Abstract
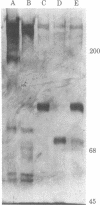
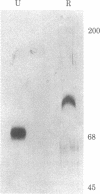
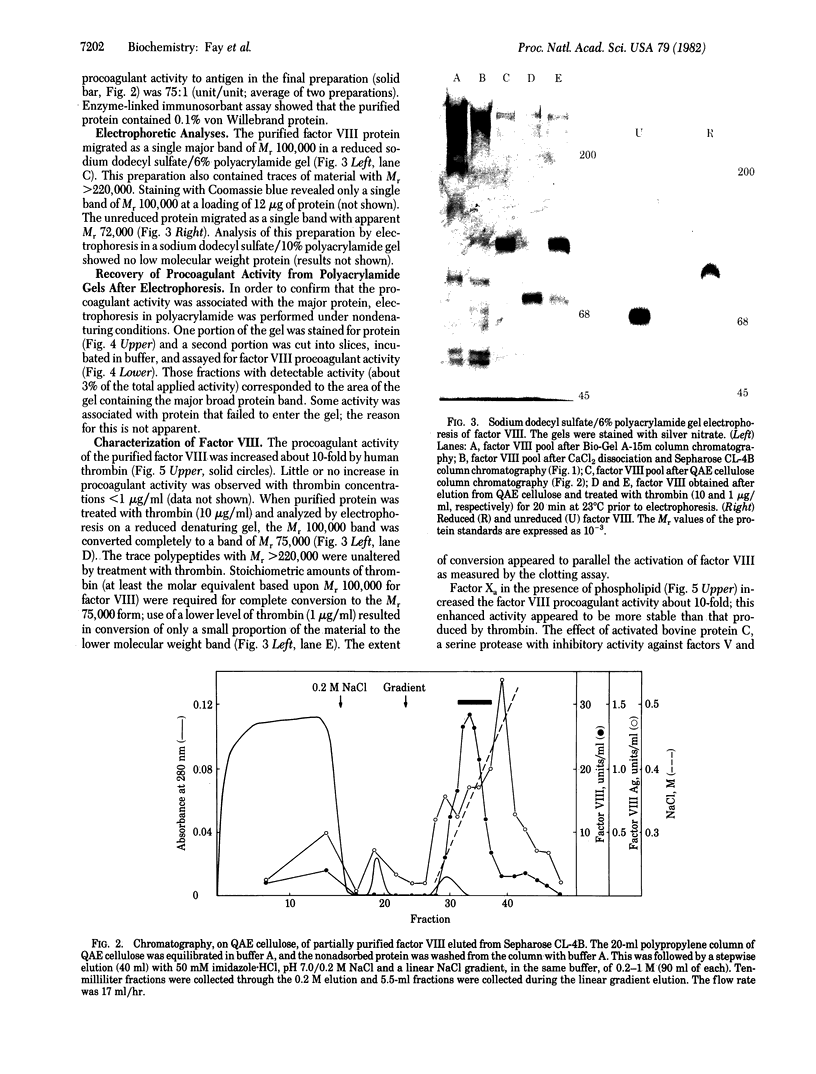
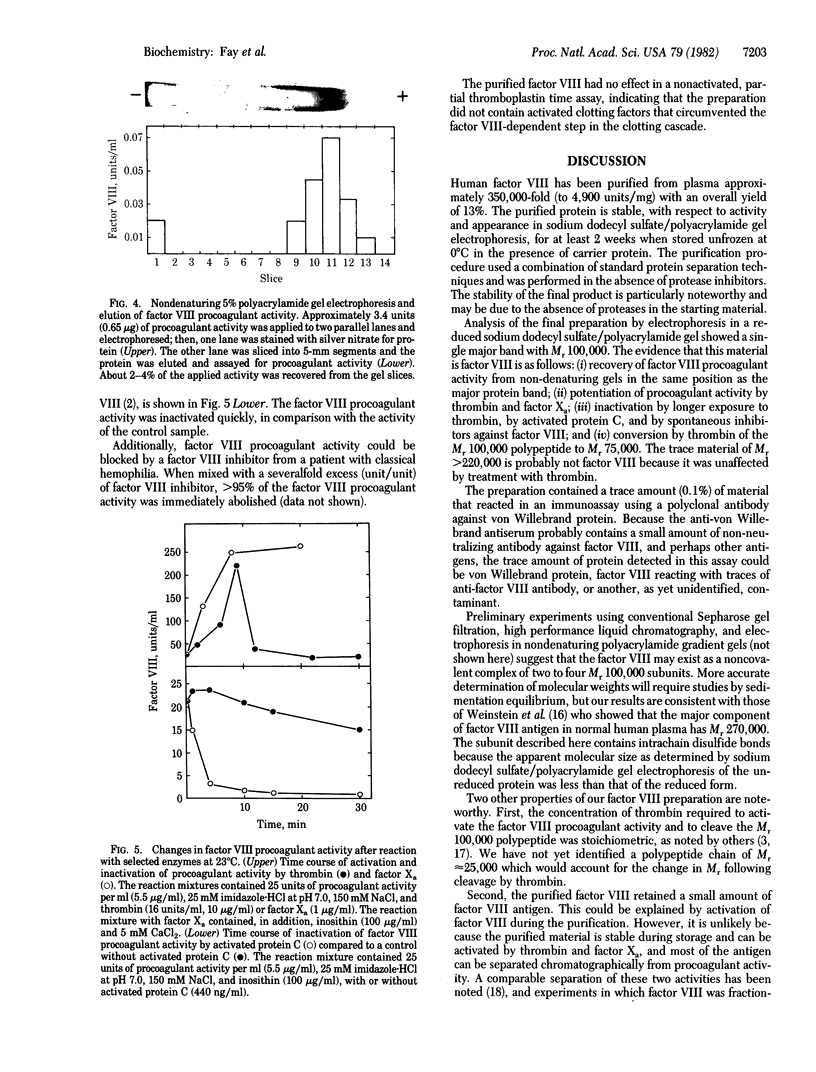
Human factor VIII was purified 350,000-fold (relative to plasma) from a commercial factor VIII concentrate. The procedure used standard protein separation techniques and was performed in the absence of protease inhibitors. The product has a specific activity of 4,900 units/mg, an activity-to-antigen ratio of 75:1 (unit/unit) and no more than 0.1% von Willebrand protein. Electrophoresis of the reduced protein in a denaturing polyacrylamide gel showed a single major band of Mr 100,000. Procoagulant activity was eluted from a nondenaturing gel after electrophoresis in the region of the single major band. Thrombin converted the Mr 100,000 polypeptide to a polypeptide of Mr 75,000. The procoagulant activity was increased 10-fold by thrombin or factor Xa and was completely inhibited by activated protein C or factor VIII inhibitor plasma. This factor VIII preparation consists of a single high molecular weight polypeptide chain and has the highest specific activity thus far reported for human factor VIII.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Davie E. W. Activation of human factor X (Stuart factor) by a protease from Russell's viper venom. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5253–5260. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass D. N., Knutson G. J., Katzmann J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to porcine factor VIII coagulant and their use in the isolation of active coagulant protein. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):594–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Zimmerman T. S. Characterization of the human factor VIII procoagulant protein with a heterologous precipitating antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. Cancer Res. 1960 Nov;20:1495–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. The factor VIII complex: structure and function. Blood. 1981 Jul;58(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Trabold N. C. The effect of thrombin on human factor VIII. Cleavage of the factor VIII procoagulant protein during activation. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jan;97(1):50–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. The synthesis of sulfated dextran beads for isolation of human plasma coagulation factors II, IX, and X. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):304–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner H. M., Barrow E. S., Graham J. B. Radioimmunoassay for coagulant factor VIII-related antigen (VIII:CAg). Thromb Res. 1979 Jan;14(1):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Reactions of thrombin with human factor VIII/von Willebrande factor protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10606–10611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Studies on human antihemophilic factor. Evidence for a covalently linked subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):925–937. doi: 10.1172/JCI108369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M., Chute L., Deykin D. Analysis of factor VIII coagulant antigen in normal, thrombin-treated, and hemophilic plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5137–5141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Powell A. E. Immunologic differentiation of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and von Willebrand's dissase, with observations on combined deficiencies of antihemophilic factor and proaccelerin (factor V) and on an acquired circulating anticoagulant against antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI106480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]