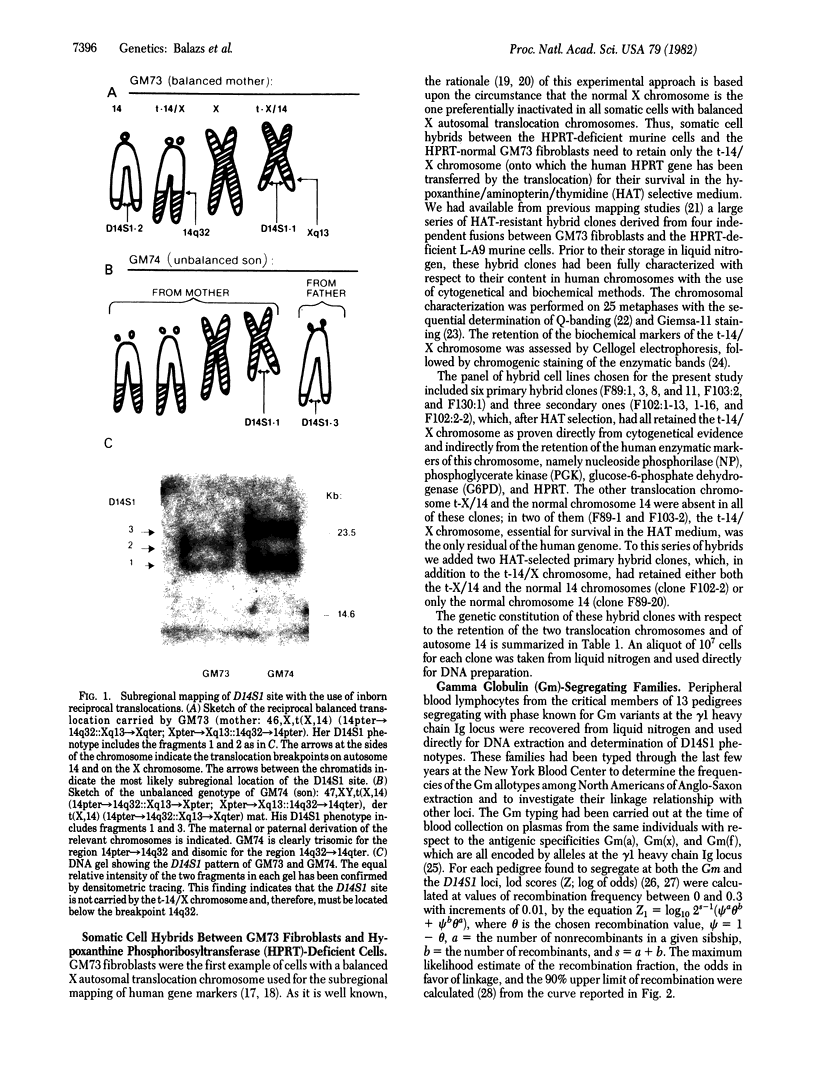
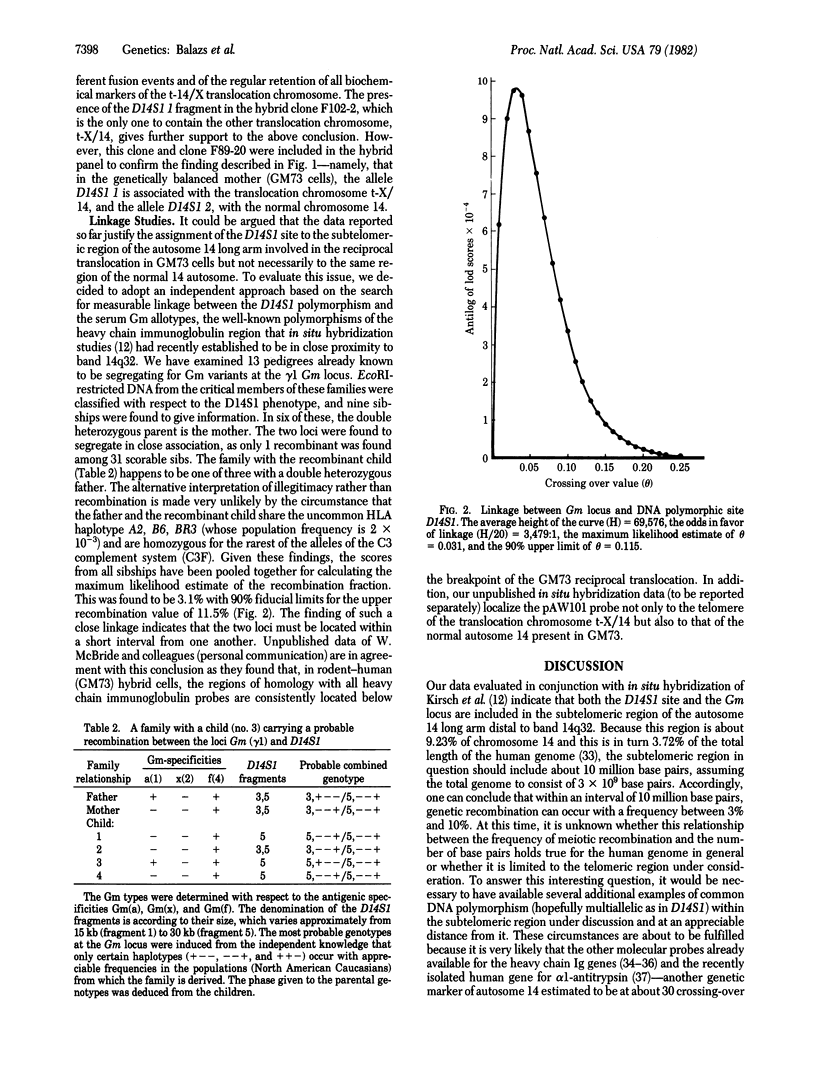
Abstract
Using a phage λ Charon 4A recombinant DNA clone (λCH4A-rHs18) from a human genomic library, Wyman and White detected a multiallelic common polymorphism at an EcoRI site (D14S1) flanking the DNA region homologous to the probe [Wyman, A. R. & White, R. (1980) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 6754-6758]. Subsequent studies, carried out with the cell hybrid approach and the use of a subclonal derivative (pAW101) from λCH4A-rHs18 have assigned this locus to autosome 14 between 14q21 and 14qter [De Martinville, B., Wyman, A. R., White, R. & Franke, U. (1982) Am. J. Hum. Gen. 34, 216-226]. The data presented here permit the precise mapping of this locus to the subtelomeric region of autosome 14, below band 14q32, in close proximity to the heavy chain γ1 immunoglobulin locus. These conclusions are supported by three independent lines of evidence, including studies on gene dosage, somatic cell hybrids, and pedigree analysis. Our results are in agreement with the recent assignment of the heavy chain γ1 immunoglobulin locus to band 14q32 [Kirsch, I. R., Morton, C. C., Nakahara, K. & Leder, P. (1982) Science 216, 301-303] and are consistent with the generally held contention that one unit of meiotic recombination corresponds approximately to one million base pairs. It is to be expected that the location of the highly polymorphic D14S1 site at a measurable distance from the cluster of the heavy chain genes will provide new opportunities for a genetic approach to the question of the specific gene order within the cluster, its possible individual variation, and its biological significance in normal development and disease. It is worthwhile to point out that such a highly polymorphic DNA sequence is located in the same chromosomal region where so much somatic rearrangement goes on normally (i.e., switch region between classes of heavy chain constant region genes) and which is involved with de novo translocations associated with malignancies.
Keywords: human genetics, DNA polymorphism, linkage analysis
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bobrow M., Cross J. Differential staining of human and mouse chromosomes in interspecific cell hybrids. Nature. 1974 Sep 6;251(5470):77–79. doi: 10.1038/251077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckton K. E., Jacobs P. A., Rae L. A., Newton M. S., Sanger R. An inherited X-autosome translocation in man. Ann Hum Genet. 1971 Oct;35(2):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1956.tb01390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Johansson C., Modest E. J. Identification of human chromosomes by DNA-binding fluorescent agents. Chromosoma. 1970;30(2):215–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00282002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Buxbaum J., Hood L. Nucleotide sequence of a human immunoglobulin C gamma 4 gene. DNA. 1981;1(1):11–18. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Hood L. Linkage and sequence homology of two human immunoglobulin gamma heavy chain constant region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1984–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuhara S., Shirakawa S., Uchino H. Specific marker chromosome 14 in malignant lymphomas. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):210–211. doi: 10.1038/259210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedde-Dahl T., Jr, Frants R. R., Olaisen B., Eriksson A. W., van Loghem E., Lamm L. The Gm--Pi linkage heterogeneity in view of Pi M subtypes. Ann Hum Genet. 1981 May;45(Pt 2):143–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1981.tb00316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeschik K. H., Allderdice P. W., Grzeschik A., Opitz J. M., Miller O. J., Siniscalco M. Cytological mapping of human X-linked genes by use of somatic cell hybrids involving an X-autosome translocation (mouse-hamster-human X-linked markers). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):69–73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht F., McCaw B. K., Koler R. D. Ataxia-telangiectasia--clonal growth of translocation lymphocytes. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 9;289(6):286–291. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308092890603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Clustered arrangement of immunoglobulin lambda constant region genes in man. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):536–540. doi: 10.1038/294536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Kataoka T., Yaoita Y., Shimizu A., Takahashi N., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Nikaido T., Nakai S., Obata M., Kawakami T. Organization and reorganization of immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):913–923. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén M. Chiasma distribution at diakinesis in the normal human male. Hereditas. 1974;76(1):55–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1974.tb01177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch I. R., Morton C. C., Nakahara K., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes map to a region of translocations in malignant B lymphocytes. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):301–303. doi: 10.1126/science.6801764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Further scoring types in sequential linkage tests, with a critical review of autosomal and partial sex linkage in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1957 Mar;9(1):55–75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Sequential tests for the detection of linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1955 Sep;7(3):277–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolov G., Manolova Y. Marker band in one chromosome 14 from Burkitt lymphomas. Nature. 1972 May 5;237(5349):33–34. doi: 10.1038/237033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolova Y., Manolov G., Kieler J., Levan A., Klein G. Genesis of the 14q+ marker in Burkitt's lymphoma. Hereditas. 1979;90(1):5–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1979.tb01288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Ayme S., Mattei J. F., Aurran Y., Giraud F. Distribution of spontaneous chromosome breaks in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;23(1-2):95–102. doi: 10.1159/000131309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaw B. K., Hecht F., Harnden D. G., Teplitz R. L. Somatic rearrangement of chromosome 14 in human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P. Enzyme electrophoresis on cellulose acetate gel: zymogram patterns in mgh-mouse and man--Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Aug;145(2):470–483. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz J., Pallister P. D., Ruddle F. H. An (X;14) translocation, balanced, 46 chromosomes. Repository identification No. GM-73. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1973;12(4):289–290. doi: 10.1159/000130464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz J., Pallister P. D., Ruddle F. H. An (X;14) translocation, unbalanced, 47 chromosomes. Repository identification No. GM-74. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1973;12(4):291–292. doi: 10.1159/000130465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciuti F. C., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of three gene loci (PGK, HGPRT, G6PD) to the long arm of the human X chromosome by somatic cell genetics. Genetics. 1973 Aug;74(4):661–678. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.4.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekhon G. S., Taysi K., Rath R. Partial trisomy for the short arm of chromosome 2 due to familial balance translocation. Hum Genet. 1978 Oct 19;44(1):99–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00283579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seravalli E., DeBona P., Velivasakis M., Pagan-Charry I., Hershberg A., Siniscalco M. Further data on the cytologic mapping of the human X chromosome with man-mouse cell hybrids. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1976;12(7):219–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Takahashi N., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Nishida Y., Kataoka T., Honjo T. Ordering of mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain genes by molecular cloning. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):149–153. doi: 10.1038/289149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A. Linkage scores and corrections in simple two- and three-generation families. Ann Hum Genet. 1968 Oct;32(2):127–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1968.tb00058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D., Weinberg R. A. The integrated genome of murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. High resolution of human chromosomes. Science. 1976 Mar 26;191(4233):1268–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.1257746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zech L., Haglund U., Nilsson K., Klein G. Characteristic chromosomal abnormalities in biopsies and lymphoid-cell lines from patients with Burkitt and non-Burkitt lymphomas. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):47–56. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martinville B., Wyman A. R., White R., Francke U. Assignment of first random restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) locus ((D14S1) to a region of human chromosome 14. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):216–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]