Abstract
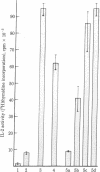
The production of hybridomas between immunologically activated T cells and malignant T-cell lines offers a potentially unlimited source of soluble T-cell-derived products. Recently, human T-T hybrids have been described; however, their use has been hampered by slow growth and chromosomal instability due at least in part to the presence of thymidine in the traditional hypoxanthine/aminopterin/thymidine (HAT) selection medium. In this report, we describe the development of a rapidly growing hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase-deficient human T-cell line designated J3R7, the use of azaserine/hypoxanthine (AH) medium as an alternative selection medium to HAT medium, and the production of functional T-T hybrids by using the J3R7 line and the AH selection technique. Hybrids selected in AH medium were 4-fold greater in number and 3-fold faster in growth rate than hybrids grown in HAT medium. No stable clones were obtained from HAT cultures whereas AH-derived hybrids could be readily cloned by the method of limiting dilution. Evidence for hybridization included (i) the presence of approximately twice the number of chromosomes in hybrids than in J3R7 cells; (ii) the presence on hybrid cells of the Leu-3a surface antigen, present on normal helper T cells but not on J3R7 cells; (iii) the expression of HLA antigens of both the normal T-cell partner and the J3R7 line; and (iv) the constitutive secretion of interleukin 2 from multiple hybrid clones but not from the J3R7 cell line. Thus far, these clones have maintained their rapid growth, chromosome number, surface phenotype, and constitutive secretion of interleukin 2 for 4 months.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B., Germain R. N. A single major pathway of T-lymphocyte interactions in antigen-specific immune suppression. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R. In vitro approaches to the mechanism of cell-mediated immune reactions. Adv Immunol. 1971;13:101–208. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. A one-stage procedure for isolation of granulocytes and lymphocytes from human blood. General sedimentation properties of white blood cells in a 1g gravity field. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:51–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Benike C. J., Grumet F. C., Evans R. L. Activation of human T lymphocyte subsets: helper and suppressor/cytotoxic T cells recognize and respond to distinct histocompatibility antigens. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):2124–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Benjamin W. R., Hilfiker M. L., Howard M., Farrar W. L., Fuller-Farrar J. The biochemistry, biology, and role of interleukin 2 in the induction of cytotoxic T cell and antibody-forming B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:129–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. M., Tripp E. H., Tattersall M. H. Mechanism of deoxycytidine rescue of thymidine toxicity in human T-leukemic lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1980 May;40(5):1718–1721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillot-Courvalin C., Brouet J. C., Berger R., Bernheim A. Establishment of a human T-cell hybrid line with suppressive activity. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):844–845. doi: 10.1038/292844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irigoyen O., Rizzolo P. V., Thomas Y., Rogozinski L., Chess L. Generation of functional human T cell hybrids. J Exp Med. 1981 Dec 1;154(6):1827–1837. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.6.1827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J. A., Araneo B. A., Clevinger B. L. Suppression of antibody and T cell proliferative responses to L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 by a specific monoclonal T cell factor. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):235–240. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston R. B., Venditti J. M., Cooney D. A., Carter S. K. Glutamine antagonists in chemotherapy. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1970;8:57–120. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60594-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Yoshimura N., Kaieda T., Yamamura Y., Kishimoto T. Establishment and characterization of human T hybrid cells secreting immunoregulatory molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7717–7721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin H., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Ruscetti F. W., Neubauer R. H., Brown R. L., Kawakami T. G. Spontaneous release of a factor with properties of T cell growth factor from a continuous line of primate tumor T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Bendtzen K., Greineder D. Mediators of immunity: lymphokines and monokines. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:55–136. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]