Abstract
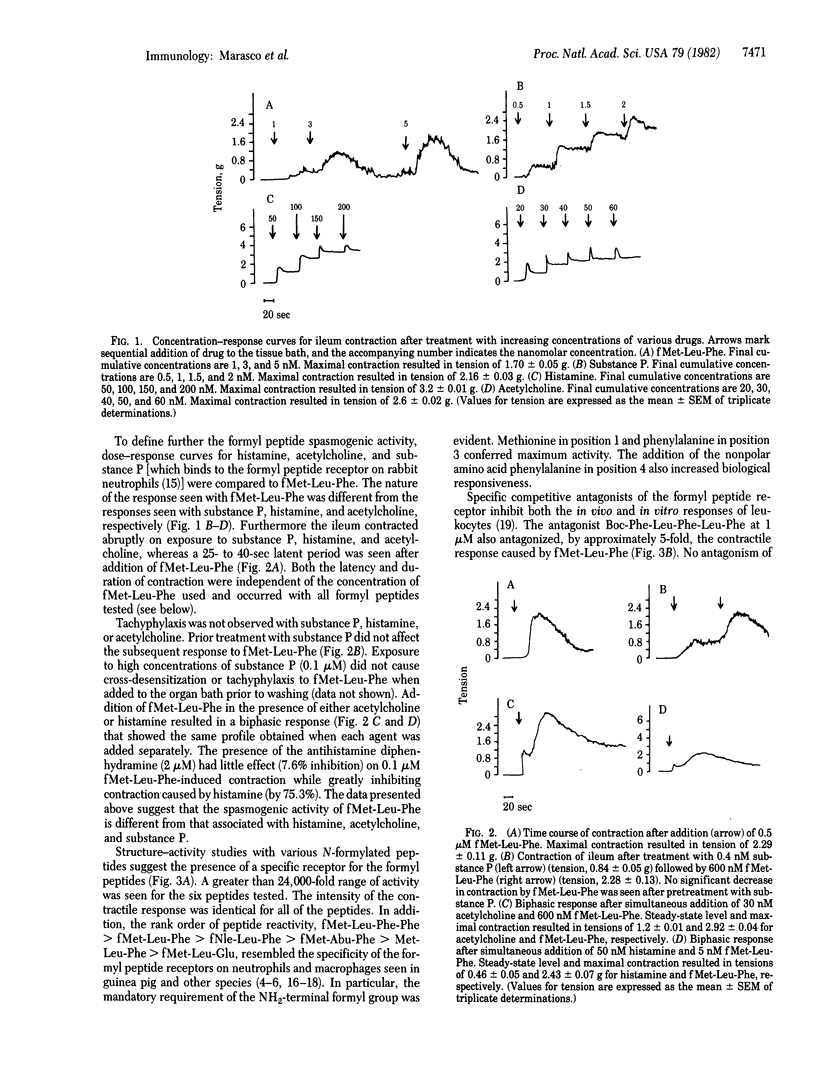
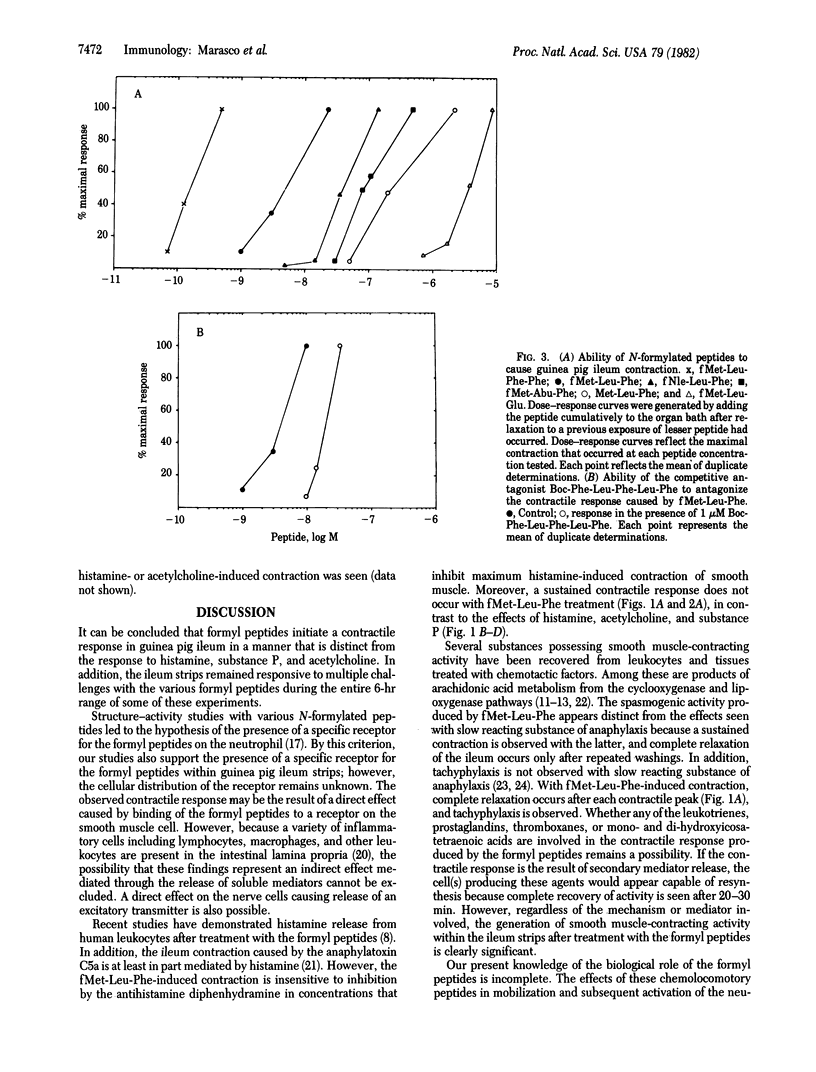
The chemotactic N-formylated oligopeptides are potent spasmogenic agents for guinea pig ileum. Structure-activity studies with various N-formylated peptides suggest the presence of a specific receptor that resembles in specificity the formyl peptide receptor on leukocytes. A competitive antagonist of the formyl peptide receptor on leukocytes also inhibits formyl peptide-induced ileum contraction, whereas the antihistamine diphenhydramine is without effect. The contractile response caused by the synthetic N-formylated peptides differs from those induced by acetylcholine, histamine, and substance P. In particular, a latent period after treatment with the N-formyl peptides is seen before the onset of the response, and a sustained contractile response is not maintained. In addition, tachyphylaxis does occur, but complete recovery of activity is seen after a 20- to 30-min rest period. These observations suggest broad biological roles of prokaryotic signal peptides from bacteria as acute inflammatory mediators.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L. A multifunctional receptor on the neutrophil for synthetic chemotactic oligopeptides. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Dec;26(Suppl):701–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. P., Hirth K. P., Fuchs E., Sarvas M., Warren G. B. The bacterial factors which stimulate neutrophils may be derived from procaryote signal peptides. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 11;116(1):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80528-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodammer G., Vogt W. Contraction of the guinea-pig ileum induced by anaphylatoxin independent of histamine release. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(5-6):648–657. doi: 10.1159/000230389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bury R. W., Mashford M. L. Interactions between local anesthetics and spasmogens on the guinea-pig ileum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):633–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. M., Doig M. V., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Smith M. J. Prostaglandin and thromboxane production by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes and rat macrophages. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1980;8:1661–1663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDBERG K. D., ENGELHARDT G., MEINEKE F. UNTERSUCHUNGEN UEBER DIE ANAPHYLATOXIN-TACHYPHYLAXIE UND UEBER IHRE BEDEUTUNG FUER DEN ABLAUF ECHTER ANAPHYLAKTISCHER REAKTIONEN. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1964;25:154–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer R. J., Day A. R., Radding J. A., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Further studies on the structural requirements for synthetic peptide chemoattractants. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2404–2410. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook W. A., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Siraganian R. P. Histamine release by chemotactic, formyl methionine-containing peptides. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):594–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Substance P binds to the formylpeptide chemotaxis receptor on the rabbit neutrophil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1065–1072. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90727-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Becker E. L. Anti-f Met-Leu-Phe: similarities in fine specificity with the formyl peptide chemotaxis receptor of the neutrophil. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):956–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A., Becker E. L. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro neutrophil responses to chemotactic factors by a competitive antagonist. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1326–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Austen K. F. Slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis. Adv Immunol. 1969;10:105–144. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60416-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orning L., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene D: a slow reacting substance from rat basophilic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2014–2017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regal J. F., Pickering R. J. C5a-induced tracheal contraction: effect of an SRS-A antagonist and inhibitors of arachidonate metabolism. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):313–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Showell H. V., Corcoran B. A., Ward P. A., Smith E., Becker E. L. The isolation and partial characterization of neutrophil chemotactic factors from Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1831–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Fudman E. J. Demonstration of a chemotactic factor receptor on macrophages. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2754–2757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimler N. P., Brocklehurst W. E., Bloor C. M., Hugli T. E. Anaphylatoxin-mediated contraction of guinea pig lung strips: a nonhistamine tissue response. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2258–2261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



