Abstract
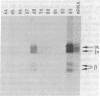
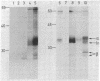
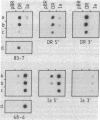
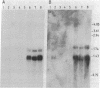
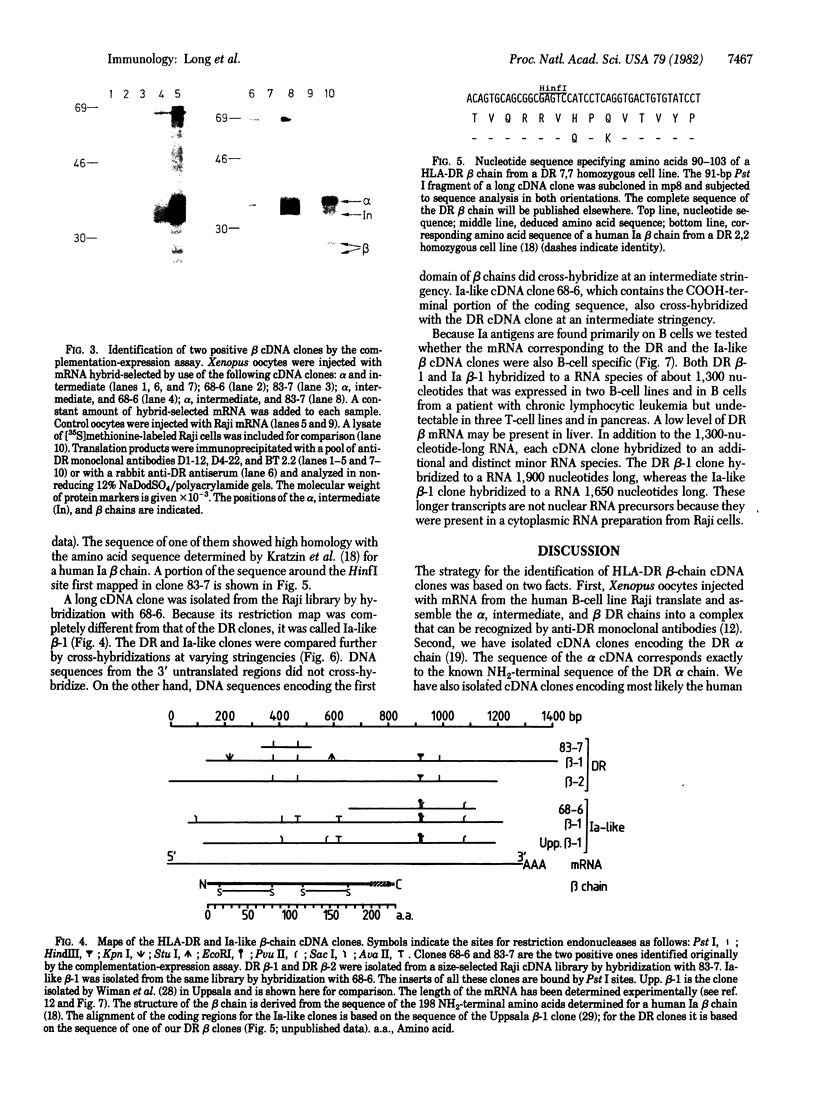
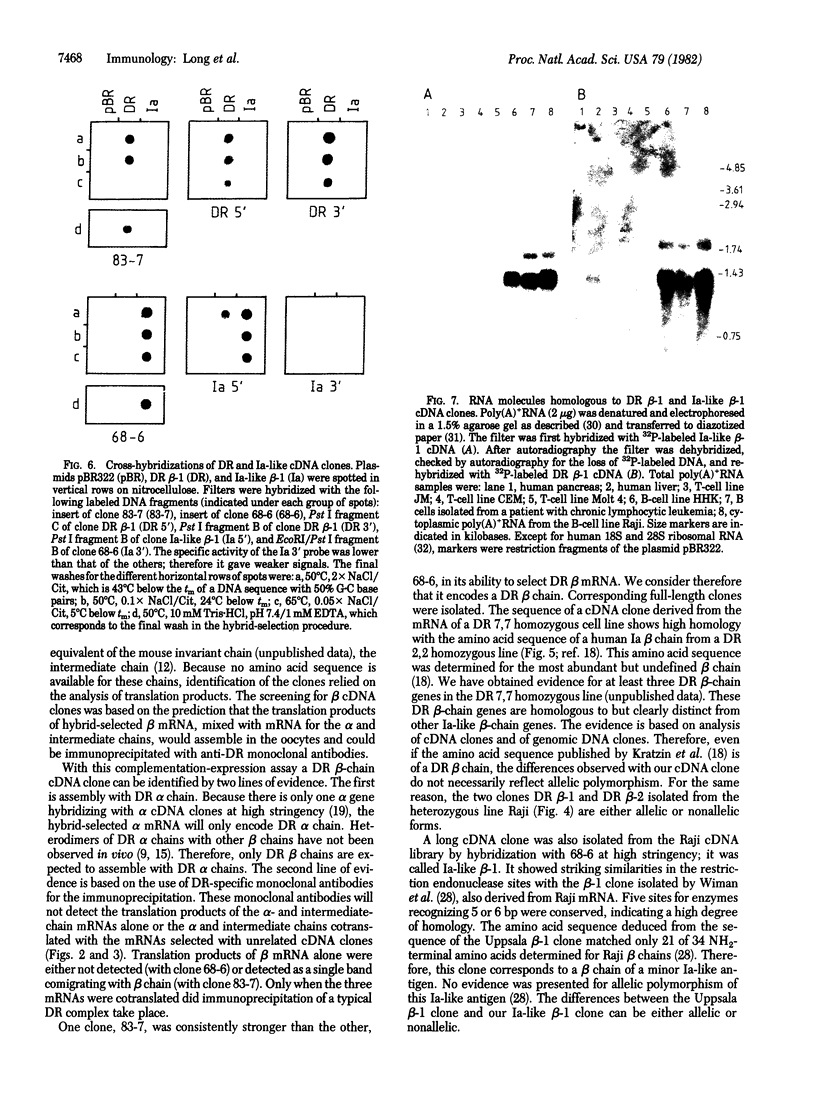
cDNA clones encoding different human Ia antigen beta chains were isolated by use of a complementation-expression assay in Xenopus oocytes. The assay was based on two previous findings. First, oocytes injected with mRNA from a human B-cell line express HLA-DR antigen. The three intracellular DR chains are assembled in oocytes and can be immunoprecipitated with anti-DR monoclonal antibodies. Second, we have isolated cDNA clones encoding DR alpha and intermediate chains. In order to identify beta-chain cDNA clones, mRNA was hybrid-selected with pools of cDNA clones, mixed with mRNA for the alpha and intermediate chains, and injected into oocytes. We isolated two distinct clones that could select DR beta-chain mRNA as demonstrated by assembly of the translation product with DR alpha chains and immunoprecipitation with DR-specific monoclonal antibodies. One clone is specific for a beta chain of the DR locus. The other clone, much weaker in its ability to select DR mRNA, encodes another Ia-like beta chain. Full-length cDNA clones corresponding to the DR and Ia-like beta chains were isolated and compared. Cross-hybridization was detectable in the coding regions but not in the 3' untranslated regions. Distinct RNAs homologous to the DR and the Ia-like beta-chain clones were present in B cells but were undetectable in three T-cell lines.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accolla R. S., Gross N., Carrel S., Corte G. Distinct forms of both alpha and beta subunits are present in the human Ia molecular pool. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4549–4551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Accolla R. S., Sekaly R. P., McDonald A. P., Corte G., Gross N., Carrel S. Demonstration at the single-cell level of the existence of distinct clusters of epitopes in two predefined human Ia molecular subsets. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Feb;12(2):166–169. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. H., van Rood J. J. The major histocompatibility complex--genetics and biology. (First of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 7;295(15):806–813. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610072951504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Analysis of HLA-D region-associated molecules with monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Characterization of HLA-D-region antigens by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Molecular-genotyping. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):18s–36s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Kurer V., Smith H. O. Sequence organization of a cloned tDNA met fragment from Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corte G., Calabi F., Damiani G., Bargellesi A., Tosi R., Sorrentino R. Human Ia molecules carrying DC1 determinants differ in both alpha- and beta-subunits from Ia molecules carrying DR determinants. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):357–360. doi: 10.1038/292357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Lifton R. P., Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Isolation of specific RNA's using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:206–220. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. The major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):516–521. doi: 10.1126/science.104386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Yang C. Y., Götz H., Pauly E., Kölbel S., Egert G., Thinnes F. P., Wernet P., Altevogt P., Hilschmann N. Primärstruktur menschlicher Histokompatibilitätsantigene der Klasse II. 1. Mitteilung: Aminosäuresequenz der N-terminalen 198 Reste der beta-Kette des HLA-Dw2,2;DR2,2-Alloantigens. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Dec;362(12):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Wiman K., Claesson L., Peterson P. A., Dobberstein B. Membrane insertion and oligomeric assembly of HLA-DR histocompatibility antigens. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Schenning L., Gustafsson K., Wiman K., Claesson L., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Complete amino acid sequence of an HLA-DR antigen-like beta chain as predicted from the nucleotide sequence: similarities with immunoglobulins and HLA-A, -B, and -C antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3687–3691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Gross N., Wake C. T., Mach J. P., Carrel S., Accolla R., Mach B. Translation and assembly of HLA-DR antigens in Xenopus oocytes injected with mRNA from a human B-cell line. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):649–654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Kissonerghis A. M., Lodish H. F., Crumpton M. J. Biosynthesis and maturation of HLA-DR antigens in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8987–8993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A., Dausset J. Genetics of HLA disease association. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:169–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Mann D. L., van Rood J. J., Ferrara G. B., Strominger J. L. Human B-cell alloantigens DC1, MT1, and LB12 are identical to each other but distinct from the HLA-DR antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4566–4570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Strominger J. L. Demonstration of structural polymorphism among HLA-DR light chains by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):144–165. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., DeMars R., Schlossman S. F., Smith P. L., Lampson L. A., Nadler L. M. Serologic identification of the human secondary B cell antigens. Correlations between function, genetics, and structure. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):731–743. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Ferrone S. Structural polymorphism of human DR antigens. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):436–437. doi: 10.1038/279436a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi R., Tanigaki N., Centis D., Ferrara G. B., Pressman D. Immunological dissection of human Ia molecules. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1592–1611. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Long E. O., Strubin M., Gross N., Accolla R., Carrel S., Mach B. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding HLA-DR alpha chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6979–6983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Isolation and sequence organization of human ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):289–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman K., Larhammar D., Claesson L., Gustafsson K., Schenning L., Bill P., Böhme J., Denaro M., Dobberstein B., Hammerling U. Isolation and identification of a cDNA clone corresponding to an HLA-DR antigen beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1703–1707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]