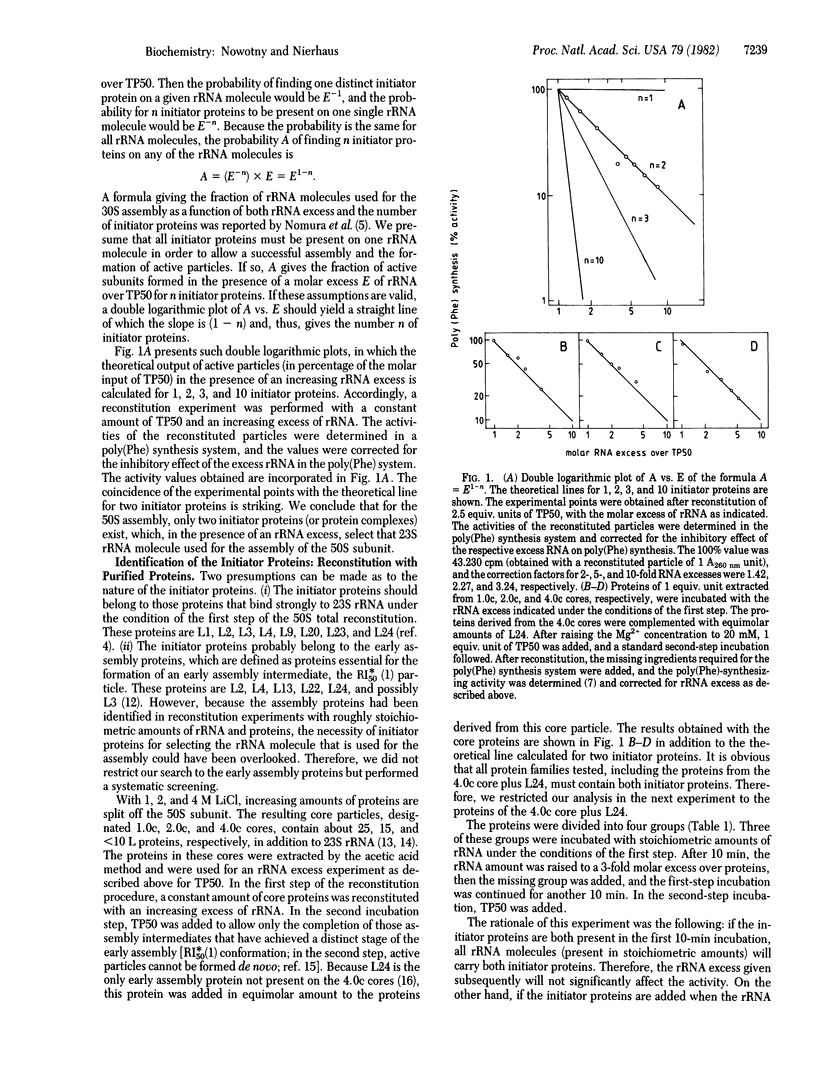
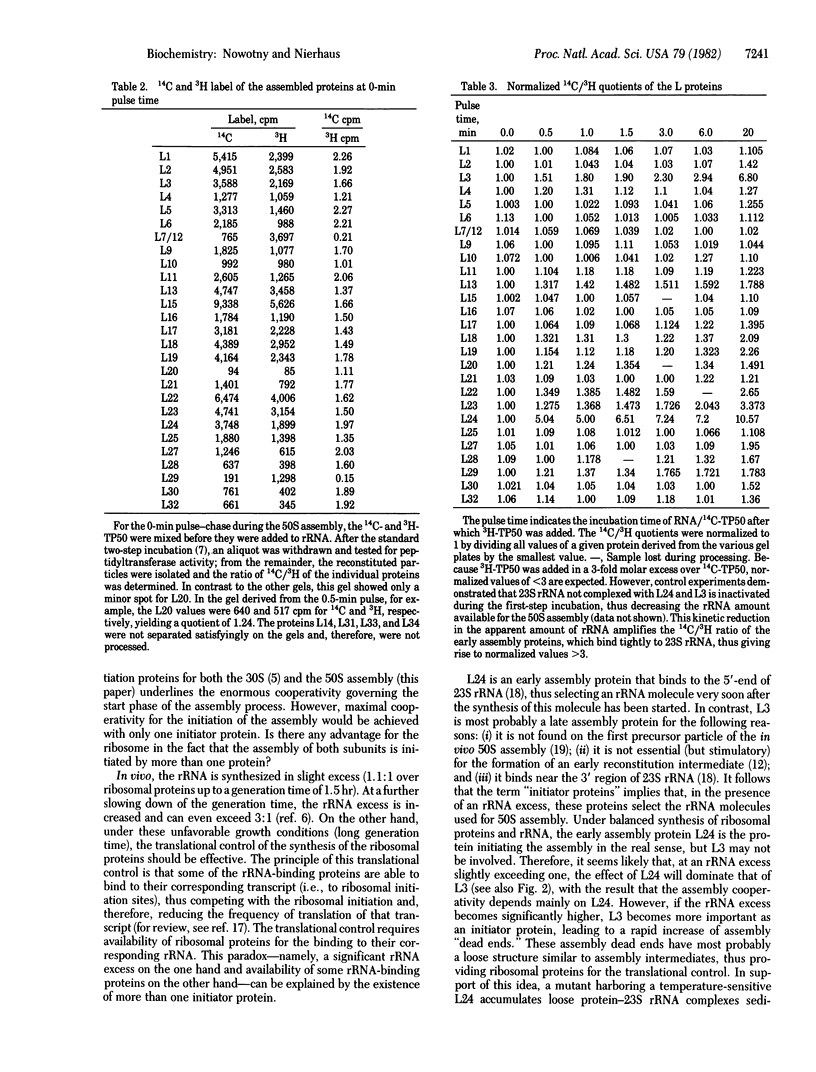
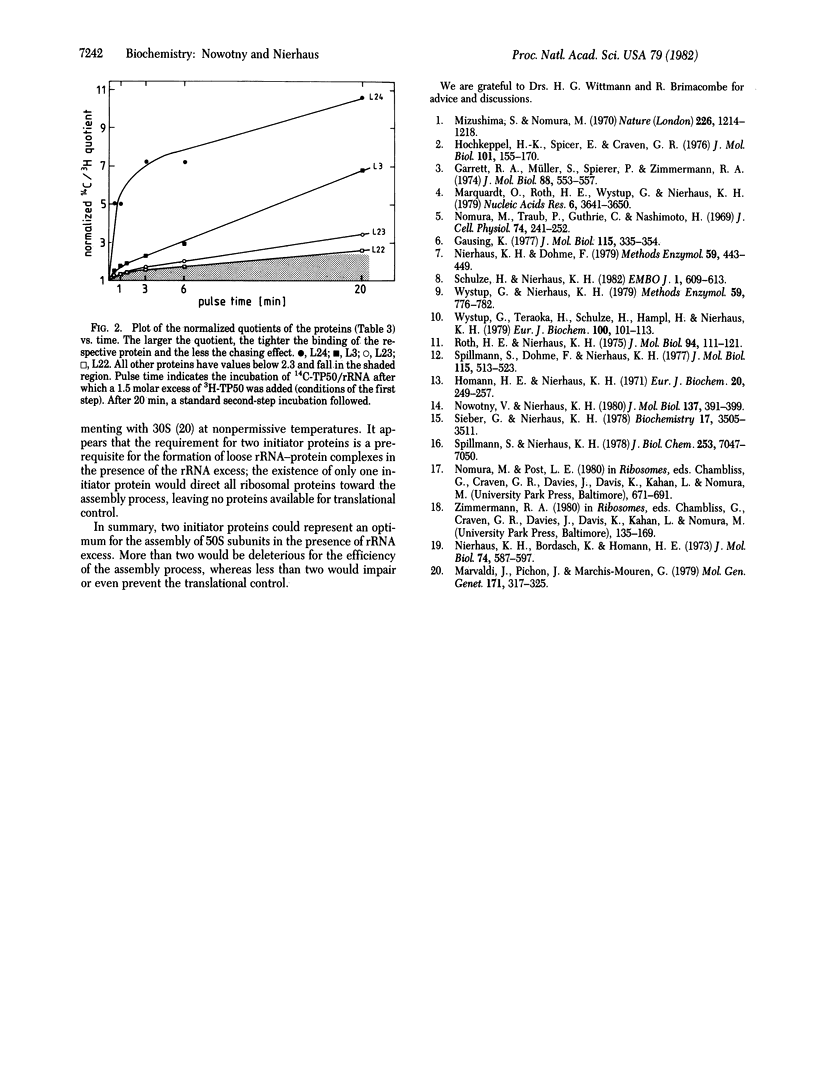
Abstract
An rRNA-binding protein that binds to the rRNA independently of other proteins during the course of ribosomal assembly is termed "assembly initiator protein." In spite of the large number of rRNA-binding proteins (more than 17 out of 32 proteins have been identified in the case of the large ribosomal subunit), only a very small number of proteins should actually initiate ribosomal assembly for theoretical reasons. Here we demonstrate that only two of the L proteins derived from the large subunit (50S) function as assembly initiator proteins. Two different techniques are used to identify these initiator proteins: reconstitution experiments with purified proteins and pulse-chase experiments during in vitro assembly. Both methods independently identify L24 and L3 as initiator proteins for the 50S assembly. The existence of two initiator proteins (not just one) resolves an apparent contradiction--namely, that on the one hand, rRNA is synthesized in excess under unfavorable growth conditions, whereas on the other hand, rRNA-binding proteins should be available for translational control.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Garret R. A., Müller S., Spierer P., Zimmermann R. A. Letter: Binding of 50 S ribosomal subunit proteins to 23 S RNA of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):553–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90503-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gausing K. Regulation of ribosome production in Escherichia coli: synthesis and stability of ribosomal RNA and of ribosomal protein messenger RNA at different growth rates. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):335–354. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochkeppel H. K., Spicer E., Craven G. R. A method of preparing Escherichia coli 16 S RNA possessing previously unobserved 30 S ribosomal protein binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1976 Feb 25;101(2):155–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90369-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homann H. E., Nierhaus K. H. Ribosomal proteins. Protein compositions of biosynthetic precursors and artifical subparticles from ribosomal subunits in Escherichia coli K 12. Eur J Biochem. 1971 May 28;20(2):249–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt O., Roth H. E., Wystup G., Nierhaus K. H. Binding of Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins to 23S RNA under reconstitution conditions for the 50S subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3641–3650. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvaldi J., Pichon J., Marchis-Mouren G. On the control of ribosomal protein biosynthesis in E. coli. IV. Studies on a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in the assembly of 50S subunits. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 27;171(3):317–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00267587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30S ribosomal proteins from E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1214–1214. doi: 10.1038/2261214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Bordasch K., Homann H. E. Ribosomal proteins. 43. In vivo assembly of Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Dohme F. Total reconstitution of 50 S subunits from Escherichia coli ribosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:443–449. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Traub P., Guthrie C., Nashimoto H. The assembly of ribosomes. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Oct;74(2 Suppl):241+–241+. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040740428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny V., Nierhaus K. H. Protein L20 from the large subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes is an assembly protein. J Mol Biol. 1980 Mar 15;137(4):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth H. E., Nierhaus K. H. Structural and functional studies of ribonucleoprotein fragments isolated from Escherichia coli 50 S ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze H., Nierhaus K. H. Minimal set of ribosomal components for reconstitution of the peptidyltransferase activity. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):609–613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieber G., Nierhaus K. H. Kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the assembly in vitro of the large subunit from Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3505–3511. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillmann S., Dohme F., Nierhaus K. H. Assembly in vitro of the 50 S subunit from Escherichia coli ribosomes: proteins essential for the first heat-dependent conformational change. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillmann S., Nierhaus K. H. The ribosomal protein L24 of Escherichia coli is an assembly protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):7047–7050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wystup G. M., Nierhaus K. H. A method for the 14C-labeling of proteins from the large ribosomal subunit, without loss of biological activity. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:776–782. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59124-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wystup G., Teraoka H., Schulze H., Hampl H., Nierhaus K. H. 50-S subunit from Escherichia coli ribosomes. Isolation of active ribosomal proteins and protein complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):101–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



