Abstract
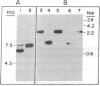
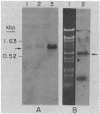
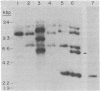
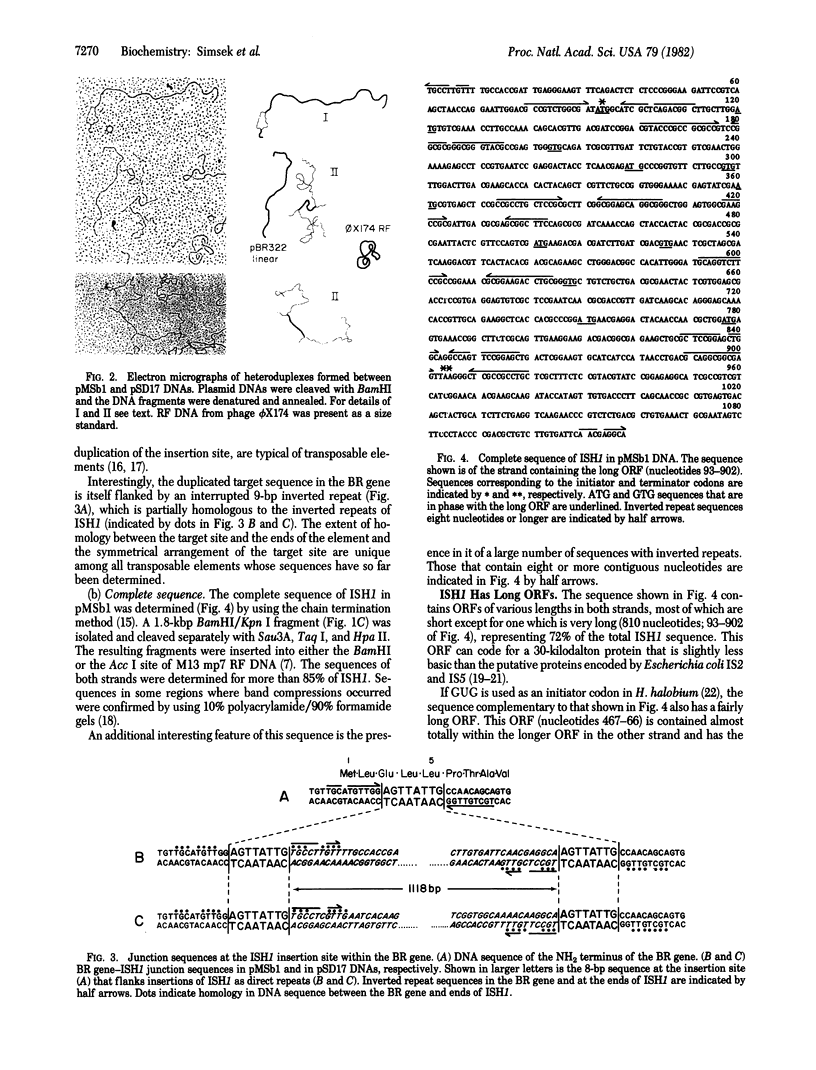
We describe the characterization of a transposable element from an archaebacterium. The bacteriorhodopsin genes from the wild-type and two mutant Halobacterium halobium strains have been cloned as BamHI fragments in pBR322. The cloned DNA fragments from the two mutants both contain a 1.1-kilobase-pair insertion sequence (ISH1) near the NH2 terminus of the bacteriorhodopsin coding sequence. ISH1 is present in the two mutants in an identical palindromic site but in opposite orientations. The complete sequence of ISH1 has been determined; it is 1,118 nucleotides long, it has 8-base-pair interrupted inverted repeats at the ends, and it duplicates an 8-base-pair (A-G-T-T-A-T-T-G) target sequence upon insertion. As for most eukaryotic and some prokaryotic transposable elements, the sequence of the ISH1 begins with T-G and ends in C-A. ISH1 contains an open reading frame 810 nucleotides long and codes for an RNA approximately 900 nucleotides long. The copy number of ISH1 ranges from one to five or more in different H. halobium strains. In at least one of the strains, one copy of ISH1 is present also on a plasmid DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. H., Majumdar A., Dunn R., Makabe O., RajBhandary U. L., Khorana H. G., Ohtsuka E., Tanaka T., Taniyama Y. O., Ikehara M. Bacteriorhodopsin: partial sequence of mRNA provides amino acid sequence in the precursor region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3398–3402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deonier R. C., Hadley R. G. IS2-IS2 and IS3-IS3 relative recombination frequencies in F integration. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):48–64. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., Sommer H., Saedler H. Nucleotide sequence of the transposable DNA-element IS2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):1111–1122. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling S. M., Kleckner N. A symmetrical six-base-pair target site sequence determines Tn10 insertion specificity. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90385-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Insertion of a movable genetic element, 297, into the T-A-T-A box for the H3 histone gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4143–4147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger M., Hobom G. Structural analysis of insertion sequence IS5. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):159–162. doi: 10.1038/297159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein C., Brenner S. Unique insertion site of Tn7 in the E. coli chromosome. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):601–603. doi: 10.1038/297601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Kumar A. Mapping tRNA structure in solution using double-strand-specific ribonuclease V1 from cobra venom. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5125–5140. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet A., van de Sande J. H., Loewen P. C., Khorana H. G., Raae A. J., Lillehaug J. R., Kleppe K. Physical characterization and simultaneous purification of bacteriophage T4 induced polynucleotide kinase, polynucleotide ligase, and deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5045–5050. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Genetic variability in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):375–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.375-381.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rak B., Lusky M., Hable M. Expression of two proteins from overlapping and oppositely oriented genes on transposable DNA insertion element IS5. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):124–128. doi: 10.1038/297124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read H. A., Das Sarma S., Jaskunas S. R. Fate of donor insertion sequence IS1 during transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Doolittle W. F. Unusual physical organization of the Halobacterium genome. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):384–389. doi: 10.1038/295384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Jelinek W. R. The Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1065–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6281889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Origin of retroviruses from cellular moveable genetic elements. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidinger G., Klotz G., Goebel W. A large plasmid from Halobacterium halobium carrying genetic information for gas vacuole formation. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]