable of responding differently to physiological stimuli.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett G. S., Fellini S. A., Toyama Y., Holtzer H. Redistribution of intermediate filament subunits during skeletal myogenesis and maturation in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):577–584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral F., Gottesman M. M. Phosphorylation of the 10-nm filament protein from Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6203–6206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Bell P. B., Lazarides E. Coexistence of desmin and the fibroblastic intermediate filament subunit in muscle and nonmuscle cells: identification and comparative peptide analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3894–3898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Cyclic AMP-modulated phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins in cultured avian myogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. The synthesis and distribution of desmin and vimentin during myogenesis in vitro. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90408-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Comparison of the proteins of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filaments by amino acid sequence analysis: desmin and vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4120–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Desmin and vimentin coexist at the periphery of the myofibril Z disc. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. The existence of an insoluble Z disc scaffold in chicken skeletal muscle. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1253–1268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments--chemical heterogeneity in differentiation. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):649–650. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Balzer D. R., Jr, Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of subunit proteins of intermediate filaments from chicken muscle and nonmuscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):819–823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins by cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter R. L., Taylor S. S. Correlation of the cAMP binding domain with a site of autophosphorylation on the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II from porcine skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9000–9005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Coffino P. Two-dimensional gel analysis of cyclic AMP effects in cultured S49 mouse lymphoma cells: protein modifications, inductions and repressions. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):719–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Cabral F., Gottesman M. M., Goldman R. D. In vitro assembly of homopolymer and copolymer filaments from intermediate filament subunits of muscle and fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3692–3696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments of baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells and bovine epidermal keratinocytes have similar ultrastructures and subunit domain structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4534–4538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Bennett G. S., Toyama Y., Kleinbart F., Holtzer H. Intermediate filament proteins in the developing chick spinal cord. Dev Biol. 1981 Aug;86(1):40–54. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman S. J., Cohen P., Watson D. C., Dixon G. H. The substrate specificity of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):411–421. doi: 10.1042/bj1620411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]