Abstract
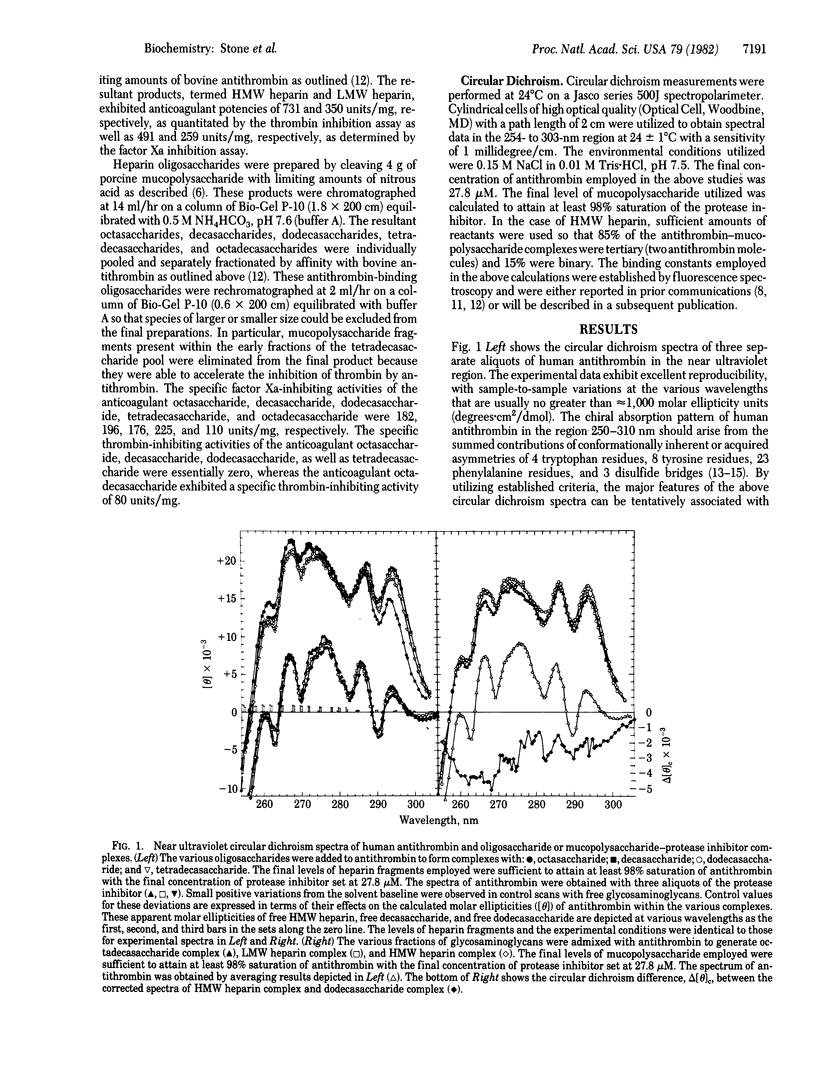
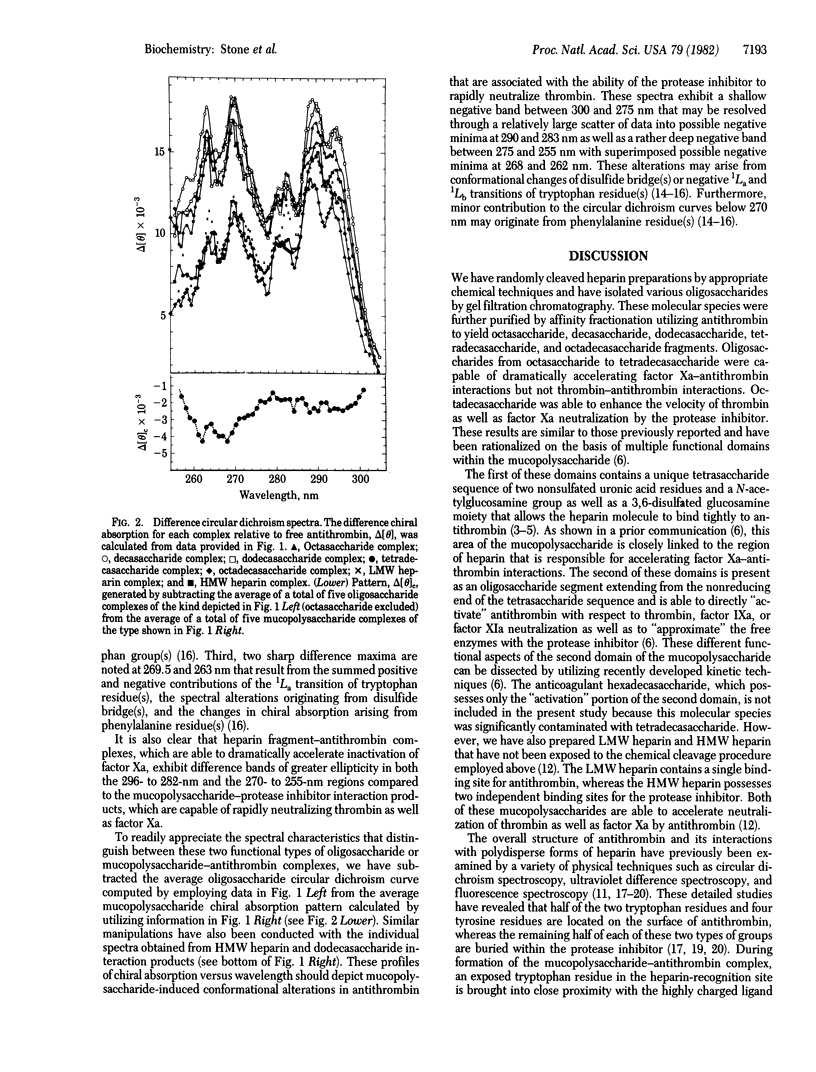
We have utilized circular dichroism spectroscopy to examine the interaction of antithrombin with heparin-derived oligosaccharides and mucopolysaccharides of various sizes. Our studies demonstrate that the various complexes exhibit two major types of chiral absorption spectra. The first of these patterns is seen when octasaccharide, decasaccharide, dodecasaccharide, or tetradecasaccharide fragments bind to the protease inhibitor. The circular dichroism spectra of these complexes when compared to the spectrum of free antithrombin show several distinguishing characteristics. On the one hand, there is a marked general increase in positive chiral absorption that is maximal at 296 and 288 nm and 290 and 282.5 nm. These observations indicate perturbation of “buried” and “exposed” tryptophan residues. On the other hand, a significant augmentation in circular dichroism that peaks at 269.5 and 263 nm is noted. These findings are probably due to the summed positive and negative contributions arising from tryptophan residue(s), disulfide bridge(s), and phenylalanine residue(s). Given that these heparin fragments are able to accelerate factor Xa-antithrombin interactions but not thrombin-antithrombin interactions, the above spectral transitions must be associated with either the binding of a critical domain of the oligosaccharides to the protease inhibitor or the “activation” of the protease inhibitor with respect to factor Xa neutralization. The second of these patterns is apparent when octadecasaccharide, low molecular weight heparin (6,500), and high molecular weight heparin (22,000) interact with antithrombin. The circular dichroism spectra of these complexes compared to the spectrum of free protease inhibitor are similar to the first pattern except for changes within the 292- to 282-nm and 275- to 255-nm regions. The subtraction of the first pattern from the second pattern reveals a shallow negative band between 300 and 275 nm with potential negative minima at 290 and 283 nm as well as a deep negative band between 275 and 255 nm with possible negative minima at 268 and 262 nm. This chiral absorption profile is most likely to arise from conformational changes of a disulfide bridge(s). However, we cannot completely exclude the possibility that the above circular dichroism difference curve might be explained on the basis of transitions originating from a tryptophan residue(s). Given our method for generating the above data, these spectral alterations must be associated with the binding of a second critical domain of the mucopolysaccharide to antithrombin that is required for rapid complex formation with thrombin or the activation of the protease inhibitor with respect to the neutralization of the latter enzyme.
Keywords: oligosaccharides, mucopolysaccharides, conformational change
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler D., Rosenberg R., Jordan R. Fractionation of low molecular weight heparin species and their interaction with antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2902–2913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn M. N., Sibley C. C. The heparin binding site of antithrombin III. Evidence for a critical tryptophan residue. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):824–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Björk I., Hopwood J., Lindahl U. Anticoagulant activity of heparin: separation of high-activity and low-activity heparin species by affinity chromatography on immobilized antithrombin. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 1;66(1):90–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan R. E., Favreau L. V., Braswell E. H., Rosenberg R. D. Heparin with two binding sites for antithrombin or platelet factor 4. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan R. E., Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Rosenberg R. D. The binding of low molecular weight heparin to hemostatic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10073–10080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam L. H., Silbert J. E., Rosenberg R. D. The separation of active and inactive forms of heparin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):570–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Thunberg L., Leder I. G. Evidence for a 3-O-sulfated D-glucosamine residue in the antithrombin-binding sequence of heparin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longas M. O., Ferguson W. S., Finlay T. H. A disulfide bond in antithrombin is required for heparin-accelerated thrombin inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3436–3441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Björk I. Binding of low-affinity and high-affinity heparin to antithrombin. Ultraviolet difference spectroscopy and circular dichroism studies. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3339–3344. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Nyström C., Björk I. The size and shape of human and bovine antithrombin III. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):195–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. T., Shore J. D. Binding of high affinity heparin to antithrombin III. Characterization of the protein fluorescence enhancement. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11065–11072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. T., Srinivasan K. R., Björk I., Shore J. D. Binding of high affinity heparin to antithrombin III. Stopped flow kinetic studies of the binding interaction. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11073–11079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. Multiple functional domains of the heparin molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):829–833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Armand G., Lam L. Structure-function relationships of heparin species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3065–3069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Lam L. Correlation between structure and function of heparin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1218–1222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H. Aromatic contributions to circular dichroism spectra of proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):113–175. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H., Horwitz J., Billups C. Fine structure in the near-ultraviolet circular dichroism and absorption spectra of tryptophan derivatives and chymotrypsinogen A at 77 degrees K. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3205–3213. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villaneuva G. B., Danishefsky I. Evidence for a heparin-induced conformational change on antithrombin III. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):803–809. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



