Abstract
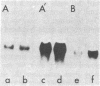
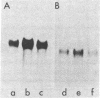
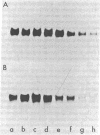
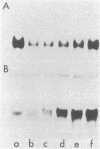
Auxin-responsive cDNA clones have been isolated from a cDNA library prepared from elongating soybean hypocotyl poly(A)+RNA. The expression of two such sequences has been assessed by RNA blot hybridization analyses during normal developmental transitions in the soybean hypocotyl and during incubation of sections excised from the region of cell elongation. The concentrations of these poly(A)+RNAs are higher in the elongating zone than in the apical and mature zones of the hypocotyl. Both poly(A)+RNAs are depleted during incubation of the sections in the absence of auxin. The loss of one of these sequences (pJCW1) is prevented by the addition of auxin to the incubation medium while the other sequence (pJCW2) increases above the initial level in the presence of auxin. The addition of auxin to auxin-depleted tissue in which the sequences are depleted results in rapid accumulation of these poly(A)+RNAs; pJCW1 accumulates to the control level while pJCW2 increases well above the control level. These data along with others [Baulcombe, D. C. & Key, J. L. (1980) J. Biol. Chem. 255, 8907-8913] demonstrate directly a highly selective effect of auxin on the expression of a small number of mRNAs in tissues undergoing both cell elongation and cell division in response to auxin. Although the data are suggestive of a close association betwen auxin action and altered gene expression, a causal relationship is not established. It seems highly unlikely, however, that such specific effects of auxin on gene expression are unimportant in auxin physiology.
Keywords: hormone action, cell elongation, gene expression
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazaral M., Helinski D. R. Circular DNA forms of colicinogenic factors E1, E2 and E3 from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 14;36(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Rosbash M. Polynucleotide sequences in eukaryotic DNA and RNA that form ribonuclease-resistant complexes with polyuridylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Erlich H. A., Schimke R. T., Cohen S. N. Phenotypic expression in E. coli of a DNA sequence coding for mouse dihydrofolate reductase. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):617–624. doi: 10.1038/275617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. L., Ray P. M. Timing of the auxin response in coleoptiles and its implications regarding auxin action. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Jan;53(1):1–20. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield V., Boyer H. W., Yanofsky C., Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Plasmid ColEl as a molecular vehicle for cloning and amplification of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Barnett N. M., Lin C. Y. RNA and protein biosynthesis and the regulation of cell elongation by auxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Aug 9;144(1):49–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb34000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Hanson J. B. Some effects of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on soluble nucleotides & nucleic acid of soybean seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1961 Mar;36(2):145–152. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Ingle J. REQUIREMENT FOR THE SYNTHESIS OF DNA-LIKE RNA FOR GROWTH OF EXCISED PLANT TISSUE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52(6):1382–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L. Ribonucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis as Essential Processes for Cell Elongation. Plant Physiol. 1964 May;39(3):365–370. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noodén L. D., Thimann K. V. EVIDENCE FOR A REQUIREMENT FOR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS FOR AUXIN-INDUCED CELL ENLARGEMENT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50(2):194–200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebstock T. L., Hamner C. L., Sell H. M. The Influence of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid on the Phosphorus Metabolism of Cranberry Bean Plants (Phaseolus vulgaris). Plant Physiol. 1954 Sep;29(5):490–491. doi: 10.1104/pp.29.5.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOOG F. Substances involved in normal growth and differentiation of plants. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1953 Aug;6:1-16; discussion, 16-21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöffl F., Key J. L. An analysis of mRNAs for a group of heat shock proteins of soybean using cloned cDNAs. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):301–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Hammett J. R., Key J. L. Sequence complexity of polyadenylated ribonucleic acid from soybean suspension culture cells. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2725–2731. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologis A., Ray P. M. Early auxin-regulated polyadenylylated mRNA sequences in pea stem tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):418–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhoef L. N., Stahl C. A. Separation of two responses to auxin by means of cytokinin inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1822–1825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma D. P., Maclachlan G. A., Byrne H., Ewings D. Regulation and in vitro translation of messenger ribonucleic acid for cellulase from auxin-treated pea epicotyls. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1019–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Buell G. N., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of double-stranded DNA complementary to lysozyme, ovomucoid, and ovalbumin mRNAs. Optimization for full length second strand synthesis by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2483–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurfluh L. L., Guilfoyle T. J. Auxin- and ethylene-induced changes in the population of translatable messenger RNA in Basal sections and intact soybean hypocotyl. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):338–340. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurfluh L. L., Guilfoyle T. J. Auxin-induced changes in the patterns of protein synthesis in soybean hypocotyl. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):357–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurfluh L. L., Guilfoyle T. J. Auxin-induced changes in the population of translatable messenger RNA in elongating sections of soybean hypocotyl. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):332–337. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]