Abstract
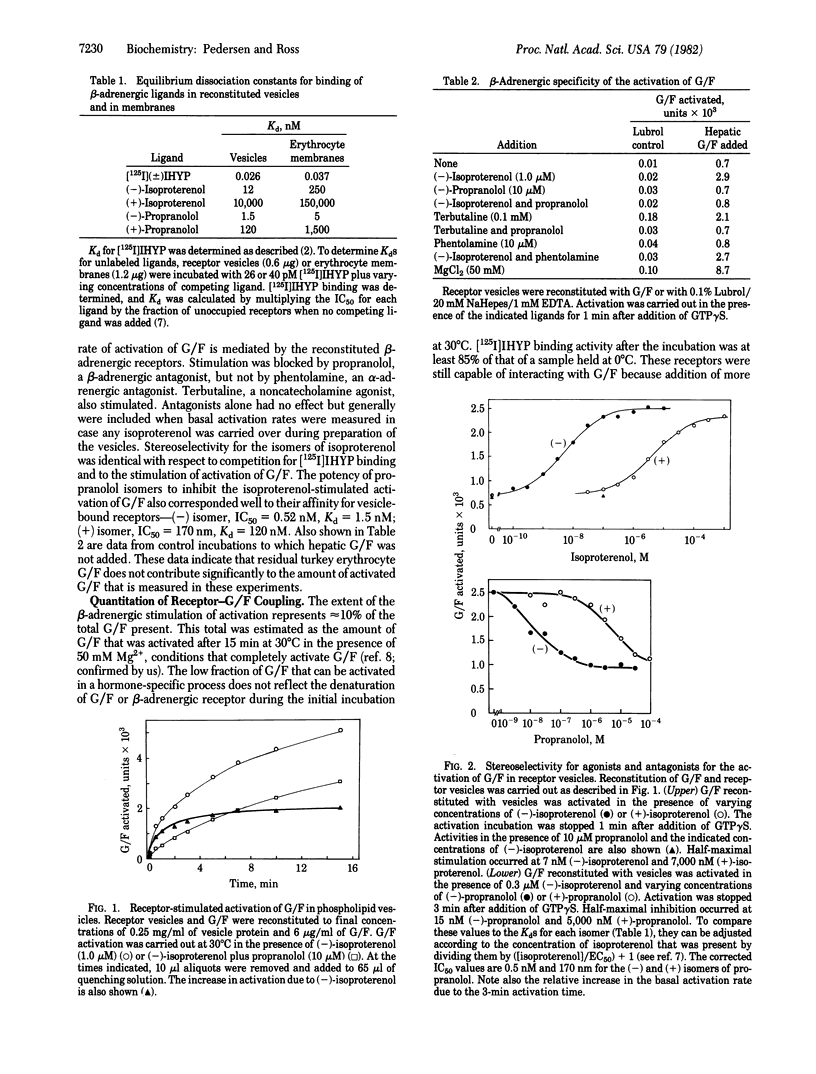
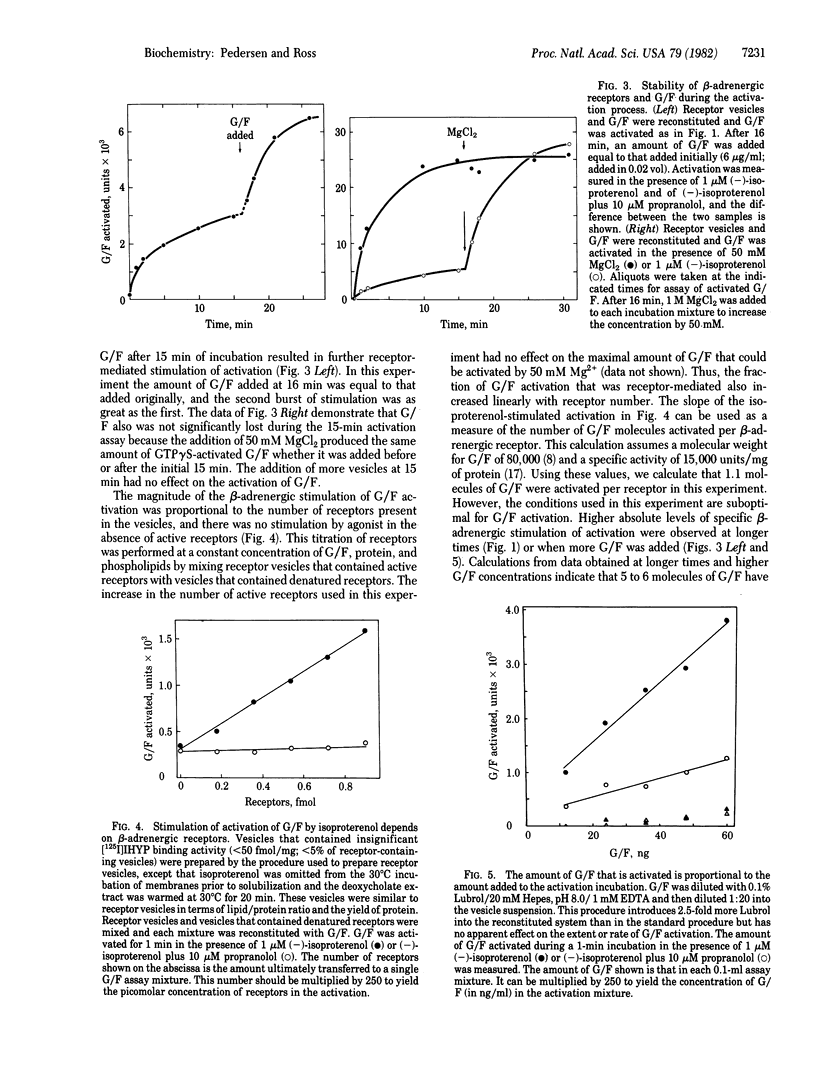
A procedure for the functional reconstitution of beta-adrenergic receptors and the stimulatory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G/F) of adenylate cyclase in phospholipid vesicles is described. beta-Adrenergic receptors were solubilized from turkey erythrocyte plasma membranes and reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles by the addition of dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine and removal of detergent by gel filtration. This procedure restored the ability to bind [125I]iodohydroxybenzylpindolol and [3H]dihydroalprenolol. Purified rabbit hepatic G/F that was added to the receptor vesicles could be stably activated by guanosine 5'-[3-thio]triphosphate at a low rate, and this activation was increased up to 4-fold in the presence of beta-adrenergic agonists. This stimulation of the activation of G/F was specific for beta-adrenergic agonists and could be specifically blocked by beta-adrenergic antagonists. Stimulation was proportional to the concentration of vesicles containing active beta-adrenergic receptor. Under optimal conditions, 5 to 6 molecules of G/F were activated per receptor, indicating that catalytic activation of G/F by receptor was reconstituted.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Citri Y., Schramm M. Resolution, reconstitution and kinetics of the primary action of a hormone receptor. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):297–300. doi: 10.1038/287297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F., Cassel D., Levkovitz H., Lowe M., Selinger Z. Guanosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate). An inhibitor of adenylate cyclase stimulation by guanine nucleotides and fluoride ions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9829–9834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eimerl S., Neufeld G., Korner M., Schramm M. Functional implantation of a solubilized beta-adrenergic receptor in the membrane of a cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):760–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. W., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of beta-adrenergic receptors into phospholipid vesicles: restoration of [125I]iodohydroxybenzylpindolol binding to digitonin-solubilized receptors. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(6):407–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Dromerick A. W., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Purification and properties of the turkey erythrocyte protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12911–12919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Mason J. T. Geometric packing constraints in egg phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):308–310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Gill D. M., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-promoted coupling of the beta-adrenergic receptor with the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):775–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Wiklund R. A., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Binding of (125I)iodohydroxybenzylpindolol to putative beta-adrenergic receptors of rat glioma cells and other cell clones. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1221–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The guanine nucleotide activating site of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Identification by ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11416–11423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Resolution of some components of adenylate cyclase necessary for catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):6966–6969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Maguire M. E., Sturgill T. W., Biltonen R. L., Gilman A. G. Relationship between the beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5761–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Schatz G. Purification of subunit composition of cytochrome c1 from bakers' yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:222–229. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4888–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11517–11526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



