Abstract
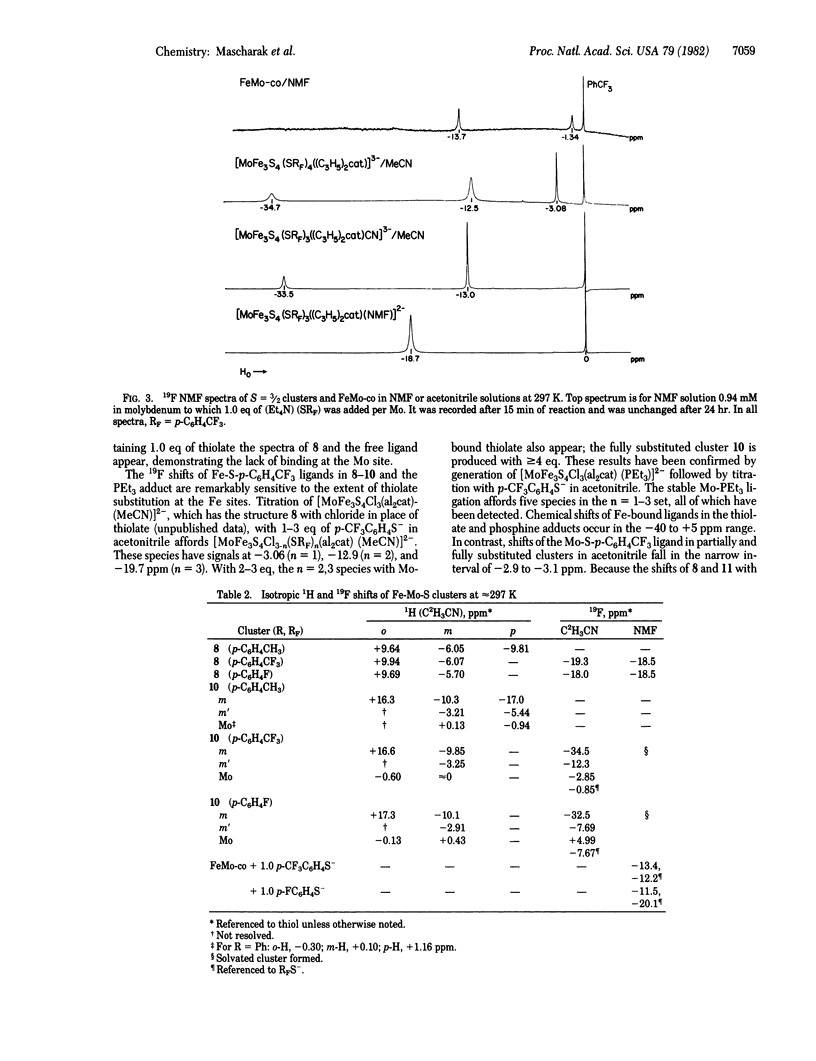
Several properties of the FeMo-cofactor (co) of nitrogenase in N-methylformamide solution at ambient temperature have been investigated by means of 19F NMR spectroscopy. With C6H5CF3 reference signals the magnetic moment per Mo atom was found to be approximately equal to 3.9 BM, consistent with S = 3/2 ground state identified by other spectroscopic methods at low temperature. Reaction of FeMo-co with 1.0 eq of RFS- (RF = p-C6H4CF3, p-C6H4F) afforded isotropically shifted signals indicative of binding to a paramagnetic cluster. By comparison with the spectra of Fe-S and Fe-Mo-S species derivatized with RFS-, including the cubane-type MoFe3S4 clusters with S = 3/2 ground states, it was concluded that the essential FeMo-co cluster structure remains intact and a Fe atom is the probable thiolate binding site. An interaction of FeMo-co with C6H5S- had been detected earlier by low temperature EPR spectroscopy. The binding site assignment is based on large observed isotropic shifts (ca. -12ppm) compared to the much smaller values found for Mo-SRF ligands in MoFe3S4 clusters and anticipated in FeMo-co on the basis of recent spectroscopic results. Isotropic 19F shifts have proven extremely sensitive to electronic and structural features of Fe-S and Fe-Mo-S clusters. The inclusion of a 19F NMR label in FeMo-co should prove of utility in further investigation of cofactor properties and reactions.
Full text
PDF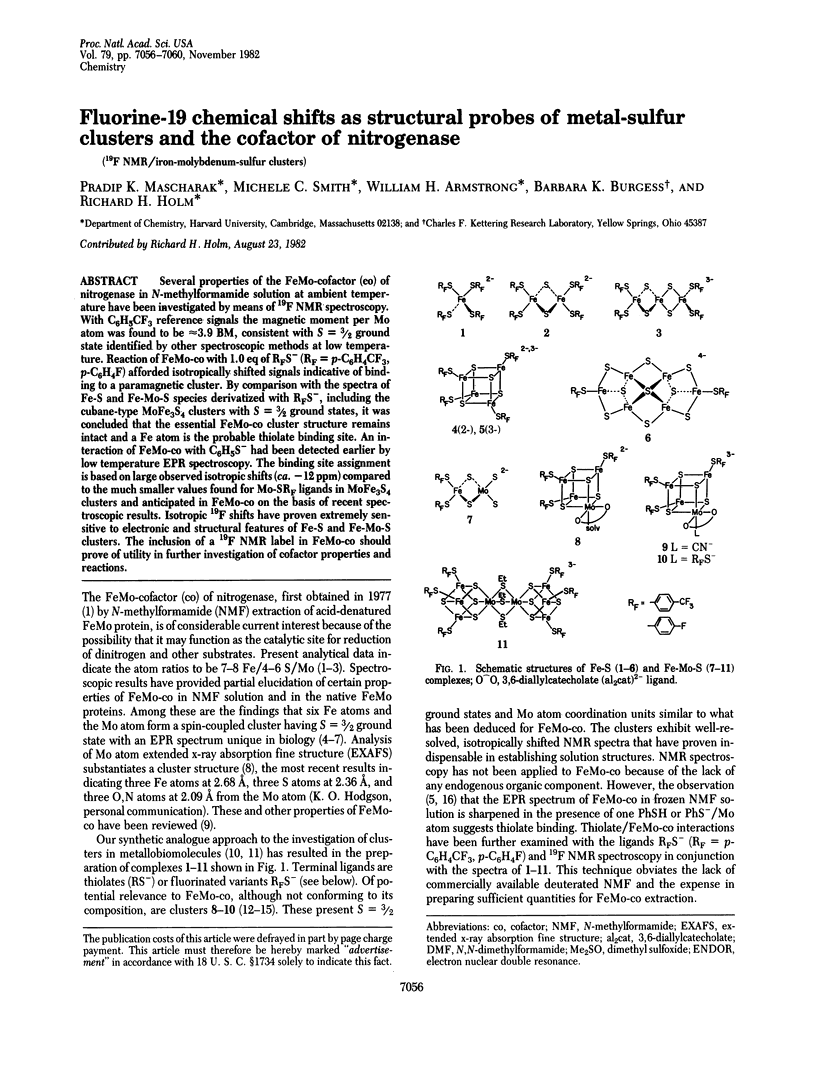



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonio M. R., Averill B. A., Moura I., Moura J. J., Orme-Johnson W. H., Teo B. K., Xavier A. V. Core dimensions in the 3Fe cluster of Desulfovibrio gigas ferredoxin II by extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6646–6649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess B. K., Jacobs D. B., Stiefel E. I. Large-scale purification of high activity Azotobacter vinelandII nitrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 10;614(1):196–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess B. K., Stiefel E. I., Newton W. E. Oxidation-reduction properties and complexation reactions of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):353–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D., O'Donnell S., Furey W., Jr, Robbins A. H., Stout C. D. Iron-sulfur clusters and protein structure of Azotobacter ferredoxin at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 15;158(1):73–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90451-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh B. H., Münck E., Orme-Johnson W. H. Nitrogenase XI: Mössbauer studies on the cofactor centers of the MoFe protein from Azotobacter vinelandii OP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 25;576(1):192–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90497-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibers J. A., Holm R. H. Modeling coordination sites in metallobiomolecules. Science. 1980 Jul 11;209(4453):223–235. doi: 10.1126/science.7384796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz D. M., Jr, McMillan R. S., Burgess B. K., Mortenson L. E., Holm R. H. Identification of iron-sulfur centers in the iron-molybdenum proteins of nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4986–4989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münck E., Rhodes H., Orme-Johnson W. H., Davis L. C., Brill W. J., Shah V. K. Nitrogenase. VIII. Mössbauer and EPR spectroscopy. The MoFe protein component from Azotobacter vinelandii OP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 21;400(1):32–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. D., Poe M. Contact shifts and magnetic susceptibilities in iron-sulfur proteins as determined from nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:304–317. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings J., Shah V. K., Chisnell J. R., Brill W. J., Zimmermann R., Münck E., Orme-Johnson W. H. Novel metal cluster in the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Spectroscopic evidence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1001–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. S., Pan W. H., Friesen G. D., Burgess B. K., Corbin J. L., Stiefel E. I., Newton W. E. Iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Modified extraction methods as probes for composition. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8042–8048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G. Isolation of thiomolybdate compounds from the molybdenum-iron protein of clostridial nitrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):345–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



