Abstract
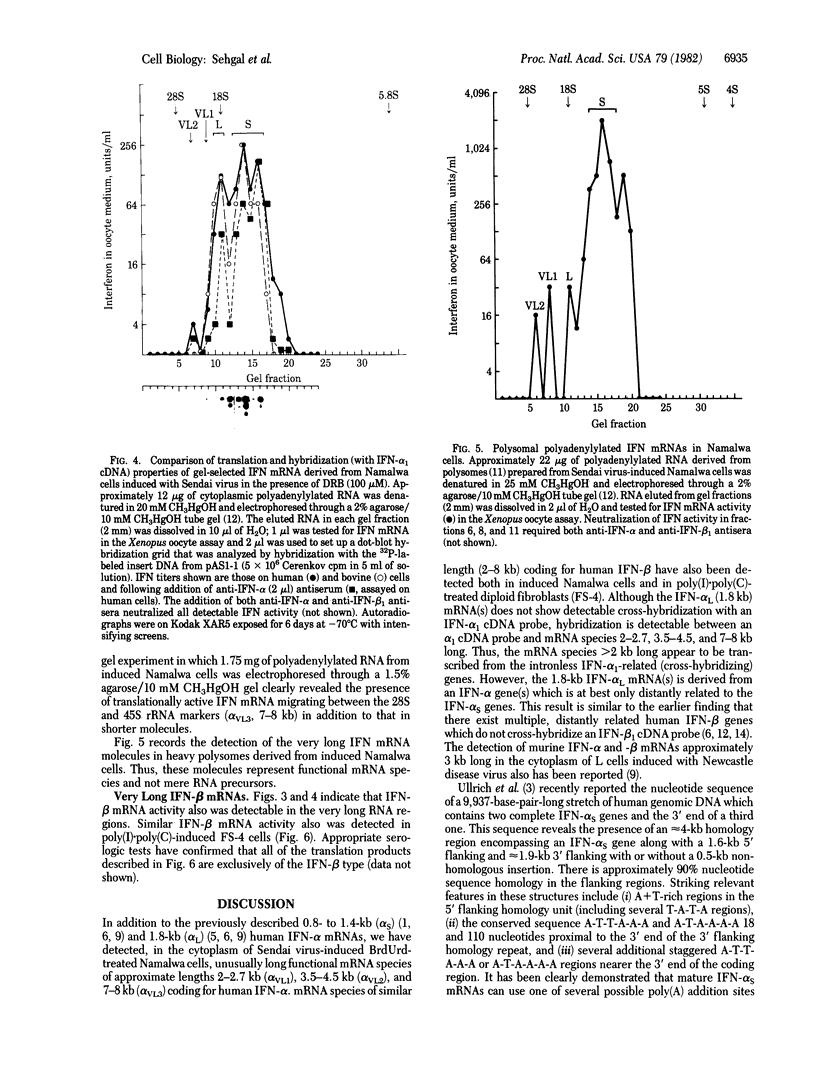
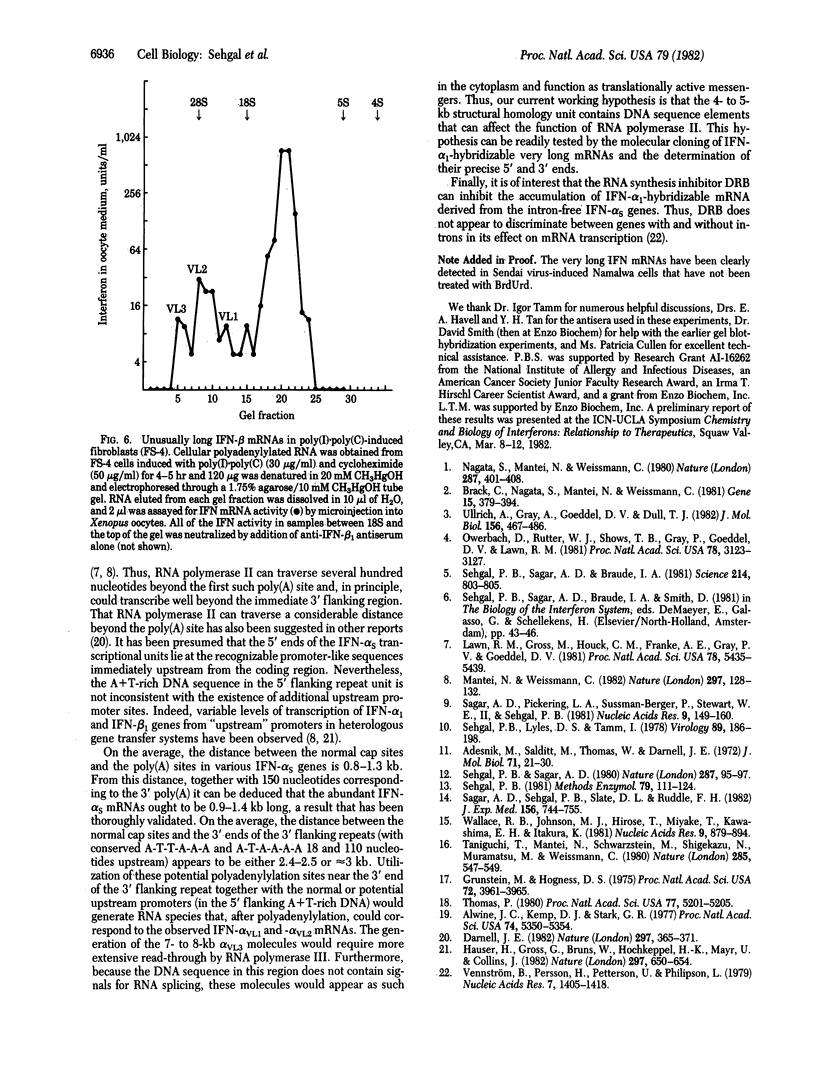
Each of the several intronless interferon (IFN) alpha S genes is embedded in 4- to 5-kilobase (kb) DNA homology units which are arranged more or less in tandem in the human genome. In addition to the expected 0.8- to 1.4-kb-long IFN-alpha S mRNA species, we have detected polyadenylylated RNA molecules approximately 2-2.7, 3.5-4.5, and 7-8 kb long derived from IFN-alpha S genes in the cytoplasm of Sendai virus-induced bromodeoxyuridine-treated human lymphoblastoid (Namalwa) cells. These transcripts were detected by electrophoresis of cytoplasmic polyadenylylated RNA through agarose-CH3HgOH gels followed by blothybridization using an IFN-alpha 1 (a prototype alpha S) cDNA probe and also by translation of the eluted RNA into biologically active IFN in the Xenopus oocyte assay. At least some of these long translationally active RNA molecules appear to represent functional mRNA species because they can be detected in polysomes. In addition, the oocyte translation assay has revealed the presence of unusually long (2-8 kb) IFN-beta mRNA species both in Sendai virus-induced Namalwa cells and in poly(I) . poly(C)-induced diploid human fibroblasts (FS-4). The detection of very long IFN-alpha 1-related mRNA species suggests that some of the DNA sequence features observed in the flanking homology units may affect the transcription of the IFN-alpha S genes. Our hybridization analyses also indicate that the 1.8-kb human IFN-alpha L mRNA(s) shows no detectable cross-hybridization with an IFN-alpha 1 cDNA probe. Thus, this mRNA is derived from a gene(s) that is distinct from the IFN-alpha S set.
Full text
PDF

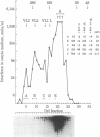
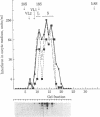
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Salditt M., Thomas W., Darnell J. E. Evidence that all messenger RNA molecules (except histone messenger RNA) contain Poly (A) sequences and that the Poly(A) has a nuclear function. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 28;71(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. Molecular analysis of the human interferon-alpha gene family. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):379–394. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Gross G., Bruns W., Hochkeppel H. K., Mayr U., Collins J. Inducibility of human beta-interferon gene in mouse L-cell clones. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):650–654. doi: 10.1038/297650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Gross M., Houck C. M., Franke A. E., Gray P. V., Goeddel D. V. DNA sequence of a major human leukocyte interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5435–5439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantei N., Weissmann C. Controlled transcription of a human alpha-interferon gene introduced into mouse L cells. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):128–132. doi: 10.1038/297128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. The structure of one of the eight or more distinct chromosomal genes for human interferon-alpha. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):401–408. doi: 10.1038/287401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Rutter W. J., Shows T. B., Gray P., Goeddel D. V., Lawn R. M. Leukocyte and fibroblast interferon genes are located on human chromosome 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3123–3127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar A. D., Pickering L. A., Sussman-Berger P., Stewart W. E., 2nd, Sehgal P. B. Heterogeneity of interferon mRNA species from Sendai virus-induced human lymphoblastoid (Namalva) cells and Newcastle disease virus-induced murine fibroblastoid (L) cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):149–160. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar A. D., Sehgal P. B., Slate D. L., Ruddle F. H. Multiple human beta interferon genes. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):744–755. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Lyles D. S., Tamm I. Superinduction of human fibroblast interferon production: further evidence for increased stability of interferon mRNA. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):186–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B. Procedures to estimate the size of interferon mRNA and use of UV irradiation to estimate the size of its primary transcript. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):111–124. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Sagar A. D., Braude I. A. Further heterogeneity of human alpha interferon mRNA species. Science. 1981 Nov 13;214(4522):803–805. doi: 10.1126/science.6170112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Sagar A. D. Heterogeneity of poly(I) x poly(C)-induced human fibroblast interferon mRNA species. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):95–97. doi: 10.1038/288095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Mantei N., Schwarzstein M., Nagata S., Muramatsu M., Weissmann C. Human leukocyte and fibroblast interferons are structurally related. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):547–549. doi: 10.1038/285547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Goeddel D. V., Dull T. J. Nucleotide sequence of a portion of human chromosome 9 containing a leukocyte interferon gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):467–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Persson H., Pettersson U., Philipson L. A DRB (5,6 dichloro-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole)-resistant adenovirus mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1405–1418. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]