Abstract
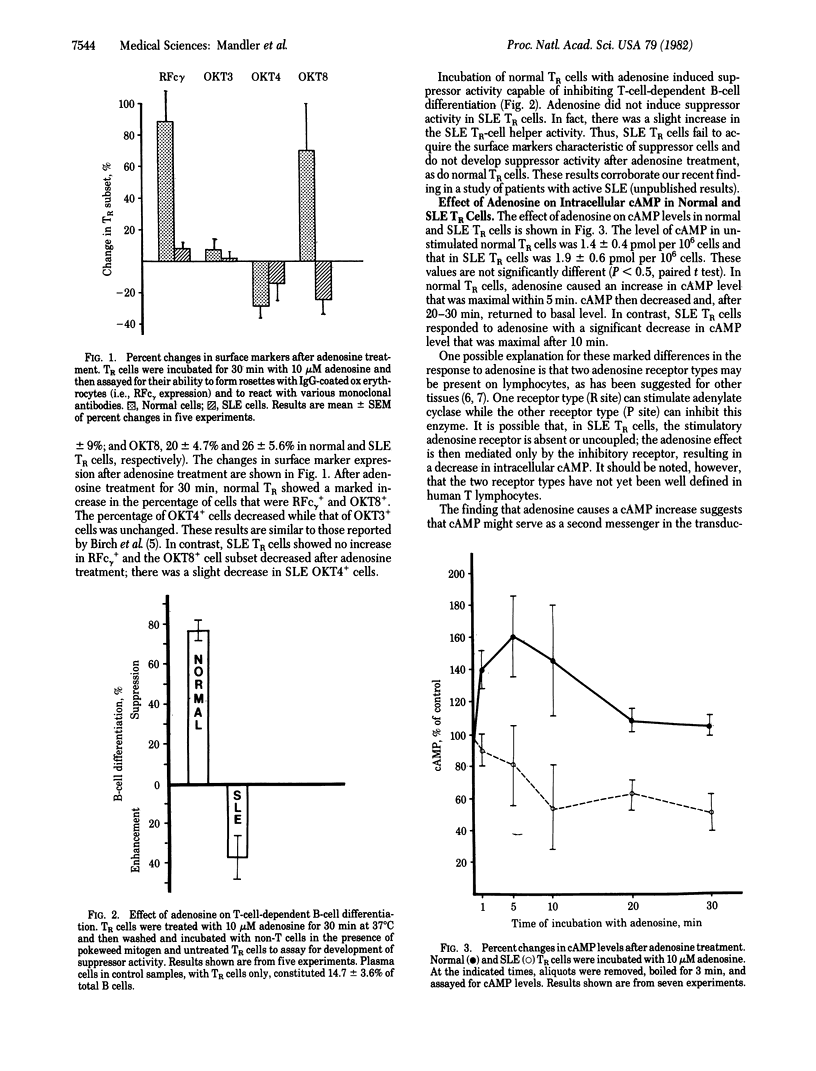
Normal human T lymphocytes incubated with adenosine (10 μM) for 30 min at 37°C show an increase in the percentage of cells expressing receptors for the Fc portion of IgG (RFcγ) and the OKT8 antigen, while the proportion of OKT4+ cells decreases. These effects occur exclusively in a subset of T cells with theophylline-resistant sheep erythrocyte receptors (TR cells) that is enriched for OKT4+ cells. Untreated normal TR cells express helper/inducer cell activity for T-cell-dependent B-cell differentiation, while adenosine-treated TR cells suppress B-cell differentiation. In contrast, in TR cells isolated from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), adenosine fails to induce immunosuppressor activity or to increase the percentage of OKT8+ and RFcγ+ cells. In addition, although incubation of normal TR cells with adenosine causes a transient increase in cAMP levels (up to 160% of control within 5 min), in SLE TR cells, cAMP levels fall by 50% within 10 min. The photoaffinity label 8-azidoadenosine cyclic [32P]monophosphate has been used to show that human T lymphocytes have a single cAMP receptor site that appears to be the regulatory subunit of type I protein kinase. In normal TR cells, this receptor becomes occupied in response to adenosine. In contrast, in SLE TR cells, no change in cAMP receptor occupancy is detected. Although adenosine has a differential effect on normal and SLE TR cells, cAMP derivatives that can traverse the cell membrane (8-bromo- and 8-azidoadenosine cyclic monophosphates) induce an increase in the RFcγ+ cell subset in both normal and SLE TR cells. These results suggest that cAMP mediates the effects of adenosine on cell surface markers of T lymphocytes. The lack of an adenosine receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase activity in SLE TR cells may account, in part, for their lack of immunosuppressive activity.
Keywords: autoimmune disease, suppressor T-cell subset, receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase, cyclic nucleotide metabolism, photoaffinity labeling
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birch R. E., Polmar S. H. Induction of Fc gamma receptors on a subpopulation of human T lymphocytes by adenosine and impromidine, an H2-histamine agonist. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jan 15;57(2):455–467. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch R. E., Polmar S. H. Pharmacological modification of immunoregulatory T lymphocytes. I. Effect of adenosine, H1 and H2 histamine agonists upon T lymphocyte regulation of B lymphocyte differentiation in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):218–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch R. E., Rosenthal A. K., Polmar S. H. Pharmacological modification of immunoregulatory T lymphocytes . II. Modulation of T lymphocyte cell surface characteristics. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):231–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. L., Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Sgherzi A. M. A simple and sensitive saturation assay method for the measurement of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):561–562. doi: 10.1042/bj1210561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F. Adenosine receptor activation in human fibroblasts: nucleoside agonists and antagonists. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;58(6):673–691. doi: 10.1139/y80-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Malbon C. C. Regulation of adenylate cyclase by adenosine. Mol Cell Biochem. 1979 Jun 15;25(3):143–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00235364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Steinberg A. D., Haynes B. F., Whalen G. Immunoregulatory aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1473–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G. Protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1972;5:99–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limatibul S., Shore A., Dosch H. M., Gelfand E. W. Theophylline modulation of E-rosette formation: an indicator of T-cell maturation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Sep;33(3):503–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Webb S. R., Grossi C. E., Lydyard P. M., Cooper M. D. Functional analysis of two human T-cell subpopulations: help and suppression of B-cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):184–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroz C., Stevens R. H. Suppression of immunoglobulin production in normal human B lymphocytes by two T-cell subsets distinguished following in vitro treatment with adenosine. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Jan;15(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz A. H., Rudolph S. A., Haley B. E., Greengard P. Photoaffinity labeling of a protein kinase from bovine brain with 8-azidoadenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3858–3862. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph S. A., Baird T. M., Wardell J. W. Cyclic AMP receptors and cation fluxes in the turkey erythrocyte. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;21(2):503–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph S. A., Krueger B. K. Endogenous protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:107–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagawa A., Abdou N. I. Suppressor-cell dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cells involved and in vitro correction. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):789–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI109190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




