Abstract
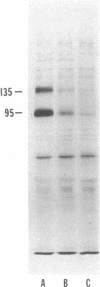
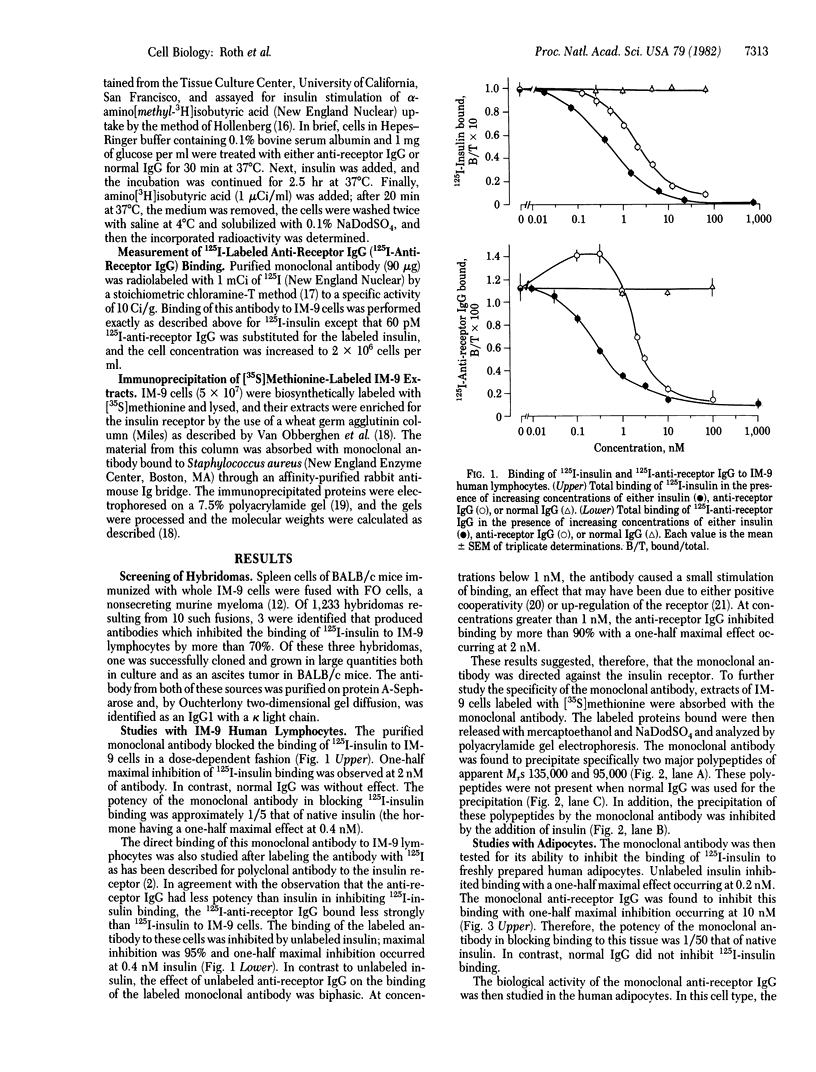
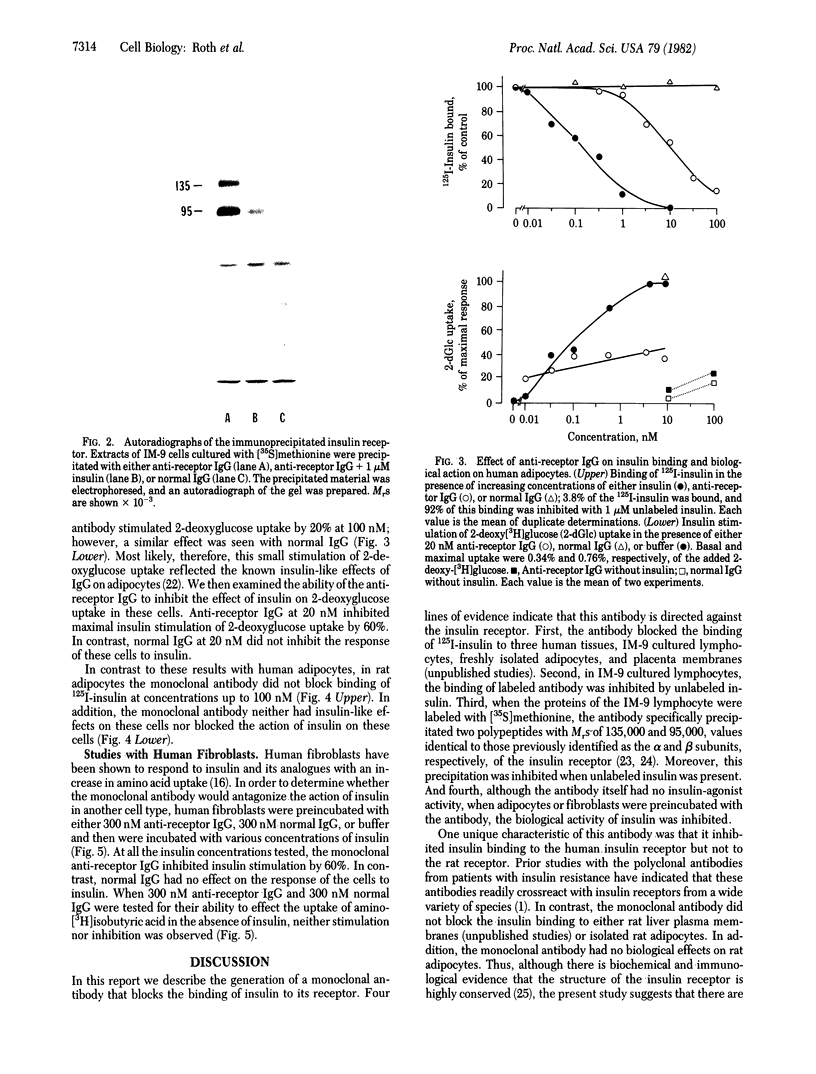
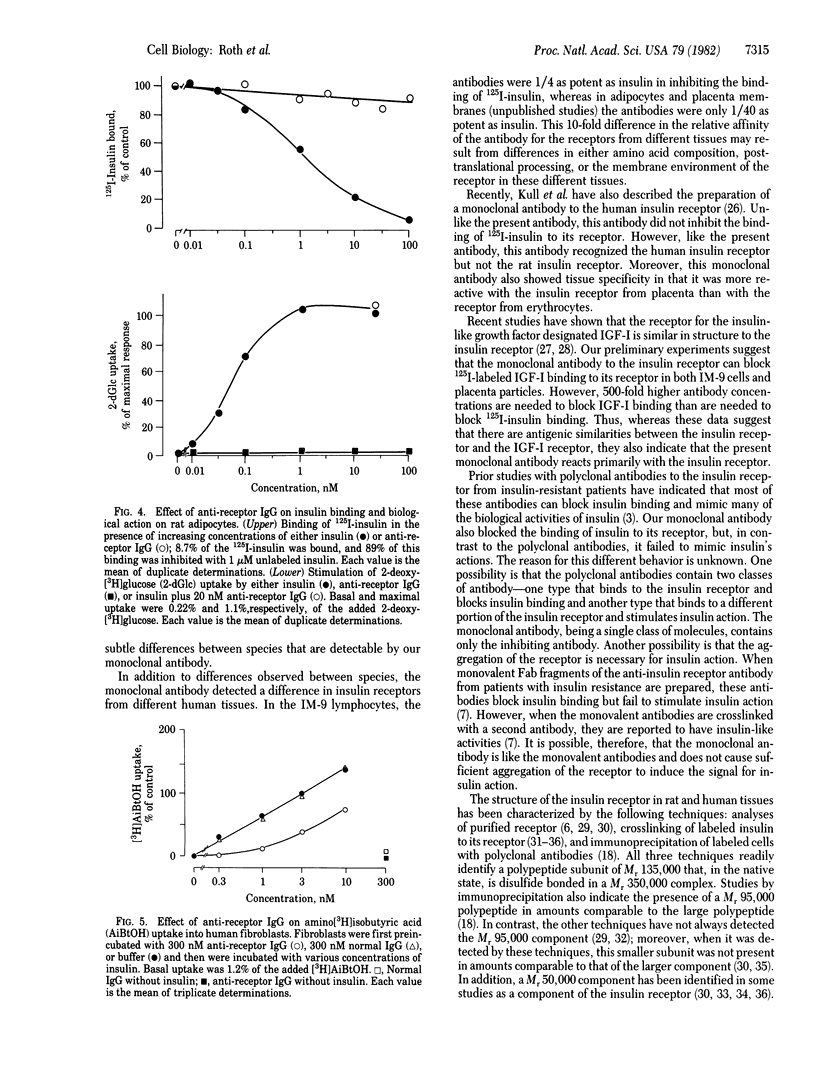
Antibodies to the insulin receptor were prepared in BALB/c mice by immunization with IM-9 human lymphocytes, a cell type that has a large number of plasma membrane insulin receptors. The spleens of these mice were then removed, and their lymphocytes were fused to a mouse myeloma cell line, FO cells. After screening over 1,200 resulting hybrids, one stable hybrid was obtained that produced IgG1 antibodies directed towards the insulin receptor. This antibody blocked 125I-labeled insulin binding to its receptor by more than 90% in three human tissues: IM-9 cultured lymphocytes, freshly isolated adipocytes, and placenta membranes. In contrast, the antibody did not inhibit insulin binding to rat adipocytes and rat liver plasma membranes, suggesting that the antibody was species specific. In IM-9 cells, which had their proteins prelabeled with [35S]methionine, the antibody precipitated two polypeptides with molecular weights of 135,000 and 95,000; these molecular weights are identical to those previously identified as the alpha and beta subunits of the insulin receptor. The monoclonal antibody inhibited the actions of insulin on both human adipocytes and fibroblasts, suggesting that the antibody was an antagonist of insulin action. The present studies suggest, therefore, that monoclonal antibodies to the insulin receptor may provide new insights into the structure of the insulin receptor and its interaction with insulin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin D., Jr, Terris S., Steiner D. F. Characterization of insulin-like actions of anti-insulin receptor antibodies. Effects on insulin binding, insulin degradation, and glycogen synthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4028–4034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Insulin action. Am J Med. 1981 Jan;70(1):142–150. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90421-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Pirro R., Lauro R., Gelli A. S., Bertoli A., Musiani P. Specificities of rabbit anti-human insulin receptor antibodies. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Apr;2(1):27–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Bar R. S. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.170678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Gliemann J. Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Gorden P., Roth J., Archer J. A., Buell D. N. Characteristics of the human lymphocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Smith G. J. Binding of insulin to isolated nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Itin A. Purification of the insulin receptor from human placenta by chromatography on immobilized wheat germ lectin and receptor antibody. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12066–12072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D. Action of insulin analogues on cultured human fibroblasts reflects biological potency. Life Sci. 1976 Mar 1;18(5):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Antibodies to purified insulin receptor have insulin-like activity. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1283–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.663609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: structure and function. Endocr Rev. 1981 Summer;2(3):251–263. doi: 10.1210/edrv-2-3-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. The subunit structure of rat liver insulin receptor. Antibodies directed against the insulin-binding subunit. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6937–6940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Hazum E., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: covalent labeling and identification of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4918–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Shechter Y., Bissell K., Cuatrecasas P. Purification and properties of insulin receptors from rat liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):981–988. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett D. B., Roth J., Kahn C. R., Flier J. S. Direct method for detection and characterization of cell surface receptors for insulin by means of 125I-labeled autoantibodies against the insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4115–4119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. L., Jarrett D. B., Flier J. S. Direct demonstration that receptor crosslinking or aggregation is important in insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4209–4213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K., Filier J. S., Jarrett D. B. Effects of autoantibodies to the insulin receptor on isolated adipocytes. Studies of insulin binding and insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1094–1106. doi: 10.1172/JCI108861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. The role of insulin receptors and receptor antibodies in states of altered insulin action. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Oct;162(1):13–21. doi: 10.3181/00379727-162-40609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Demonstration of two subtypes of insulin-like growth factor receptors by affinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5305–5308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khokher M. A., Dandona P., Janah S., Coulston G. L. Insulin-like stimulatory effect of human immunoglobulin G on adipocyte lipogenesis. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1068–1071. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Cuatrecasas P. A monoclonal antibody to human insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 15;106(3):1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91813-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Electrophoretic resolution of three major insulin receptor structures with unique subunit stoichiometries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7137–7141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggeo M., Ginsberg B. H., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, De Meyts P., Kahn C. R. The insulin receptor in vertebrates is functionally more conserved during evolution than insulin itself. Endocrinology. 1979 May;104(5):1393–1402. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-5-1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked receptor complex in fat cell and liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1722–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollet R. J., Kempner E. S., Standaert M. L., Haase B. A. Structure of the insulin receptor of the cultured human lymphoblastoid cell IM-9. Evidence suggesting that two subunits are required for insulin binding. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):894–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa A. A., Djiane J., Houdebine L. M., Kelly P. A. Stimulatory effects of prolactin and anti-prolactin receptor serum on prolactin binding sites in rat liver cells in suspension culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 14;106(1):243–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Wong K. Y., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Production of antibodies that inhibit the binding of insulin to its receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 14;101(3):979–987. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91845-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel T. W., Ganguly S., Jacobs S., Rosen O. M., Rubin C. S. Purification and properties of the human placental insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9266–9273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Ksauga M., Le Cam A., Hedo J. A., Itin A., Harrison L. C. Biosynthetic labeling of insulin receptor: studies of subunits in cultured human IM-9 lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor proteins of liver plasma membrane preparations. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 8;19(1):70–76. doi: 10.1021/bi00542a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]