Abstract
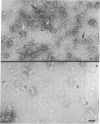
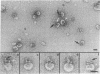
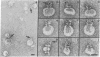
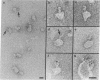
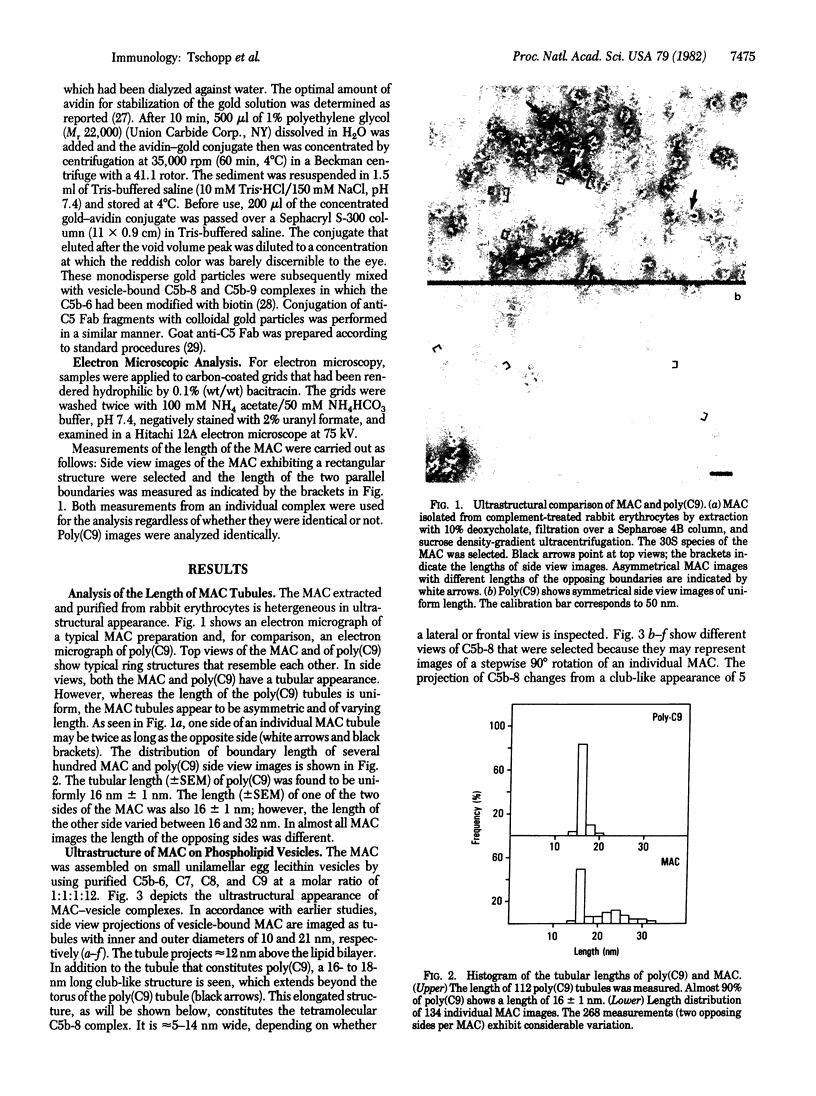
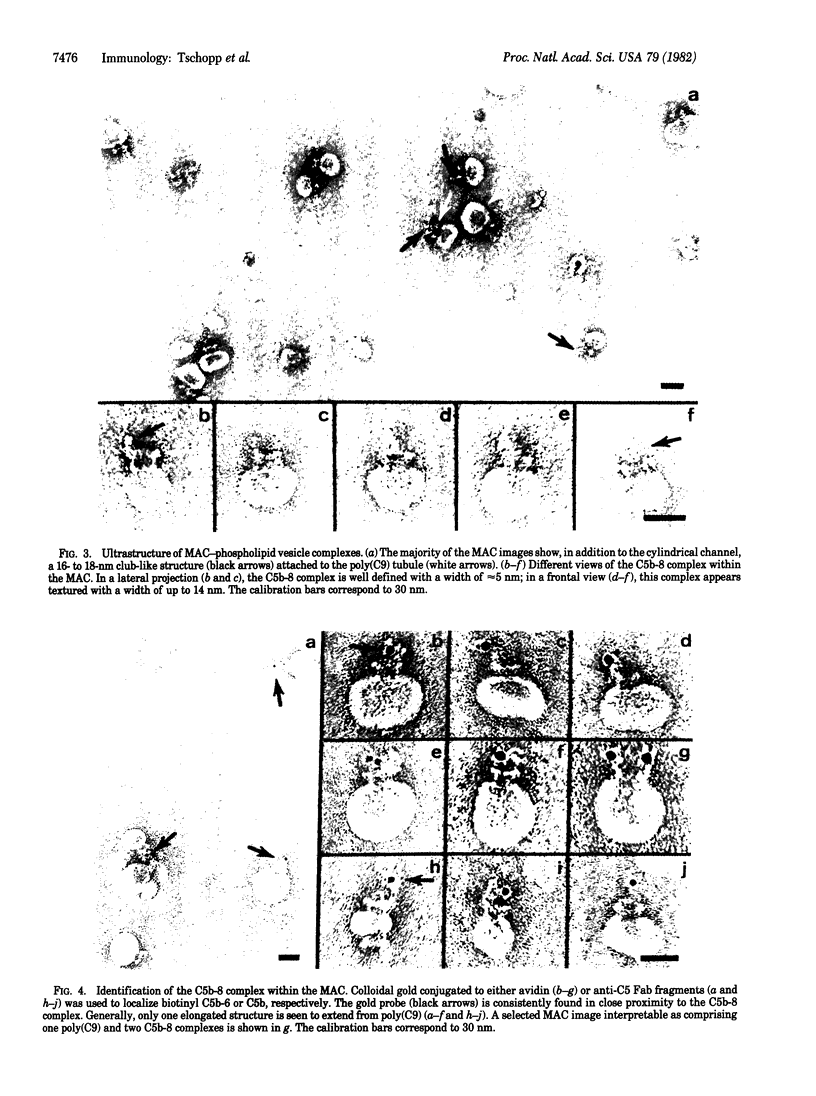
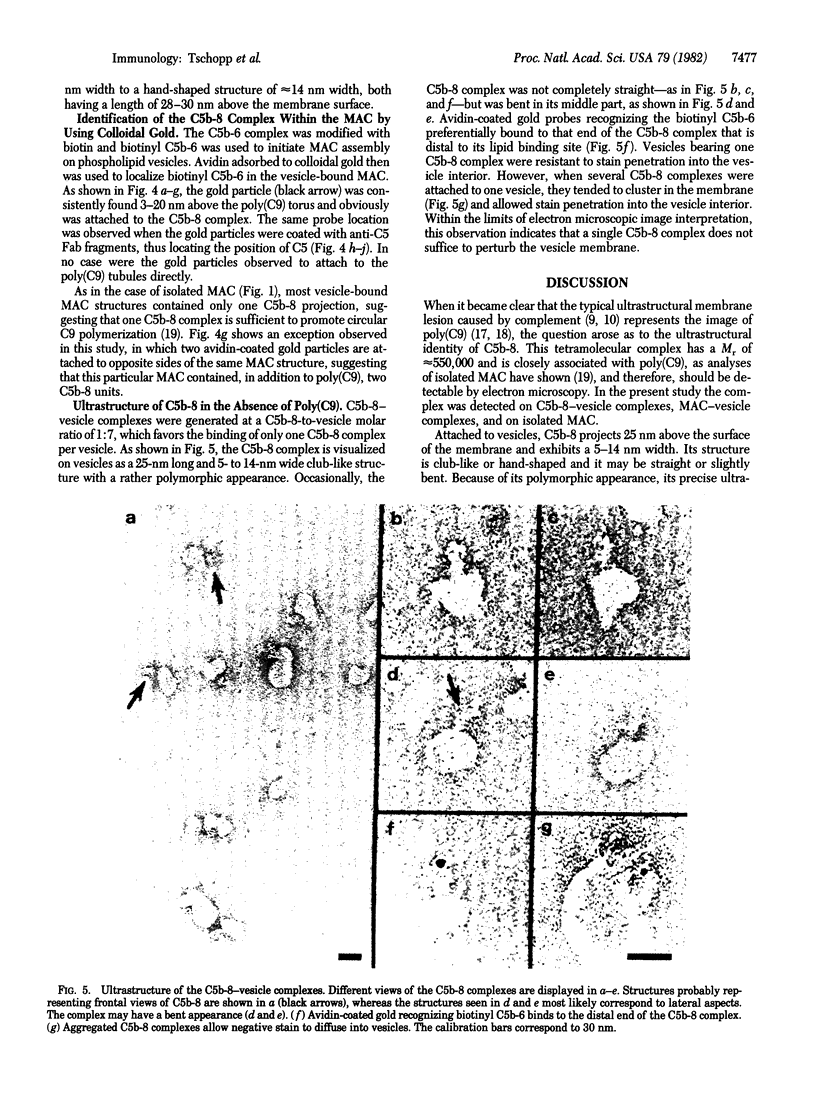
The ultrastructure of the membrane attack complex (MAC) of complement had been described as representing a hollow cylinder of defined dimensions that is composed of the proteins C5b, C6, C7, C8, and C9. After the characteristic cylindrical structure was identified as polymerized C9 [poly(C9)], the question arose as to the ultrastructural identity and topology of the C9-polymerizing complex C5b-8. An electron microscopic analysis of isolated MAC revealed an asymmetry of individual complexes with respect to their length. Whereas the length of one boundary (+/- SEM) was always 16 +/- 1 nm, the length of the other varied between 16 and 32 nm. In contrast, poly(C9), formed spontaneously from isolated C9, had a uniform tubule length (+/- SEM) of 16 +/- 1 nm. On examination of MAC-phospholipid vesicle complexes, an elongated structure was detected that was closely associated with the poly(C9) tubule and that extended 16-18 nm beyond the torus of the tubule and 28-30 nm above the membrane surface. The width of this structure varied depending on its two-dimensional projection in the electron microscope. By using biotinyl C5b-6 in the formation of the MAC and avidin-coated colloidal gold particles for the ultrastructural analysis, this heretofore unrecognized subunit of the MAC could be identified as the tetramolecular C5b-8 complex. Identification also was achieved by using anti-C5 Fab-coated colloidal gold particles. A similar elongated structure of 25 nm length (above the surface of the membrane) was observed on single C5b-8-vesicle complexes. It is concluded that the C5b-8 complex, which catalyzes poly(C9) formation, constitutes a structure of discrete morphology that remains as such identifiable in the fully assembled MAC, in which it is closely associated with the poly(C9) tubule.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORSOS T., DOURMASHKIN R. R., HUMPHREY J. H. LESIONS IN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES CAUSED BY IMMUNE HAEMOLYSIS. Nature. 1964 Apr 18;202:251–252. doi: 10.1038/202251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Ey P., Bhakdi-Lehnen B. Isolation of the terminal complement complex from target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 6;419(3):445–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular nature of the complement lesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The ninth component of human complement: purification and physicochemical characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1291–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Podack E. R., Halverson C. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C5b-9 dimer: isolation from complement lysed cells and ultrastructural identification with complement-dependent membrane lesions. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):448–458. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourmashkin R. R. The structural events associated with the attachment of complement components to cell membranes in reactive lysis. Immunology. 1978 Aug;35(2):205–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser A. F., Kolb W. P., Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular reorganization of lipid bilayers by complement: a possible mechanism for membranolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1410–1414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M., Rosset J., Bauer H. Colloidal gold granules as markers for cell surface receptors in the scanning electron microscope. Experientia. 1975 Oct 15;31(10):1147–1149. doi: 10.1007/BF02326761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu V. W., Esser A. F., Podack E. R., Wisnieski B. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: photolabeling reveals insertion of terminal proteins into target membrane. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):380–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Dourmashkin R. R. The lesions in cell membranes caused by complement. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:75–115. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klob W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: the three polypeptide chain structure of the eigth component (C8). J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1131–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular analysis of the membrane attack mechanism of complement. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):549–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Muller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Isolation and subunit composition of the C5b-9 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):724–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Verification of a stable C5-9 complex in free solution. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):438–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Complement, past and present. Harvey Lect. 1978;72:139–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Mechanism of cytolysis by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2954–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Esser A. F., Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: a structural analysis of its assembly. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):301–313. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Esser A. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Structural similarities between C6 and C7 of human complement. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1071–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Binding of desoxycholate, phosphatidylcholine vesicles, lipoprotein and of the S-protein to complexes of terminal complement components. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1025–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Horst H., Hoppe W. Membrane attach complex of complement (MAC): three-dimensional analysis of MAC-phospholipid vesicle recombinants. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2353–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Limited proteolysis of C5b-6: functional stability of the degraded complex. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):332–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement. Evidence for its dimeric structure based on hybrid formation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3145–3148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Stoffel W., Esser A. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: distribution of subunits between the hydrocarbon phase of target membranes and water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4544–4548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschoop J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular organization of C9 within the membrane attack complex of complement. Induction of circular C9 polymerization by the C5b-8 assembly. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):268–282. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschopp J. Polymerization of the ninth component of complement (C9): formation of poly(C9) with a tubular ultrastructure resembling the membrane attack complex of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):574–578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundsmo J. S., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Neoantigen of the complement membrane attack complex of cytotoxic human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2371–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranum-Jensen J., Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J., Speth V. Complement lysis: the ultrastructure and orientation of the C5b-9 complex on target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(1):45–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Podack E. R. Formation of transmembrane tubules by spontaneous polymerization of the hydrophilic complement protein C9. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):534–538. doi: 10.1038/298534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Podack E. R. Membranolysis by the ninth component of human complement. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1409–1414. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91981-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]